Maria participates in a bicycle race.
The speedway takes place on the shores of Lake Lucerne, just repeating its contour. As you know, the lake shore consists only of straight sections, directed to the north, south, east or west.
Let's introduce a system of coordinates, directing the Ox axis from west to east, and the Oy axis from south to north. As a starting position of the race the southernmost point of the track is selected (and if there are several such points, the most western among them). The participants start the race, moving to the north. At all straight sections of the track, the participants travel in one of the four directions (north, south, east or west) and change the direction of movement only in bends between the straight sections. The participants, of course, never turn back, that is, they do not change the direction of movement from north to south or from east to west (or vice versa).
Maria is still young, so she does not feel confident at some turns. Namely, Maria feels insecure if at a failed or untimely turn, she gets into the water. In other words, Maria considers the turn dangerous if she immediately gets into the water if it is ignored.
Help Maria get ready for the competition — determine the number of dangerous turns on the track.
The first line of the input contains an integer n (4 ≤ n ≤ 1000) — the number of straight sections of the track.
The following (n + 1)-th line contains pairs of integers (xi, yi) ( - 10 000 ≤ xi, yi ≤ 10 000). The first of these points is the starting position. The i-th straight section of the track begins at the point (xi, yi) and ends at the point (xi + 1, yi + 1).
It is guaranteed that:
- the first straight section is directed to the north;
- the southernmost (and if there are several, then the most western of among them) point of the track is the first point;
- the last point coincides with the first one (i.e., the start position);
- any pair of straight sections of the track has no shared points (except for the neighboring ones, they share exactly one point);
- no pair of points (except for the first and last one) is the same;
- no two adjacent straight sections are directed in the same direction or in opposite directions.
Print a single integer — the number of dangerous turns on the track.
6 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 2 2 2 2 0 0 0
1
16 1 1 1 5 3 5 3 7 2 7 2 9 6 9 6 7 5 7 5 3 4 3 4 4 3 4 3 2 5 2 5 1 1 1
6
The first sample corresponds to the picture:
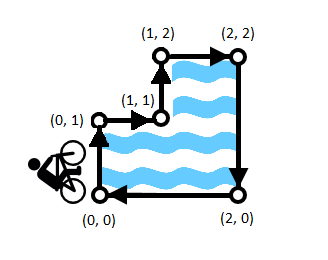
The picture shows that you can get in the water under unfortunate circumstances only at turn at the point (1, 1). Thus, the answer is 1.
AC代码:
#include<iostream>
#include<functional>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cstring>
#include<string>
#include<vector>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cmath>
#include<map>
using namespace std;
#define CRL(a) memset(a,0,sizeof(a))
#define QWQ ios::sync_with_stdio(0)
typedef unsigned __int64 LL;
typedef __int64 ll;
const int T = 100000+50;
const int mod = 1000000007;
int main()
{
#ifdef zsc
freopen("input.txt","r",stdin);
#endif
int n;
cin >> n;
cout << (n-4)/2 << endl;
return 0;
}暴力代码(长知识了):
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
#include<algorithm>
#include<vector>
#include<utility>
#include<cassert>
using namespace std;
const int MAXN = 1e4 + 30;
int n, x[MAXN], y[MAXN];
string s;
int check(string t){
if (t == "UL") return 1;
if (t == "UR") return 0;
if (t == "DL") return 0;
if (t == "DR") return 1;
if (t == "LU") return 0;
if (t == "LD") return 1;
if (t == "RU") return 1;
if (t == "RD") return 0;
assert(0);
}
int main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0);
cin >> n;
for (int i = 0; i <= n; i++) cin >> x[i] >> y[i];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++){
if (x[i] < x[i + 1]) s += 'R';
if (x[i] > x[i + 1]) s += 'L';
if (y[i] < y[i + 1]) s += 'U';
if (y[i] > y[i + 1]) s += 'D';
}
int cn = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++){
string temp;
temp += s[i];
temp += s[(i + 1) % n];
cn += check(temp);
}
cout << cn << "\n";
return 0;
}
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
int const N = 1234567;
int x[N], y[N];
int main() {
int n;
scanf("%d", &n);
scanf("%d%d", x, y);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
scanf("%d%d", x + i, y + i);
}
long long area = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
int j = (i + 1) % n;
area += x[i] * y[j] - x[j] * y[i];
}
int ans = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
int j = (i + 1) % n;
int k = (j + 1) % n;
int v = (x[j] - x[i]) * (y[k] - y[j]) - (x[k] - x[j]) * (y[j] - y[i]);
if (area > 0) {
v = -v;
}
if (v > 0) {
++ans;
}
}
printf("%d\n", ans);
}//#define MYDEBUG
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#define TASK "radio"
#pragma comment(linker, "/STACK:536870912")
#include <cstdio>
#include <iostream>
#include <iomanip>
#include <cmath>
#include <ctime>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
#include <vector>
#include <stack>
#include <queue>
#include <set>
#include <map>
#include <string>
#include <functional>
#include <cassert>
#include <bitset>
#include <unordered_set>
#include <unordered_map>
#include <random>
const int MOD = 1000000007;
const int INF = 1000000001;
const int MAXN = 100010;
const long double EPS = 1e-6;
const int HASH_POW = 29;
const long double PI = acos(-1.0);
using namespace std;
void my_return(int code)
{
#ifdef MYDEBUG
cout << "\nTime = " << fixed << setprecision(3) << double(clock()) / CLOCKS_PER_SEC << endl;
#endif
exit(code);
}
int n;
struct pt
{
int x, y;
} p[1010];
bool ccw(pt a, pt b, pt c)
{
return a.x*(b.y - c.y) + b.x*(c.y - a.y) + c.x*(a.y - b.y) > 0;
}
int main()
{
cin.sync_with_stdio(0);
cin.tie(0);
mt19937 mt_rand(time(0));
#ifdef MYDEBUG
freopen("input.txt", "r", stdin);
freopen("output.txt", "w", stdout);
#else
/*freopen(TASK".in", "rt", stdin);
freopen(TASK".out", "wt", stdout);*/
/*freopen("input.txt", "rt", stdin);
freopen("output.txt", "wt", stdout);*/
#endif
scanf("%d", &n);
for (int i = 0; i <= n; ++i)
scanf("%d %d", &p[i].x, &p[i].y);
int ans = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i)
{
pt a = p[i], b = p[(i + 1) % n], c = p[(i + 2) % n];
if (ccw(a, b, c))
++ans;
}
printf("%d\n", ans);
my_return(0);
}




















 2816
2816











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








