线程池算是Android 开发比较常用的了,涉及线程的地方大多数都会涉及线程池。

举个栗子:
假如我一个ListView,每个Item的图片需要从网上加载,如果我不使用线程池,则这样开启新线程:
new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
//网络访问
}
}).start(); 1,使用new Thread()创建线程存在的问题
2,使用线程的好处
3,ThreadPoolExecutor
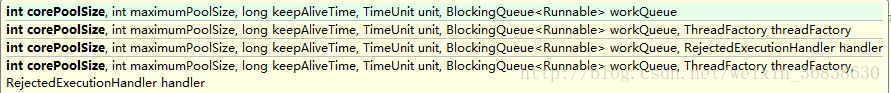
[java] view plain copy print?
/**
* Creates a {@code LinkedBlockingQueue} with a capacity of
* {@link Integer#MAX_VALUE}.
*/
public LinkedBlockingQueue() {
this(Integer.MAX_VALUE);
}
/**
* Creates a {@code LinkedBlockingQueue} with the given (fixed) capacity.
*
* @param capacity the capacity of this queue
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if {@code capacity} is not greater
* than zero
*/
public LinkedBlockingQueue(int capacity) {
if (capacity <= 0) throw new IllegalArgumentException();
this.capacity = capacity;
last = head = new Node<E>(null);
} 3,PriortyBlockingQueue:这个队列和LinkedBlockingQueue类似,不同的是PriorityBlockQueue中的元素不是按照FIFO来排序的,而是按照元素的Comparator来决定存取顺序的(这个功能也反映了存入PrioriBlockingQueue中的数据必须实现了Comparator接口)
OK,这是ThreadPoolExecutor的构造方法参数的解释,我们的线程提交到线程池之后又是按照什么样的规则去运行呢?OK,它们遵循如下规则:
1.execute一个线程之后,如果线程池中的线程数未达到核心线程数,则会立马启用一个核心线程去执行
2.execute一个线程之后,如果线程池中的线程数已经达到核心线程数,且workQueue未满,则将新线程放入workQueue中等待执行
3.execute一个线程之后,如果线程池中的线程数已经达到核心线程数但未超过非核心线程数,且workQueue已满,则开启一个非核心线程来执行任务
4.execute一个线程之后,如果线程池中的线程数已经超过非核心线程数,则拒绝执行该任务
OK,基于以上讲解,我们来看一个Demo:
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
poolExecutor = new ThreadPoolExecutor(3, 5,
1, TimeUnit.SECONDS, new LinkedBlockingDeque<Runnable>(128));
}
public void btnClick(View view) {
for (int i = 0; i < 30; i++) {
final int finalI = i;
Runnable runnable = new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
SystemClock.sleep(2000);
Log.d("google_lenve_fb", "run: " + finalI);
}
};
poolExecutor.execute(runnable);
}
} 
poolExecutor = new ThreadPoolExecutor(3, 30,
1, TimeUnit.SECONDS, new LinkedBlockingDeque<Runnable>(6)); 如上,我把最大线程数改为30,而把线程队列大小改为6(实际开发中 不会这样来设置,这里只是为了验证结论),我们来看看执行结果:

public abstract class AsyncTask<Params, Progress, Result> {
private static final String LOG_TAG = "AsyncTask";
private static final int CPU_COUNT = Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors();
private static final int CORE_POOL_SIZE = CPU_COUNT + 1;
private static final int MAXIMUM_POOL_SIZE = CPU_COUNT * 2 + 1;
private static final int KEEP_ALIVE = 1;
private static final ThreadFactory sThreadFactory = new ThreadFactory() {
private final AtomicInteger mCount = new AtomicInteger(1);
public Thread newThread(Runnable r) {
return new Thread(r, "AsyncTask #" + mCount.getAndIncrement());
}
};
private static final BlockingQueue<Runnable> sPoolWorkQueue =
new LinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable>(128);
/**
* An {@link Executor} that can be used to execute tasks in parallel.
*/
public static final Executor THREAD_POOL_EXECUTOR
= new ThreadPoolExecutor(CORE_POOL_SIZE, MAXIMUM_POOL_SIZE, KEEP_ALIVE,
TimeUnit.SECONDS, sPoolWorkQueue, sThreadFactory);
....
....
