
要知道具体的原理,可以看其他博客的作品。
代码如下:
#include<iostream>
#include<Eigen\dense>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
using namespace Eigen;
int Fisher::fisher(vector<VectorXd> x, vector<VectorXd> y, VectorXd test_vector)
//返回1,代表属于第一类;返回2,代表属于第二类。
{
if (x.size() < 0 || y.size() < 0 || x.size() != y.size())
{
cout << "两个类的样本向量个数有误。" << endl;
return 0;
}
if (x[0].size() < 1 || y[0].size() < 1 || x[0].size() != y[0].size())
{
cout << "两个类的样本向量维度有误。" << endl;
return 0;
}
if (test_vector.size() != x[0].size())
{
cout << "给定的向量有误。" << endl;
return 0;
}
int n = x[0].size();
VectorXd meanx(n), meany(n);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
meanx(i) = 0;
meany(i) = 0;
}
//对每个维度分别求和
for (int i = 0; i < x.size(); i++)
{
meanx += x[i] ;
meany += y[i];
}
//分别求平均
double c = 1.0 / x.size();
//cout << meanx << endl;
meanx = meanx * c;
meany = meany * c;
//cout << meanx << endl;
//求类内离散矩阵
MatrixXd Swx, Swy, Sw;
Swx.setZero(n, n);
Swy.setZero(n, n);
for (int i = 0; i < x.size(); i++)
{
Swx += (x[i] - meanx) * (x[i] - meanx).transpose();
Swy += (y[i] - meany) * (y[i] - meany).transpose();
}
//求类内总离散矩阵
Sw = Swx + Swy;
cout << "类内总离散矩阵:" << endl << Sw << endl;
//实现投影
MatrixXd w, w0;
w = Sw.inverse() * (meany - meanx);
w0 = (w.transpose() * meanx + w.transpose() * meany) / 2;
cout << "最佳投影方向:" << endl << w << endl << "阈值为: " << w0 << endl;
MatrixXd sample;
double w0_num = w0(0, 0);
sample = w.transpose() * test_vector;
double sample_num = sample(0, 0);
if (sample_num < w0_num)
cout << "给定的向量属于第一类。" << endl;
else
cout << "给定的向量属于第二类。" << endl;
return 1;
}
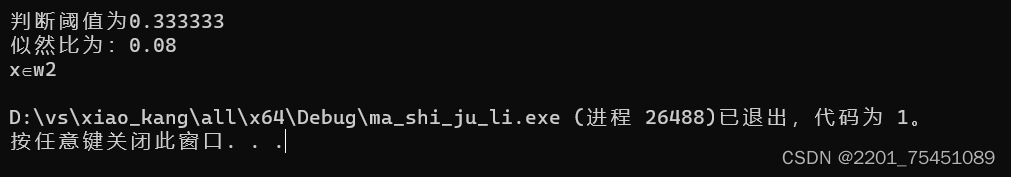
运行结果如下(基于我自己的数据):






















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








