前面通过前面篇文章介绍了
中的各项基本知识。从本篇文章开始,将对
中的
中的各项内容进行介绍:
目录
1. string类对象的常见构造:
string类对象的常见构造:
首先,对于的使用,需要引入头文件:
#include<string> 对于类中的常见构造,可以通过string::string - C++ Reference (cplusplus.com)进行查询。具体如下:

文章将对上述图片中某几个常用的函数进行介绍,其他函数的使用方法可以通过上方网址进行查阅。对于上述函数的作用,主要是用于创建一个类对象。例如,创建一个空的
类对象的方法为:
int main()
{
string s1; //创建一个空的string类对象
return 0;
} 如果想创建一个包含内容的类对象,其方法为:
string s2("hello world");上述方法是使用了一个常量字符串来初始化这个类对象。对应了上图中给出的:
string(const char* str)在上图中,有一个函数中的参数包含了引用,即:
string( const char& str)此函数的功能可以理解为一个拷贝构造函数,使用方法有如下两种:
string s3 = s2;
string s4(const char& s2);对于类对象的打印,直接使用
即可,例如:
int main()
{
string s1; //创建一个空的string类对象
string s2("hello world");
string s3 = s2;
cout << s1 << endl;
cout << s2 << endl;
cout << s3 << endl;
return 0;
}2. string类对象的赋值操作:
对于类对象的赋值操作,可以分为三类:
string& operator= (const string& str);
string& operator= (const char* s);
string& operator= (char c);对于上面三类赋值操作的使用,如下所示:
s1 = s2;
cout << s1 << endl;
s1 = 'x';
cout << s1 << endl;
s1 = "hello worle";
cout << s1 << endl;运行结果如下:
3. string类对象的访问与遍历:
3.1 string类对象的访问:
对于类对象的访问,通过
来实现。对于此函数,主要有两种形式:
char& operator[] (size_t pos);
const char& operator[] (size_t pos) const;对于二者的不同点,可以认为第一种可读可写,但是第二种只能读。例如,访问上述代码中,中下标为
的字符,即:
cout << s2[7] << endl;运行结果如下:

上面说到,对于第一种方式,不光可读,而且可写,因此,让中的第
个字符变为字母
,即:
s2[4] = 'x';
cout << s2 << endl; 运行结果如下:
3.2 string类对象的遍历:
为了遍历对象,首先需要知道其长度。对于获取类对象的长度,可以采用
函数完成,具体使用方法如下:
for (int i = 0; i < s2.size(); i++)
{
cout << s2[i] << ' ';
}运行结果如下:
通过给出的上述函数,可以完成对于的逆置。代码如下 :
int begin = 0;
int end = s2.size() - 1;
while (begin < end)
{
int tmp = s2[begin];
s2[begin] = s2[end];
s2[end] = tmp;
begin++;
end--;
}
for (int i = 0; i < s2.size(); i++)
{
cout << s2[i] << ' ';
}运行结果如下:

在上一篇关于模板的文章中C++(10)——模板-CSDN博客就以交换函数来对函数模板进行说明。在
中,提供了交换函数
的实现,即:

因此,可以通过此函数,来对上述代码完成简化,即:
int begin = 0;
int end = s2.size() - 1;
while (begin < end)
{
swap(s2[begin], s2[end]);
begin++;
end--;
}
for (int i = 0; i < s2.size(); i++)
{
cout << s2[i] << ' ';
}运行结果如下:

4. 迭代器:
对于类对象的访问,除了使用
,还可以使用迭代器进行访问。即:
 具体使用方法如下:
具体使用方法如下:
cout << "迭代器访问测试" << endl;
string::iterator i = s2.begin();
while (i != s2.end())
{
cout << *i << " ";
++i;
}
return 0;
}运行结果如下:

