目录
一、了解迷宫问题
实现迷宫问题首先要清楚在迷宫中,哪些路可以通过,哪些路不能通过,通过的路不能重复走,如何知道哪些路已经走过。
二、解决迷宫问题
1、迷宫设计
以二维数组作为迷宫,其中 以PASS为通路,WALL作为墙(即障碍,不能通过)FOOT代表走过的路径,MARK设计为前方无法通过的死路。
#define PASS 0
#define WALL 1
#define FOOT 8
#define MARK 42、结构体设计
①PosType 记录所在位置的坐标
typedef struct
{
int row;
int col;
}PosType;②SElemType 记录所走步数、所在位置以及此时所标记的方向
以数字1、2、3、4分别代表此时所走方向为左、下、右、上
typedef struct
{
int ord;//记录步数
PosType seat;
int di;// 方向 1 left 2 DOWN 3 right 4 UP
}SElemType;3、静态数组设计
以静态二维数组作为迷宫
#define ROWSIZE 10
#define COLSIZE 10
typedef int MazeType[ROWSIZE][COLSIZE];4、函数设计
①初始化静态二维数组,使其成为一个迷宫(以文件方式打开)
void InitMaze(MazeType maze)
{
FILE* fp = fopen("maze.txt", "r");
if (NULL == fp)
{
printf("file open error \n");
exit(1);
}
for (int i = 0; i < ROWSIZE; ++i)
{
for (int j = 0; j < COLSIZE; ++j)
{
fscanf(fp, "%d", &maze[i][j]);
}
}
fclose(fp);
fp = NULL;
}文件maze.txt

②路径函数
IsPass(MazeType maze,PosType pos);判断是否为通路
FootPrint(MazeType maze,PosType pos);将走过的路径设置为FOOT
NextPos(PosType pos,int di);根据所走方向,对坐标进行修改
MarkPrint(MazeType maze,PosType pos);将每一个方向都不能继续走的坐标标记为死路
MazePath(MazeType maze, const PosType start, const PosType end);将能走的通路入栈,并与出口进行比较,若不是出口,则继续走下去,否则结束。四个方向均不能通过的则出栈,直至栈内元素全部出栈。最后摧毁所使用的栈(借助通用链栈)。
static bool IsPass(MazeType maze, PosType pos)
{
return maze[pos.row][pos.col] == PASS;
}
static void FootPrint(MazeType maze, PosType pos)
{
maze[pos.row][pos.col] = FOOT;
}
static PosType NextPos(PosType pos, int di)
{
switch (di)
{
case 1: pos.col -= 1; break;
case 2: pos.row += 1; break;
case 3: pos.col += 1; break;
case 4: pos.row -= 1; break;
}
return pos;
}
static void MarkPrint(MazeType maze, PosType pos)
{
maze[pos.row][pos.col] = MARK;
}
bool MazePath(MazeType maze, const PosType start, const PosType end)
{
bool res = false;
GenLinkStack gs;
InitLinkStack(&gs, sizeof(SElemType));
PosType curpos = start;
int curstep = 1;
SElemType e;
do
{
if (IsPass(maze, curpos))
{
FootPrint(maze, curpos);
e.ord = curstep++;
e.di = 1;
e.seat = curpos;
Push(&gs, &e);
if (curpos.row == end.row && curpos.col == end.col)
{
res = true;
break;
}
curpos = NextPos(curpos, 1);
}
else
{
if (!IsEmpty(&gs))
{
Pop(&gs, &e);
while (e.di == 4 && !IsEmpty(&gs))
{
MarkPrint(maze, e.seat);
Pop(&gs, &e);
}
if (e.di < 4)
{
e.di += 1;
Push(&gs, &e);
curpos = NextPos(e.seat, e.di);
}
}
}
} while (!IsEmpty(&gs));
DestroyLinkStack(&gs);
return res;
}三、代码测试
int main()
{
MazeType maze;
InitMaze(maze);
PrintMaze(maze);
PosType start = { 1,1 };
PosType end = { 8,8 };
MazePath(maze,start,end);
PrintMaze(maze);
return 0;
}测试结果:
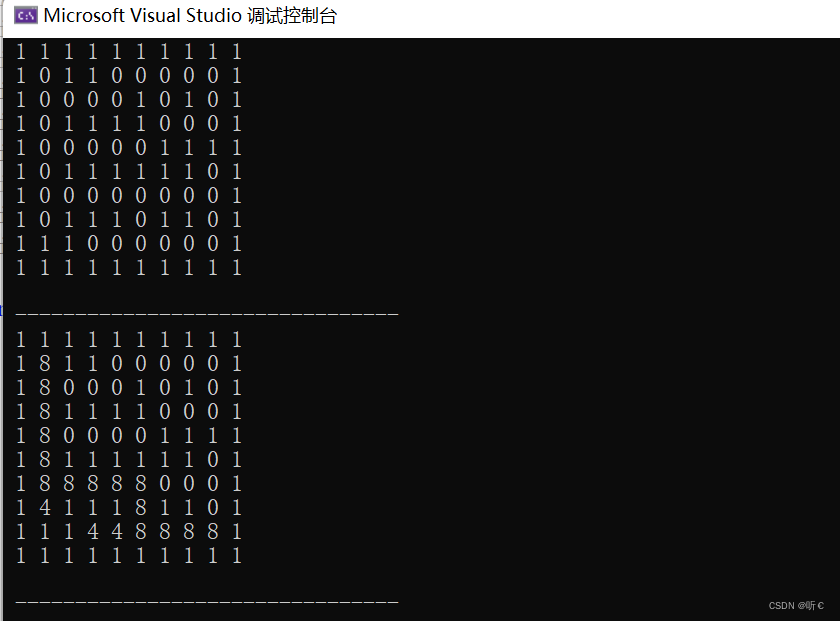





















 965
965











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








