以下为操作队列的算法,该队列为静态队列,用循环数组实现。
给该队列分配的内存长度为len+1,但实际只用了len个内存空间来保存数据,这样做是为了更方便判断队列的满与空。队列中front位置中存放的是队首的数据,rear位置的前一个位置中存放队尾的数据,而rear位置中则没有数据存放,这样做的目的是为了在入队和出队时方便对队列的操作,而不用考虑特殊情况
操作系统:ubuntu
编译软件:gcc
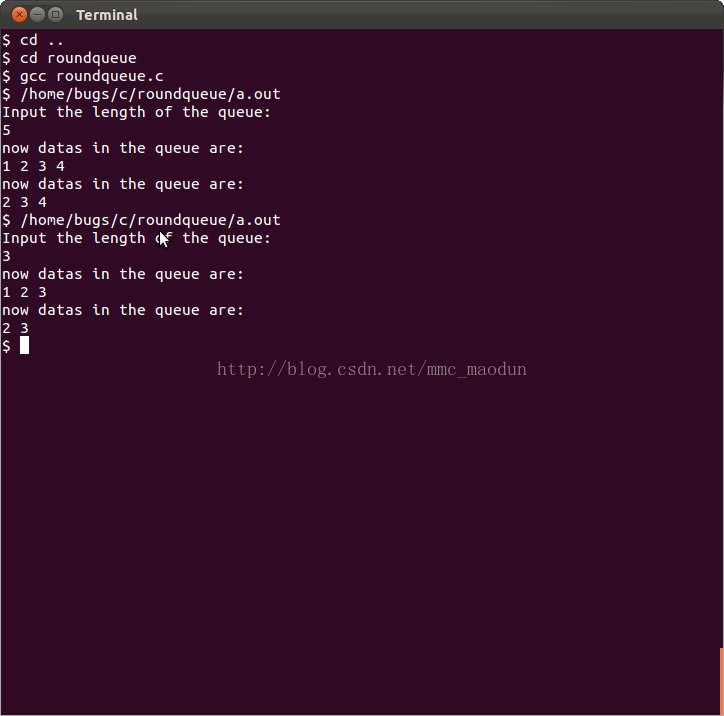
结果截图:
源代码:
- #include
- #include
- #include
-
-
- int len;
- typedef struct Queue
- {
- int *pBase;
- int front;
- int rear;
- } QUEUE,*PQUEUE;
-
-
- PQUEUE creat_queue();
- bool enter_queue(PQUEUE,int);
- bool full_queue(PQUEUE);
- bool empty_queue(PQUEUE);
- void traverse_queue(PQUEUE);
- bool out_queue(PQUEUE,int *);
-
-
- int main()
- {
- int data_save;
- PQUEUE pQueue = creat_queue();
-
- enter_queue(pQueue,1);
- enter_queue(pQueue,2);
- enter_queue(pQueue,3);
- enter_queue(pQueue,4);
- traverse_queue(pQueue);
-
- out_queue(pQueue,&data_save);
- traverse_queue(pQueue);
-
-
- return 0;
- }
-
-
-
-
-
- PQUEUE creat_queue()
- {
- printf("Input the length of the queue:\n");
- scanf("%d",&len);
- PQUEUE pQueue = (PQUEUE)malloc(sizeof(QUEUE));
- pQueue->pBase = (int *)malloc(sizeof(int)*(len+1));
- if(NULL==pQueue || NULL==pQueue->pBase)
- {
- printf("malloc failed!");
- exit(-1);
- }
- else
- {
- pQueue->front = 0;
- pQueue->rear = 0;
- }
- return pQueue;
- }
-
-
-
- bool full_queue(PQUEUE pQueue)
- {
- if(pQueue->front == (pQueue->rear+1)%(len+1))
- return true;
- else
- return false;
- }
-
-
-
- bool empty_queue(PQUEUE pQueue)
- {
- if(pQueue->front == pQueue->rear)
- return true;
- else
- return false;
- }
-
-
-
- bool enter_queue(PQUEUE pQueue,int val)
- {
- if(full_queue(pQueue))
- return false;
- else
- {
- pQueue->pBase[pQueue->rear] = val;
- pQueue->rear = (pQueue->rear+1)%(len+1);
- return true;
- }
- }
-
-
-
- bool out_queue(PQUEUE pQueue,int *out_data)
- {
- if(empty_queue(pQueue))
- return false;
- else
- {
- *out_data = pQueue->front;
- pQueue->front = (pQueue->front+1)%(len+1);
- return true;
- }
- }
-
-
-
-
-
- void traverse_queue(PQUEUE pQueue)
- {
- int i = pQueue->front;
- printf("now datas in the queue are:\n");
- while(i != pQueue->rear)
- {
- printf("%d ",pQueue->pBase[i]);
- i = (i+1)%(len+1);
- }
- printf("\n");
- return ;






















 41万+
41万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