}
OK,那么和线程池有关的最基本的ThreadPoolExecutor我们就说完了,接下来我们就来看看系统配置好的提供给我们的线程池。
4,FixedThreadPool
ExecutorService fixedThreadPool = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(3); 源码:
public static ExecutorService newFixedThreadPool(int nThreads) {
return new ThreadPoolExecutor(nThreads, nThreads,
0L, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS,
new LinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable>());
}我们看到核心线程数和最大线程数一样,说明在FixedThreadPool中没有非核心线程,所有的线程都是核心线程,且线程的超时时间为0,说明核心线程即使在没有任务可执行的时候也不会被销毁(这样可让FixedThreadPool更快速的响应请求),最后的线程队列是一个LinkedBlockingQueue,但是LinkedBlockingQueue却没有参数,这说明线程队列的大小为Integer.MAX_VALUE(2的31次方减1),OK,看完参数,我们大概也就知道了FixedThreadPool的工作特点了,当所有的核心线程都在执行任务的时候,新的任务只能进入线程队列中进行等待,直到有线程被空闲出来。OK,我们来看一个Demo:
ExecutorService fixedThreadPool = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(3);
for (int i = 0; i < 30; i++) {
final int finalI = i;
Runnable runnable = new Runnable(){
@Override
public void run() {
SystemClock.sleep(3000);
Log.d("google_lenve_fb", "run: "+ finalI);
}
};
fixedThreadPool.execute(runnable);
} 
5,SingleThreadExecutor
public static ExecutorService newSingleThreadExecutor() {
return new FinalizableDelegatedExecutorService
(new ThreadPoolExecutor(1, 1,
0L, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS,
new LinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable>()));
} ExecutorService singleThreadExecutor = Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor();
for (int i = 0; i < 30; i++) {
final int finalI = i;
Runnable runnable = new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
Log.d("google_lenve_fb", "run: " + Thread.currentThread().getName() + "-----" + finalI);
SystemClock.sleep(1000);
}
};
singleThreadExecutor.execute(runnable);
} 执行效果如下:
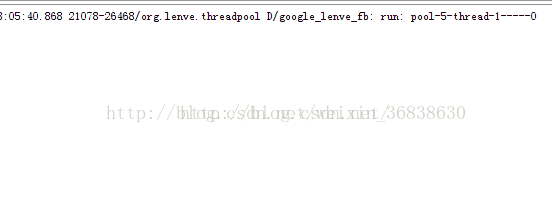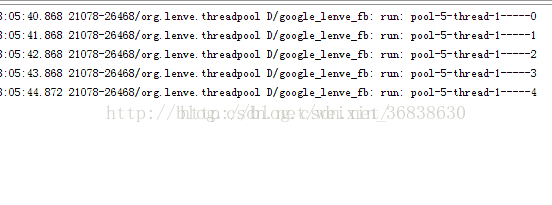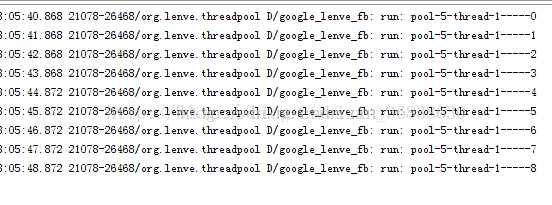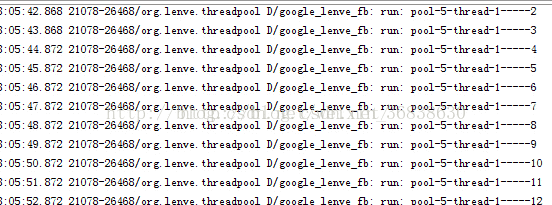
6,CachedThreadPool
public static ExecutorService newCachedThreadPool() {
return new ThreadPoolExecutor(0, Integer.MAX_VALUE,
60L, TimeUnit.SECONDS,
new SynchronousQueue<Runnable>());
} ExecutorService cachedThreadPool = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
for (int i = 0; i < 30; i++) {
final int finalI = i;
Runnable runnable = new Runnable(){
@Override
public void run() {
Log.d("google_lenve_fb", "run: " + Thread.currentThread().getName() + "----" + finalI);
}
};
cachedThreadPool.execute(runnable);
SystemClock.sleep(2000);
} 
ExecutorService cachedThreadPool = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
for (int i = 0; i < 30; i++) {
final int finalI = i;
Runnable runnable = new Runnable(){
@Override
public void run() {
SystemClock.sleep(2000);
Log.d("google_lenve_fb", "run: " + Thread.currentThread().getName() + "----" + finalI);
}
};
cachedThreadPool.execute(runnable);
SystemClock.sleep(1000);
} 
7,ScheduledThreadPool
public ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize) {
super(corePoolSize, Integer.MAX_VALUE,
DEFAULT_KEEPALIVE_MILLIS, MILLISECONDS,
new DelayedWorkQueue());
} 我们可以看到,它的核心线程数量是固定的(我们在构造的时候传入的),但是非核心线程是无穷大,当非核心线程闲置时,则会被立即回收。
使用ScheduledThreadPool时,我们可以通过如下几个方法来添加任务:
1.延迟启动任务:
public ScheduledFuture<?> schedule(Runnable command,
long delay, TimeUnit unit); ScheduledExecutorService scheduledExecutorService = Executors.newScheduledThreadPool(3);
Runnable runnable = new Runnable(){
@Override
public void run() {
Log.d("google_lenve_fb", "run: ----");
}
};
scheduledExecutorService.schedule(runnable, 1, TimeUnit.SECONDS); 2.延迟定时执行任务:
public ScheduledFuture<?> scheduleAtFixedRate(Runnable command,
long initialDelay,
