java是一个多线程的编程语言,就是说在java的应用中可以并行的执行多个线程,每个线程可以执行不同的操作。在单cpu的机器上多线程会分享cpu时间,而在多线程的机器上不同线程可以使用不同的CPU。
java线程的生命周期
java线程在他的生命周期内有几种不同的状态:线程初始化,启动,运行和死亡。
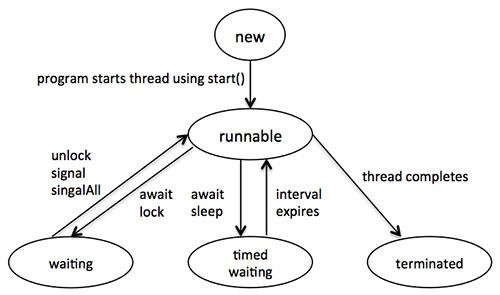
上图所示的状态解释如下:
- new 是指线程被初始化,但是还没有调用其start方法,还没有开始执行
- runnable 调用线程的start方法之后,线程开始执行其任务,这时候线程是运行状态
- waiting 有时候线程需要等待另外一个线程执行完毕之后再执行,这时候线程处于等待状态,处于等待状态的线程需要其他线程notify之后才能恢复到运行状态
- timed waiting 运行中的线程可以进入到定时等待的状态,这时候线程间隔指定的时间间隔之后就会恢复到运行状态
- terminated 当线程任务执行完毕或者被abort的时候线程处于终止状态
java线程的优先级
每一个java线程都有一个优先级,操作系统可以通过线程的优先级决定决定将cpu分配给哪个线程。优先级越高的线程越可能得到cpu资源。
java线程优先级的值在1-10之间,1是常量MIN_PRIORITY,10是常量MAX_PRIORITY 。默认情况下java的线程的优先级是NORM_PRIORITY 即5.
高优先级的线程通常更重要,更有可能获得cpu时间资源,但是并不能保证绝对可以获得cpu。
java多线程实现的两种方式
1. 使用Runnable接口实现多线程
使用Runnable接口实现多线程需要两个步骤,首先实现Runnable接口类,然后声明Thread实例,调用thread实例的start方法,开始执行。
如下代码示例:
package cn.outofmemory.java.example;
public class RunTask implements Runnable {
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i=0;i<10;i++) {
System.out.println("hello counter " + i);
try {
Thread.sleep(20);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
;
}
}
}
}package cn.outofmemory.java.example;
public class App {
public static void main(String[] args) {
for (int i = 0; i < 2; i++) {
Runnable task = new RunTask();
Thread t = new Thread(task);
t.start();
}
}
}
上面的RunTask类实现了Runnable的接口,App类的main方法for循环生成Runnable示例,并将其传递给Thread示例的构造函数中,然后调用start方法启动线程。
上面程序将输出:
hello counter 0
hello counter 0
hello counter 1
hello counter 1
hello counter 2
hello counter 2
hello counter 3
hello counter 3
hello counter 4
hello counter 4
hello counter 5
hello counter 5
hello counter 6
hello counter 6
hello counter 7
hello counter 7
hello counter 8
hello counter 8
hello counter 9
hello counter 9
可以看到两个线程在并行的执行。
2. 从Thread类继承实现java的多线程
从java的Thread类继承实现多线程,也是实现其run方法,然后声明实例,并调用实例的start方法启动线程。
代码示例如下:
package cn.outofmemory.java.example;
public class SimpleThread extends Thread {
public void run() {
for (int i=0;i<10;i++) {
System.out.println("thread " + this.getId() + " print out " + i);
try {
Thread.sleep(0);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
;
}
}
}
}
package cn.outofmemory.java.example;
public class App {
public static void main(String[] args) {
for (int i = 0; i < 2; i++) {
Thread t = new SimpleThread();
t.start();
}
}
}SimpleThead类从Thread类继承,并重写了run方法。 在App类的main方法中for循环new了两个SimpleThread的实例,并调用其start方法。
程序输出类似于:
“`
thread 12 print out 0
thread 11 print out 0
thread 12 print out 1
thread 12 print out 2
thread 12 print out 3
thread 12 print out 4
thread 12 print out 5
thread 12 print out 6
thread 11 print out 1
thread 11 print out 2
thread 12 print out 7
thread 11 print out 3
thread 12 print out 8
thread 12 print out 9
thread 11 print out 4
thread 11 print out 5
thread 11 print out 6
thread 11 print out 7
thread 11 print out 8
thread 11 print out 9
java Thread类的主要方法介绍
“`
java线程示例1: 如何使用interupt方法中断线程
public class GeneralInterrupt extends Object
implements Runnable {
public void run() {
try {
System.out.println("in run() - about to work2()");
work2();
System.out.println("in run() - back from work2()");
}
catch (InterruptedException x) {
System.out.println("in run() - interrupted in work2()");
return;
}
System.out.println("in run() - doing stuff after nap");
System.out.println("in run() - leaving normally");
}
public void work2() throws InterruptedException {
while (true) {
if (Thread.currentThread().isInterrupted()) {
System.out.println("C isInterrupted()="
+ Thread.currentThread().isInterrupted());
Thread.sleep(2000);
System.out.println("D isInterrupted()="
+ Thread.currentThread().isInterrupted());
}
}
}
public void work() throws InterruptedException {
while (true) {
for (int i = 0; i < 100000; i++) {
int j = i * 2;
}
System.out.println("A isInterrupted()="
+ Thread.currentThread().isInterrupted());
if (Thread.interrupted()) {
System.out.println("B isInterrupted()="
+ Thread.currentThread().isInterrupted());
throw new InterruptedException();
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
GeneralInterrupt si = new GeneralInterrupt();
Thread t = new Thread(si);
t.start();
try {
Thread.sleep(2000);
}
catch (InterruptedException x) {
}
System.out.println("in main() -
interrupting other thread");
t.interrupt();
System.out.println("in main() - leaving");
}
}以上程序输出:
in run() - about to work2()
in main() - interrupting other thread
in main() - leaving
C isInterrupted()=true
in run() - interrupted in work2()
java线程示例2:后台线程示例
package cn.outofmemory.java.example;
public class DaemonThread implements Runnable {
public void run() {
System.out.println("entering run()");
try {
System.out.println("in run(): currentThread() is"
+ Thread.currentThread());
while (true) {
try {
Thread.sleep(500);
} catch (InterruptedException x) {
}
System.out.println("in run(): woke up again");
}
} finally {
System.out.println("leaving run()");
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("entering main()");
Thread t = new Thread(new DaemonThread());
t.setDaemon(true);
t.start();
try {
Thread.sleep(3000);
} catch (InterruptedException x) {
}
System.out.println("leaving main()");
}
}
程序运行将输出如下内容:
entering main()
entering run()
in run(): currentThread() isThread[Thread-0,5,main]
in run(): woke up again
in run(): woke up again
in run(): woke up again
in run(): woke up again
in run(): woke up again
leaving main()
in run(): woke up again
java多线程还有很多高级的内容,本文只是阐述了Thread类的基础用法。
本文转载自:http://outofmemory.cn/java/java.util.concurrent/multi-threading,仅供参考学习























 164
164

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








