类似windows上对CPU、内存、硬盘存储空间占用模拟和网络上下行速率的模拟,我们可以对Android设备上的CPU、内存、存储空间大小和网络上下行速率进行模拟,并作为移动测试系统中的一项测试服务。这个很早之前做的,但一直卡在网络上下行速率限速的功能上。在这小结下之前的工作。
CPU占用模拟
对CPU占用模拟,主要是在现有CPU占用率至100%之间进行动态调节。
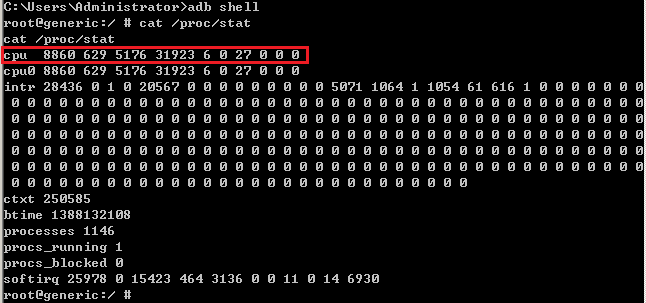
需要先计算CPU占用率,与CPU时间相关。CPU时间可以通过读取/proc/stat系统文件获取或通过top等命令获取,如下:
CPU时间包括:
系统时间sy(System time):CPU在内核运行的时间
用户时间us(User time):CPU执行用户进程的时间
空闲时间id(Idle time):系统处于空闲期的时间
等待时间wa(Waiting time):CPU在等待IO所花费的时间
Nice时间ni(Nice time):系统调整进程优先级所花费的时间
硬中断处理时间hi(Hard Irq time):系统硬件中断所花费时间
软中断时间si(Soft Irq time):系统处理软件中断所花费时间
丢失时间st(Steal time):被强制等待虚拟CPU的时间
CPU占用率主要关心系统态占用率(sys)、 用户态占用率(user)和空闲态占用率(idle),CPU占用率的计算公式如下:
(1)CPU时间=sy+us+id+wa+ni+hi+si+st
(2)%us=(user+system)/cpu时间*100%
(3)%sy=(system+hardIrq+softIrq)/CPU时间*100%
(4)%id=(Idle)/CPU时间*100%
提高CPU占用率,最简单有效的方法就是通过死循环+sleep来实现:
while(true){
if(CPU占用率 > 设定的值){
sleep(一段时间)
}
}为了保证CPU占用率稳定在用户自定义的占用率附近,需要准确确定“一段时间”值。
具体实现的主要代码如下:
“`
//读取文件获取CPU使用率信息
public static CPUInfo getCpuTime() {
CPUInfo cInfo = null;
long[] cpuTime = new long[Config.CPU_TIME_NUM];
try {
BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(
new FileInputStream("/proc/stat")), 1000);
String info = reader.readLine();
reader.close();
info = info.replaceAll("\\s+", " ");
String[] cpuInfo = info.split(" ");
for (int i = 1; i < Config.CPU_TIME_NUM + 1; i++) {
cpuTime[i - 1] = Long.parseLong(cpuInfo[i]);
}
long totalTime = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < Config.CPU_TIME_NUM; i++) {
totalTime += cpuTime[i];
}
cInfo = new CPUInfo(totalTime, totalTime - cpuTime[Config.CPU_IDLE_INDEX]);
} catch (IOException ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
}
return cInfo;
}
//获取CPU占用率
public double getCPUUSageRatio(CPUInfo oldCpuInfo) {
if (oldCpuInfo.getBusyCPUTime() == this.getBusyCPUTime()) {
return 0;
} else {
return (this.getBusyCPUTime() - oldCpuInfo.getBusyCPUTime())
/ (double) (this.getTotalCPUTime() - oldCpuInfo
.getTotalCPUTime());
}
//设置CPU占用率调控按钮事件处理函数
private void setCPUButtonEvent() {
Button showCpuButton = (Button)findViewById(R.id.showCpu);
showCpuButton.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View arg0) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
Intent intent = new Intent();
intent.putExtra("cpuRatio",
Integer.parseInt(cpuRatioEditText.getText().toString()));
intent.setClass(MainActivity.this, CPUActivity.class);
startActivity(intent);
}
});
//设置CPU占用率调控按钮事件处理函数
Button setCpuButton = (Button) findViewById(R.id.setCpu);
setCpuButton.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View arg0) {
final int setRatio = Integer.parseInt(cpuRatioEditText
.getText().toString());
cpuRatio = setRatio / 100.0;
if (sleepTime < 0) {
sleepTime = 50 - (int) (cpuRatio * 50);
//开启的线程数等于CPU核心的个数
for (int i = 0; i < cpuNewValue.getCoreNum(); i++) {
new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
CPUInfo coldValue;
CPUInfo cnewValue;
coldValue = Util.getCpuTime();
while (true) {
cnewValue = Util.getCpuTime();
if (cnewValue.getCPUUSageRatio(coldValue) > cpuRatio) {
try {
Log.d("sleepTime",String.valueOf(sleepTime));
coldValue = cnewValue;
Thread.sleep(sleepTime);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
} else {
coldValue = cnewValue;
}
}
}
}).start();
}
} else {
sleepTime = 50 - (int) (cpuRatio * 50);
}
}
});
}
```
内存占用率模拟
内存分类(可读取/proc/meminfo获取):
VSS(Virtual Set Size)虚拟内存占用;
RSS(Resident Set Size)实际占用的物理内存包含共享库占用
PSS(Proportional Set Size)实际占用包含比例分配共享库占用
