在这篇博客的创作中,需要用到redis作为大缓存,单独对一下小缓存则使用ehcache,这篇博文就是将ehcache和spring整合起来。
首先需要的maven依赖为:
<!--ehcache-->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.googlecode.ehcache-spring-annotations</groupId>
<artifactId>ehcache-spring-annotations</artifactId>
<version>${ehcache-spring.version}</version>
<type>jar</type>
<scope>compile</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>net.sf.ehcache</groupId>
<artifactId>ehcache-core</artifactId>
<version>${ehcache-core.version}</version>
</dependency>spring的maven依赖就不在展示出来。
ehcache需要一个配置文件,为ehcache.xml,内容为:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<ehcache xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:noNamespaceSchemaLocation="http://ehcache.org/ehcache.xsd" updateCheck="false">
<diskStore path="java.io.tmpdir" /> <!-- 缓存存放目录(此目录为放入系统默认缓存目录),也可以是”D:/cache“ java.io.tmpdir -->
<defaultCache
maxElementsInMemory="10000"
eternal="false"
timeToIdleSeconds="120"
timeToLiveSeconds="120"
overflowToDisk="true"
maxElementsOnDisk="10000000"
diskPersistent="false"
diskExpiryThreadIntervalSeconds="120"
memoryStoreEvictionPolicy="LRU"
/>
<!--
name:Cache的唯一标识
maxElementsInMemory:内存中最大缓存对象数
maxElementsOnDisk:磁盘中最大缓存对象数,若是0表示无穷大
eternal:Element是否永久有效,一但设置了,timeout将不起作用
overflowToDisk:配置此属性,当内存中Element数量达到maxElementsInMemory时,Ehcache将会Element写到磁盘中
timeToIdleSeconds:设置Element在失效前的允许闲置时间。仅当element不是永久有效时使用,可选属性,默认值是0,也就是可闲置时间无穷大
timeToLiveSeconds:设置Element在失效前允许存活时间。最大时间介于创建时间和失效时间之间。仅当element不是永久有效时使用,默认是0.,也就是element存活时间无穷大
diskPersistent:是否缓存虚拟机重启期数据
diskExpiryThreadIntervalSeconds:磁盘失效线程运行时间间隔,默认是120秒
diskSpoolBufferSizeMB:这个参数设置DiskStore(磁盘缓存)的缓存区大小。默认是30MB。每个Cache都应该有自己的一个缓冲区
memoryStoreEvictionPolicy:当达到maxElementsInMemory限制时,Ehcache将会根据指定的策略去清理内存。默认策略是LRU(最近最少使用)。你可以设置为FIFO(先进先出)或是LFU(较少使用)
-->
</ehcache> 在spring的applicationContext.xml的配置文件的编写为:
<!-- 引用ehCache的配置 -->
<bean id="defaultCacheManager" class="org.springframework.cache.ehcache.EhCacheManagerFactoryBean">
<property name="configLocation">
<value>classpath:/ehcache.xml</value>
</property>
</bean>
<!-- 定义ehCache的工厂,并设置所使用的Cache name -->
<bean id="ehCache" class="org.springframework.cache.ehcache.EhCacheFactoryBean">
<property name="cacheManager">
<ref local="defaultCacheManager"/>
</property>
<property name="cacheName">
<value>DEFAULT_CACHE</value>
</property>
</bean>如此配置,基本spring整合ehcache就完成了,但还是要单独测试一下,编写一个测试程序:
package cn.com.ecache;
import cn.com.container.ServiceProvinder;
import net.sf.ehcache.Cache;
import net.sf.ehcache.Element;
import org.junit.Test;
/**
* Created by Administrator on 2016/1/24.
*/
public class TestEcache {
@Test
public void Test() {
Cache cache = (Cache) ServiceProvinder.getService("ehCache");
Element lgElement = new Element("loginName", "xiaxuan");
Element pwElement = new Element("password", "xiaxuan");
cache.put(lgElement);
cache.put(pwElement);
System.out.println(cache.get("loginName"));
}
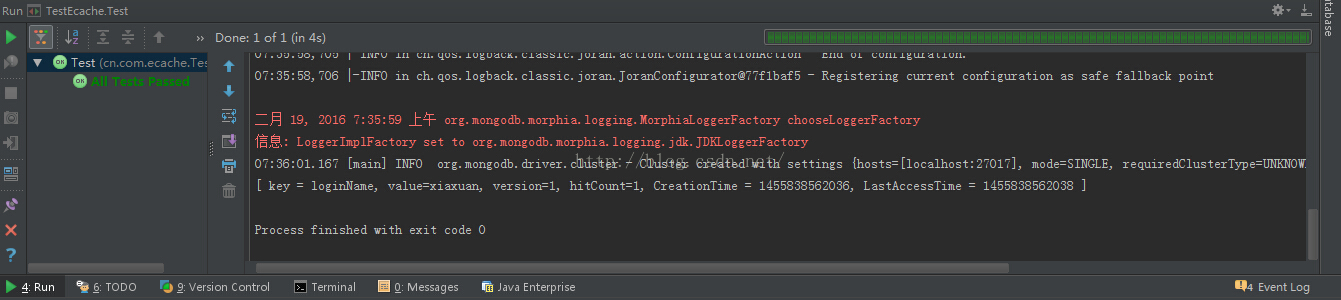
}测试结果为:
既可以存放数据到缓存中,又可以从缓存中拿到数据,spring和ehcache的整合基本成功。
如上,就是spring和ehcache整合。







 本文详细介绍如何将Ehcache与Spring框架进行整合,包括所需Maven依赖、ehcache.xml配置文件的设置以及spring配置文件的编写。通过一个简单的测试案例验证了整合的成功。
本文详细介绍如何将Ehcache与Spring框架进行整合,包括所需Maven依赖、ehcache.xml配置文件的设置以及spring配置文件的编写。通过一个简单的测试案例验证了整合的成功。
















 22万+
22万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