long period,
TimeUnit unit); ScheduledExecutorService scheduledExecutorService = Executors.newScheduledThreadPool(3);
Runnable runnable = new Runnable(){
@Override
public void run() {
Log.d("google_lenve_fb", "run: ----");
}
};
scheduledExecutorService.scheduleAtFixedRate(runnable, 1, 1, TimeUnit.SECONDS); 延迟1秒之后每隔1秒执行一次新任务。
public ScheduledFuture<?> scheduleWithFixedDelay(Runnable command,
long initialDelay,
long delay,
TimeUnit unit); ScheduledExecutorService scheduledExecutorService = Executors.newScheduledThreadPool(3);
Runnable runnable = new Runnable(){
@Override
public void run() {
Log.d("google_lenve_fb", "run: ----");
}
};
scheduledExecutorService.scheduleWithFixedDelay(runnable, 1, 1, TimeUnit.SECONDS);第一次延迟1秒之后,以后每次也延迟1秒执行。
OK,至此,Android开发中常用的线程池就说完了。
8,线程池其他常用功能
1.shutDown() 关闭线程池,不影响已经提交的任务
2.shutDownNow() 关闭线程池,并尝试去终止正在执行的线程
3.allowCoreThreadTimeOut(boolean value) 允许核心线程闲置超时时被回收
4.submit 一般情况下我们使用execute来提交任务,但是有时候可能也会用到submit,使用submit的好处是submit有返回值,举个栗子:
public void submit(View view) {
List<Future<String>> futures = new ArrayList<>();
ThreadPoolExecutor threadPoolExecutor = new ThreadPoolExecutor(3, 5, 1,
TimeUnit.SECONDS, new LinkedBlockingDeque<Runnable>());
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
Future<String> taskFuture = threadPoolExecutor.submit(new MyTask(i));
//将每一个任务的执行结果保存起来
futures.add(taskFuture);
}
try {
//遍历所有任务的执行结果
for (Future<String> future : futures) {
Log.d("google_lenve_fb", "submit: " + future.get());
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (ExecutionException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
class MyTask implements Callable<String> {
private int taskId;
public MyTask(int taskId) {
this.taskId = taskId;
}
@Override
public String call() throws Exception {
SystemClock.sleep(1000);
//返回每一个任务的执行结果
return "call()方法被调用----" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + "-------" + taskId;
}
}
5. 自定义线程池
除了使用submit来定义线程池获取线程执行结果之外,我们也可以通过自定义ThreadPoolExecutor来实现这个功能,如下:
public void customThreadPool(View view) {
final MyThreadPool myThreadPool = new MyThreadPool(3, 5, 1, TimeUnit.MINUTES, new LinkedBlockingDeque<Runnable>());
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
final int finalI = i;
Runnable runnable = new Runnable(){
@Override
public void run() {
SystemClock.sleep(100);
Log.d("google_lenve_fb", "run: " + finalI);
}
};
myThreadPool.execute(runnable);
}
}
class MyThreadPool extends ThreadPoolExecutor{
public MyThreadPool(int corePoolSize, int maximumPoolSize, long keepAliveTime, TimeUnit unit, BlockingQueue<Runnable> workQueue) {
super(corePoolSize, maximumPoolSize, keepAliveTime, unit, workQueue);
}
@Override
protected void beforeExecute(Thread t, Runnable r) {
super.beforeExecute(t, r);
Log.d("google_lenve_fb", "beforeExecute: 开始执行任务!");
}
@Override
protected void afterExecute(Runnable r, Throwable t) {
super.afterExecute(r, t);
Log.d("google_lenve_fb", "beforeExecute: 任务执行结束!");
}
@Override
protected void terminated() {
super.terminated();
//当调用shutDown()或者shutDownNow()时会触发该方法
Log.d("google_lenve_fb", "terminated: 线程池关闭!");
}
} 执行结果如下:
D/google_lenve_fb: beforeExecute: 开始执行任务!
D/google_lenve_fb: run: 0
D/google_lenve_fb: beforeExecute: 任务执行结束!
D/google_lenve_fb: beforeExecute: 开始执行任务!
D/google_lenve_fb: run: 1
D/google_lenve_fb: beforeExecute: 任务执行结束!
D/google_lenve_fb: beforeExecute: 开始执行任务!
D/google_lenve_fb: run: 2
D/google_lenve_fb: beforeExecute: 任务执行结束!
参考资料
1.http://blog.csdn.net/u010687392/article/details/49850803
2.《Android开发艺术探索》

























 1万+
1万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