USS(Unique Set Size)进程独自占用但不包含共享库占用
其中,VSS>=RSS>=PSS>=USS。
(1)直接在应用层使用new/delete的问题:
Android内存分为:虚拟机堆和native堆。Android虚拟机堆有最大内存限制如32MB。
不能控制进程什么时候把内存还给操作系统
(2)利用mmap让应用程序直接访问设备内存
不直接单独使用malloc/free,无法控制进程将内存还给系统的时间
使用mmap()映射匿名文件到共享区域申请内存
使用munmap()取消映射来释放内存
在这我们使用Android NDK来实现对内存占用的模拟,底层C代码allocateMem.c简化如下:
“`JNIEXPORT void JNICALL Java_com_netease_AllocateMemory_allocateMem
(JNIEnv * ev, jclass c, jint size) {
int allocateSize = (memSize + size) - (memSize + size)%(1024*8);
if(memSize + size >= 0) {
if(p) {
munmap(p,memSize);
}
p = (char *)mmap(0,allocateSize,PROT_READ|PROT_WRITE,MAP_ANON|MAP_PRIVATE,-1,0);
} else {
return;
}
if(p) {
memSize = allocateSize;
}
Android.mk文件如下:
LOCAL_PATH := $(call my-dir)
include $(CLEAR_VARS)
LOCAL_MODULE := memManage
LOCAL_SRC_FILES := allocateMem.c
include $(BUILD_SHARED_LIBRARY)
生成动态链接库文件.so文件后,上层即可实现调用:public class AllocateMemory {
public static native void allocateMem(int size);
static {
System.loadLibrary("memManage");
}
}
```
存储空间大小模拟
磁盘存储空间大小获取和占用模拟:
(1)获取Android设备内部存储控件大小或SD卡大小。
(2)向存储空间内读写文件实现存储空间占用模拟
向存储空间写文件的主要代码如下:
//向存储空间写文件
public boolean writeToSdCard(String fileName, long fileSize) {
fillSize = getFileSize(fileName);
System.out.println(fillSize);
try {
// 判断是否有挂载sdcard
if (Environment.getExternalStorageState().equals(
Environment.MEDIA_MOUNTED)) {
// 得到sdcar文件目录
File dir = Environment.getExternalStorageDirectory();
File file = new File(dir, fileName);
if (fileSize > 0) {
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(file, true);
int number = (int) (fileSize / Config.MAX_FILE_SIZE);
int left = (int) (fileSize % Config.MAX_FILE_SIZE);
byte[] fill = new byte[Config.MAX_FILE_SIZE];
for (int i = 0; i < number; i++) {
fos.write(fill);
fos.flush();
}
fill = new byte[left];
fos.write(fill);
fos.flush();
fos.close();
} else {
if (fileSize + fillSize < 0) {
return false;
} else {
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(file);
int number = (int) ((fileSize + fillSize) / Config.MAX_FILE_SIZE);
int left = (int) ((fileSize + fillSize) % Config.MAX_FILE_SIZE);
byte[] fill = new byte[Config.MAX_FILE_SIZE];
for (int i = 0; i < number; i++) {
fos.write(fill);
fos.flush();
}
fill = new byte[left];
fos.write(fill);
fos.flush();
fos.close();
}
}
} else {
return false;
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return true;
}网络上下行速率模拟
网络上下行速率模拟方法:
(1)获取网络上下行速率(TrafficStats类)
(2)利用hook和函数拦截进行上下行速率模拟
(3)或使用netfilter框架,流入和流出的信息进行细化控制,实现上下行速率模拟
网络上下行速率和带宽的主要代码如下:
public FlowInfo() {
upStreamSize = TrafficStats.getTotalTxBytes();
downStreamSize = TrafficStats.getTotalRxBytes();
systemTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
}
public double getUpBandWidth(FlowInfo oldFlowInfo) {
return (this.upStreamSize - oldFlowInfo.getUpStreamSize())
/ ((this.systemTime - oldFlowInfo.getSystemTime()) / 1000.0 * 1024.0);
}
public double getDownBandWidth(FlowInfo oldFlowInfo){
return (this.downStreamSize - oldFlowInfo.getDownStreamSize())
/ ((this.systemTime - oldFlowInfo.getSystemTime()) / 1000.0 * 1024.0);
}对于第二个方法,类似于在windows系统上拦截应用层的ws2_32.dll中的winsock或spi,还没有具体实现,简单思路如下:
so注入(inject)和挂钩(hook):libinject代码(ARM)
(1)在目标进程中分配内存,用来写shellcode和参数
(2)往目标进程中写入shellcode, shellcode调用dlopen来载入我们的库
(3)运行目标进程中的shellcode
函数截获:
(1)挂钩相关进程(网络或渲染Surfaceflinger)
(2)找到共享库中的函数
(3)装载.so文件
(4)函数重定向
(5)获取数据
转载地址:http://www.gitzx.com/android-cpu-mem-disk/























 509
509

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








