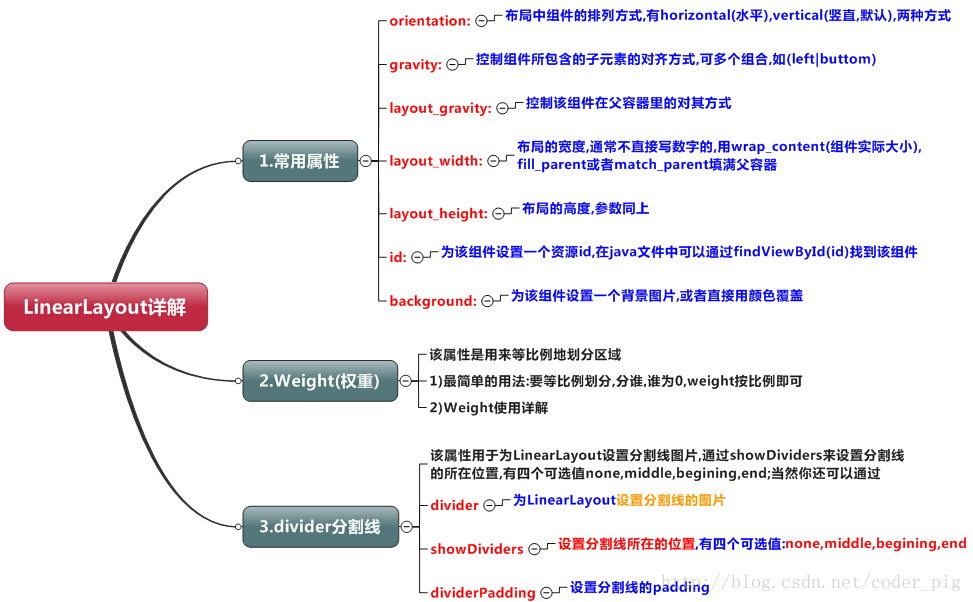
Android中有六大布局,分别是: LinearLayout(线性布局),RelativeLayout(相对布局),TableLayout(表格布局) FrameLayout(帧布局),AbsoluteLayout(绝对布局),GridLayout(网格布局) 而今天我们要讲解的就是第一个布局,LinearLayout(线性布局),我们屏幕适配的使用 用的比较多的就是LinearLayout的weight(权重属性),在这一节里,我们会详细地解析 LinearLayout,包括一些基本的属性,Weight属性的使用,以及比例如何计算,另外还 会说下一个用的比较少的属性:android:divider绘制下划线!
1.weight(权重)属性使用详解:
① 0dp时设置weight(也是最简单的方式)
代码如下:
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:id="@+id/LinearLayout1"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="horizontal">
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="fill_parent"
android:background="#ADFF2F"
android:layout_weight="1"/>
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="fill_parent"
android:background="#DA70D6"
android:layout_weight="2"/>
</LinearLayout> 要实现第一个的1:1的效果,只需要分别把两个LinearLayout的weight改成1和1就可以了 用法归纳: 按比例划分水平方向:将涉及到的View的android:width属性设置为0dp,然后设置为android weight属性设置比例即可;类推,竖直方向,只需设android:height为0dp,然后设weight属性即可! 大家可以自己写个竖直方向的等比例划分的体验下简单用法!
② wrap_content 时设置weight
wrap_content比较简单,直接就按比例的了

代码如下:
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:id="@+id/LinearLayout1"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="horizontal" >
<TextView
android:layout_weight="1"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="fill_parent"
android:text="one"
android:background="#98FB98"
/>
<TextView
android:layout_weight="2"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="fill_parent"
android:text="two"
android:background="#FFFF00"
/>
<TextView
android:layout_weight="3"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="fill_parent"
android:text="three"
android:background="#FF00FF"
/>
</LinearLayout> ③match_parent(fill_parent) 设置weight, 这个则需要计算了
代码如下:
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:id="@+id/LinearLayout1"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent" >
<TextView
android:layout_weight="1"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent"
android:text="one"
android:background="#98FB98"
/>
<TextView
android:layout_weight="2"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent"
android:text="two"
android:background="#FFFF00"
/>
<TextView
android:layout_weight="3"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent"
android:text="three"
android:background="#FF00FF"
/>
</LinearLayout> 这就有疑问了,怎么设置明明是1:2:3,结果确实2:1,且第三个都无法显示出来?
真正的原因是Layout_width="fill_parent"的原因造成的。依照上面理解我们来分析:系统先给3个textview分配他们所要的宽度fill_parent,也就是说每一都是填满他的父控件,这里就是屏幕的宽度,那么这时候的剩余空间=1*parent_width - 3*parent_width = -2*parent_width (parent_width指的是屏幕宽度 )
那么第一个TextView的实际所占宽度应该=fill_parent的宽度, 即1*parent_width + 他所占剩余空间的权重比列1/6 * 剩余空间大小(即-2 parent_width)=2/3*parent_width,即占屏幕宽度的2/3显示;
同理第二个TextView的实际所占宽度=1*parent_width + 2/6*(-2*parent_width)=1/3*parent_width,即占屏幕的1/3显示;
第三个TextView的实际所占宽度=1*parent_width + 3/6*(-2parent_width)=0*parent_width;所以就不能显示。
④在JAVA代码中设置weight属性的方式
setLayoutParams(new LayoutParams(LayoutParams.FILL_PARENT,
LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT, 1)); 2. layout_gravity 和 gravity属性介绍
layout_gravity控制该组件在父容器中的对齐方式
gravity 控制该组件所包含的子VIEW的对其方式
当 android:orientation="vertical" 时, 只有水平方向的设置才起作用,垂直方向的设置不起作用。 即:left,right,center_horizontal 是生效的。
当 android:orientation="horizontal" 时, 只有垂直方向的设置才起作用,水平方向的设置不起作用。 即:top,bottom,center_vertical 是生效的。
不过,控制复杂的布局,最好使用RelativeLayout相对布局。
























 4663
4663

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








