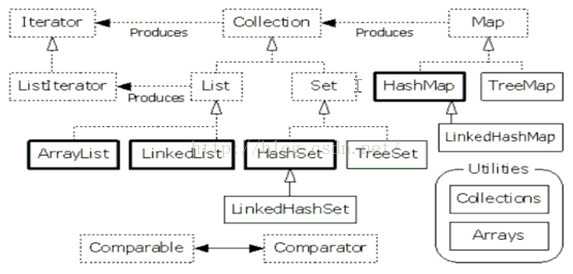
在Java中提供了多种集合的实现,并且都继承自Collenction
关系图:
Collection的常用方法:
添加方法:
boolean add(Object obj); 添加一个对象
boolean addAll(Collection coll); 复制另一个集合的数据到当前集合、
删除方法
boolean remove(Object obj); 移除一个对象
boolean removeAll(Collection coll); 移除包含coll集合元素的数据
void clear(); 清除集合中的数据
判断方法:
boolean contains(Object obj); 如果此 collection 包含指定的元素,则返回true。
boolean containsAll(Collection coll); 如果此 collection 包含指定 collection 中的所有元素,则返回true。
boolean isEmpty(); 判断集合中是否有元素。
获取方法:
int size(); 获取集合大小
Iterator iterator(); 得到一个迭代器。
其他方法:
boolean retainAll(Collection coll); 仅保留此 collection 中那些也包含在指定 collection 的元素(可选操作)。
Object toArray(); 返回包含此 collection 中所有元素的数组。
示例代码:
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Collection coll = new ArrayList();
print(coll);
Collection c1 = new ArrayList();
Collection c2 = new ArrayList();
print(c1, c2);
}
public static void print(Collection colletion) {
// 添加元素
colletion.add("c1");
colletion.add("c2");
colletion.add("c3");
System.out.println("colletion:" + colletion);
// 删除元素
colletion.remove("c2");// 会改变集合的长度
System.out.println("colletion:" + colletion);
// 判断是否包含c1
System.out.println(colletion.contains("c1"));
// 清空集合
colletion.clear();
System.out.println("colletion:" + colletion);
}
public static void print(Collection colletion1, Collection colletion2) {
// 添加元素
colletion1.add("c1");
colletion1.add("c2");
colletion1.add("c3");
colletion1.add("c4");
System.out.println("colletion1:" + colletion1);
// 添加元素
colletion2.add("c2");
colletion2.add("c6");
colletion2.add("c7");
System.out.println("colletion2:" + colletion2);
// 将colletion1中的元素添加到colletion2中
colletion1.addAll(colletion2);
// 从c1集合中删除与c2集合相同的元素
boolean b = colletion1.removeAll(colletion2);
System.out.println("removeAll:" + b);
boolean b1 = colletion1.containsAll(colletion2);
System.out.println("containsAll:" + b1);
// 取交集
boolean b2 = colletion1.retainAll(colletion2);
System.out.println("colletion1、colletion2交集:" + colletion1);
}
}
输出结果:
colletion:[c1, c2, c3]
colletion:[c1, c3]
true
colletion:[]
colletion1:[c1, c2, c3, c4]
colletion2:[c2, c6, c7]
removeAll:true
containsAll:false
colletion1、colletion2交集:[]
List与Set集合
List:有序,允许重复元素。
Set:无序,不允许重复。
List的示例代码:
public static void main(String[] args){
List list = new ArrayList();
//添加元素
list.add( "list1" );
list.add( "list2" );
list.add( "list3" );
System.out.println(list);
//0在1位置插入元素
list.add(0, "list2_insert" );
//删除元素
System.out.println(list.remove(2));
//修改元素
System.out.println(list.set(2,"listupdata" ));
//获取元素:
System.out.println(list.get(0));
//获取子列表
System.out.println(list.subList(1,3));
System.out.println(list);
}
输出结果:
[list1, list2, list3]
list2
list3
list2_insert
[list1, listupdata]
[list2_insert, list1, listupdata]
Set集合的示例代码:
public static void main(String[] args){
Set set = new HashSet();
//添加元素
set.add( "set1" );
set.add( "set2" );
set.add( "set3" );
System.out.println(set);
//删除元素
System.out.println(set.remove("set2"));
System.out.println(set);
}
输出结果:
[set3, set2, set1]
true
[set3, set1]
ArrayList与LinkedList
ArrayList的特点:底层实现是数组,增删慢,查找快
LinkedList的特点:底层实现是链表,增删快,查找慢
HashSet与TreeSet
HashSet的特点:底层实现是哈希表,无序
TreeSet的特点:底层实现是二叉树,有许
Map集合:
Map集合存储的是一组键值的映射关系,是双列集合,而Collection集合存储的是值,是单列集合,Map集合的键是唯一的
常用方法:
添加
value put(key,value): 返回前一个和key关联的值,如果没有返回null。
删除
void clear(): 清空map集合。
value remove(Object key): 根据指定的key删除这个键值对。
判断
boolean containsKey(key); 判断集合中是否有这个键
boolean containsValue(value); 判断集合中是否有这个值
boolean isEmpty(); 判断集合中是否有元素
获取
value get(key): 通过键获取值,如果没有该键返回null。
当然可以通过返回null,来判断是否包含指定键。
int size(): 获取键值对个数。
示例代码:
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map<String, String> map = new HashMap<String, String>();
// 添加元素
System.out.println(map.put("aa", "bb"));
System.out.println(map.put("cc", "dd"));
System.out.println(map);
map.put("11", "22");
map.put("33", "44");
System.out.println(map);
// 删除
System.out.println(map.remove("bb"));
// 判断
System.out.println(map.containsKey("cc"));
// 获取
System.out.println(map.get("11"));
}
输出结果:
null
null
{aa=bb, cc=dd}
{aa=bb, cc=dd, 11=22, 33=44}
null
true
22
HashTable:底层实现是哈希表,线程安全。不允许null作为键,null作为值。
HashMap:底层实现是哈希表,线程不安全。允许null作为键,null作为值。
TreeMap:底层实现是二叉树,线程不安全。可以对Map中的键进行排序。





















 244
244











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








