How fast can we sort?
Depends on the computational model of what you can do with the elements.
Comparison sorting model:
Only use comparisons to determine the relative order of elements.

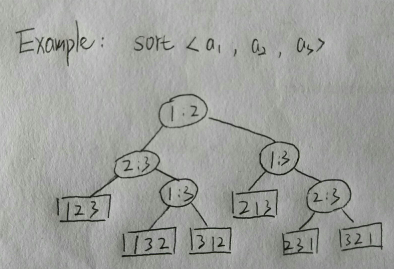
Decision-tree model comparison sorts:
--one tree for each n
--view algorithm as splitting whenever it make a comparison
--tree lists comparisons along all possible instruction traces
--running time (# comparisons) = length of path
--worst-case run time = height of tree
--the # of leaves is n factorial

Corollary: Merge sort and heapsort are asymptotically optimal comparison sorts.
Randomized quick sort is too, in expectation.

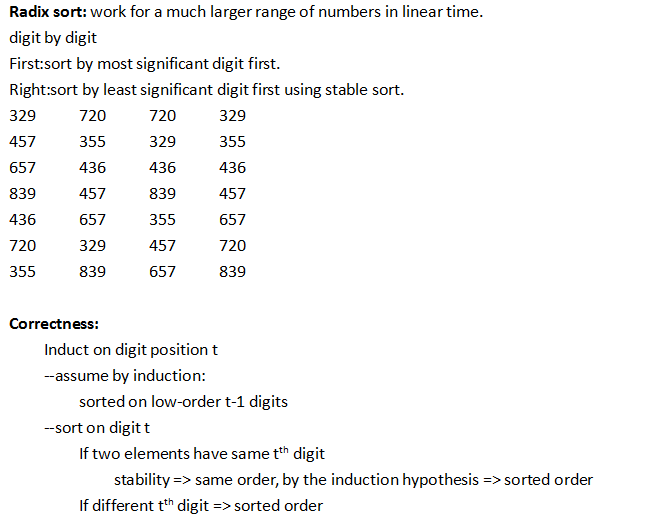
Theoretically Radix sort is very beautiful, but it not very good on cache, so in practice it is not that fast unless the number of sorting is really small. Something like quick sort can do better.









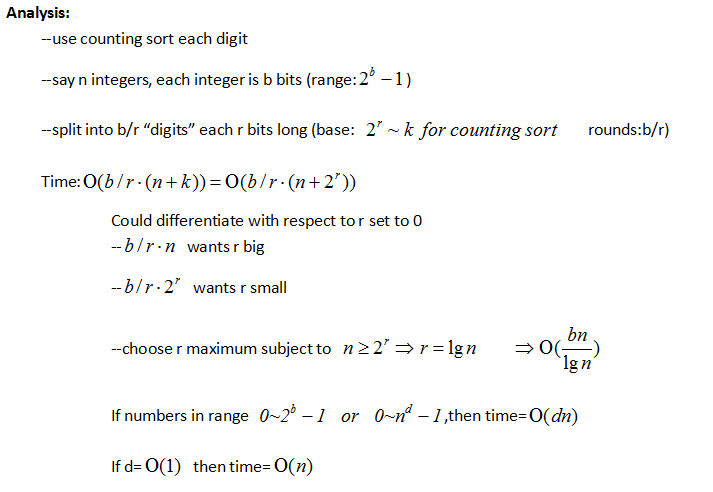














 393
393

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








