先来看看ThreadLocal的源码,get()方法时先获得当前线程的对象,这个对象有一个ThreadLocalMap类型的变量threadLocals,这个变量中保存着当前线程的所有线程变量,然后通过ThreadLocal对象作为key取出对应的值即为当前的ThreadLocal变量在当前线程对应的对象。
public class ThreadLocal<T> {
/**
* ThreadLocals rely on per-thread linear-probe hash maps attached
* to each thread (Thread.threadLocals and
* inheritableThreadLocals). The ThreadLocal objects act as keys,
* searched via threadLocalHashCode. This is a custom hash code
* (useful only within ThreadLocalMaps) that eliminates collisions
* in the common case where consecutively constructed ThreadLocals
* are used by the same threads, while remaining well-behaved in
* less common cases.
*/
private final int threadLocalHashCode = nextHashCode();
/**
* The next hash code to be given out. Updated atomically. Starts at
* zero.
*/
private static AtomicInteger nextHashCode =
new AtomicInteger();
/**
* The difference between successively generated hash codes - turns
* implicit sequential thread-local IDs into near-optimally spread
* multiplicative hash values for power-of-two-sized tables.
*/
private static final int HASH_INCREMENT = 0x61c88647;
/**
* Returns the next hash code.
*/
private static int nextHashCode() {
return nextHashCode.getAndAdd(HASH_INCREMENT);
}
/**
* Returns the current thread's "initial value" for this
* thread-local variable. This method will be invoked the first
* time a thread accesses the variable with the {@link #get}
* method, unless the thread previously invoked the {@link #set}
* method, in which case the <tt>initialValue</tt> method will not
* be invoked for the thread. Normally, this method is invoked at
* most once per thread, but it may be invoked again in case of
* subsequent invocations of {@link #remove} followed by {@link #get}.
*
* <p>This implementation simply returns <tt>null</tt>; if the
* programmer desires thread-local variables to have an initial
* value other than <tt>null</tt>, <tt>ThreadLocal</tt> must be
* subclassed, and this method overridden. Typically, an
* anonymous inner class will be used.
*
* @return the initial value for this thread-local
*/
protected T initialValue() {
return null;
}
/**
* Creates a thread local variable.
*/
public ThreadLocal() {
}
/**
* Returns the value in the current thread's copy of this
* thread-local variable. If the variable has no value for the
* current thread, it is first initialized to the value returned
* by an invocation of the {@link #initialValue} method.
*
* @return the current thread's value of this thread-local
*/
public T get() {
Thread t = Thread.currentThread();
ThreadLocalMap map = getMap(t);
if (map != null) {
ThreadLocalMap.Entry e = map.getEntry(this);
if (e != null)
return (T)e.value;
}
return setInitialValue();
}
/**
* Variant of set() to establish initialValue. Used instead
* of set() in case user has overridden the set() method.
*
* @return the initial value
*/
private T setInitialValue() {
T value = initialValue();
Thread t = Thread.currentThread();
ThreadLocalMap map = getMap(t);
if (map != null)
map.set(this, value);
else
createMap(t, value);
return value;
}
/**
* Sets the current thread's copy of this thread-local variable
* to the specified value. Most subclasses will have no need to
* override this method, relying solely on the {@link #initialValue}
* method to set the values of thread-locals.
*
* @param value the value to be stored in the current thread's copy of
* this thread-local.
*/
public void set(T value) {
Thread t = Thread.currentThread();
ThreadLocalMap map = getMap(t);
if (map != null)
map.set(this, value);
else
createMap(t, value);
}
/**
* Removes the current thread's value for this thread-local
* variable. If this thread-local variable is subsequently
* {@linkplain #get read} by the current thread, its value will be
* reinitialized by invoking its {@link #initialValue} method,
* unless its value is {@linkplain #set set} by the current thread
* in the interim. This may result in multiple invocations of the
* <tt>initialValue</tt> method in the current thread.
*
* @since 1.5
*/
public void remove() {
ThreadLocalMap m = getMap(Thread.currentThread());
if (m != null)
m.remove(this);
}
/**
* Get the map associated with a ThreadLocal. Overridden in
* InheritableThreadLocal.
*
* @param t the current thread
* @return the map
*/
ThreadLocalMap getMap(Thread t) {
return t.threadLocals;
}
/**
* Create the map associated with a ThreadLocal. Overridden in
* InheritableThreadLocal.
*
* @param t the current thread
* @param firstValue value for the initial entry of the map
* @param map the map to store.
*/
void createMap(Thread t, T firstValue) {
t.threadLocals = new ThreadLocalMap(this, firstValue);
}
/**
* Factory method to create map of inherited thread locals.
* Designed to be called only from Thread constructor.
*
* @param parentMap the map associated with parent thread
* @return a map containing the parent's inheritable bindings
*/
static ThreadLocalMap createInheritedMap(ThreadLocalMap parentMap) {
return new ThreadLocalMap(parentMap);
}
/**
* Method childValue is visibly defined in subclass
* InheritableThreadLocal, but is internally defined here for the
* sake of providing createInheritedMap factory method without
* needing to subclass the map class in InheritableThreadLocal.
* This technique is preferable to the alternative of embedding
* instanceof tests in methods.
*/
T childValue(T parentValue) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
}
static class ThreadLocalMap {
......
}
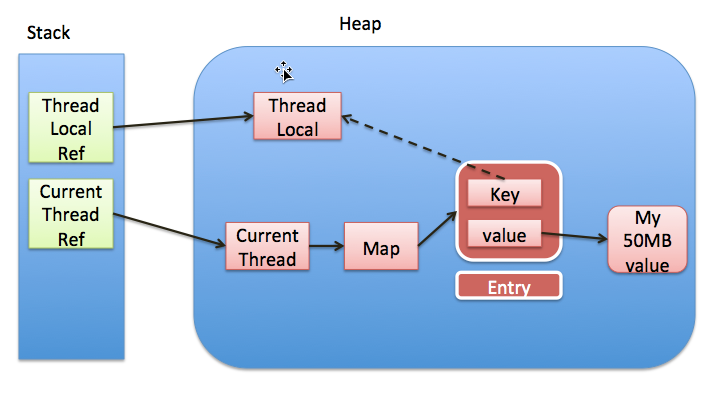
}再来看看下图,事实上,堆中只有一个ThreadLocal对象,这个对象被ThreadLocalMap中的key以一个弱引用指向,而ThreadLocalMap中value指向变量所对应真实对象
会有内存泄漏的风险么?
调用get(),set()方法就会删除ThreadLocalMap中的key为null的Entry,这样在很大程度上可以避免内存泄漏。但是如果一直不调用这两个方法也可以调用remove()手动删除。还有一种方式就是为ThreadLocal变量加上private static,这样就能确保Entry中的key不会指向null,直接用这个key就可以清除对应的Entry。






















 285
285

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