对于一个类型的对象,即:
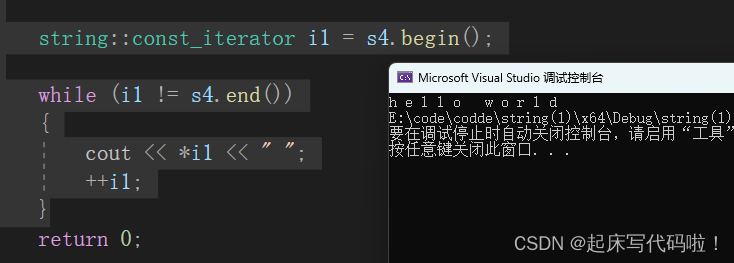
const string s4("hello world");
string::const_iterator i1 = s4.begin();
while (i1 != s4.end())
{
cout << *i1 << " ";
++i1;
}运行结果为:
对于逆置迭代器,对于和非
对象的访问方式如下:
cout << "非const对象逆置访问" << endl;
string s5("HELLO WORLD");
string::reverse_iterator i2 = s5.rbegin();
while (i2 != s5.rend())
{
cout << *i2 << ' ';
++i2;
}
cout << endl;
cout << "const类型对象逆置访问" << endl;
string::const_reverse_iterator i3 = s4.rbegin();
while (i3 != s4.rend())
{
cout << *i3 << ' ';
++i3;
}运行效果如下:

5.string类对象的容量操作:
5.1 size和capacity:
对于如何获取一个类对象的存储容量,可以用关键字
完成,即:
string s1; //创建一个空的string类对象
string s2("hello world");
cout << s1.capacity() << endl;
cout << s2.capacity() << endl;运行结果如下:

不难发现,的大小只和该类型能够存储多少内容有关,与对象中是否有内容无关。
对于前面用到的,是用于反应这个对象中字符串的长度的。与对象中是否有内容有关。例如:
cout << s1.size() << endl;
cout << s2.size() << endl;
运行结果如下:
5.2 reserve和resize:
主要用于改变
类对象的大小。对于
,假如在知道了需要扩容的大小后,可以对
类对象进行扩容,例如:
string s1; //创建一个空的string类对象
cout << "进行扩容前" << endl;
cout << s1.capacity() << endl;
cout << s1.size() << endl;
s1.reserve(500);
cout << "进行扩容后" << endl;
cout << s1.capacity() << endl;
cout << s1.size() << endl;运行结果为:

需要注意,使用进行扩容时,扩容后的大小并不一定等于预设的值,通常会大于这个值。
当使用对
类对象进行缩容操作时,例如:
string s2("hello world");
cout << " 进行缩容前" << endl;
cout << s2.capacity() << endl;
cout << s2 << endl;
cout << s2.size() << endl;
cout << " 进行缩容后" << endl;
s2.reserve(5);
cout << s2.capacity() << endl;
cout << s2 << endl;
cout << s2.size() << endl;运行结果为:
通过上述结果,不难看出,使用对
类对象进行缩容时,并不能缩小到这个对象的最小容量。同时,
只能改变空间,并不能影响对象中的内容。这一点可以从缩容前后的
值看出。
对于,与
只影响空间不影响内容不同,
对于二者都会影响。例如:
string s2("hello world"); //创建一个空的string类对象
cout << "进行扩容前" << endl;
cout << s2.capacity() << endl;
cout << s2.size() << endl;
s2.resize(500);
cout << "进行扩容后" << endl;
cout << s2.capacity() << endl;
cout << s2.size() << endl;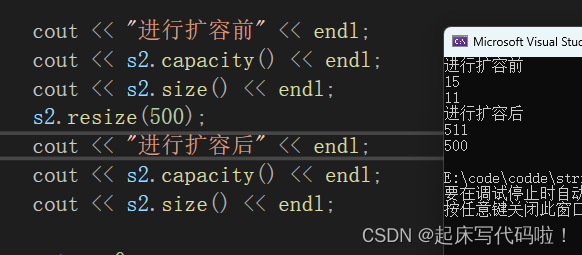
通过打印前后的结果可以看到,利用进行扩容后,对象的
都发生了变化。
对于其中内容的改变,可以通过监视窗口进行查看:
进行扩容前, 中的内容如下图所示:

进行扩容后,发现,此时扩充的部分的值全部为\0 :

对于使用进行扩容时,也可以自定义后面的扩充部分的内容,例如:
cout << "进行扩容前" << endl;
cout << s2.capacity() << endl;
cout << s2.size() << endl;
s2.resize(500,'x');
cout << "进行扩容后" << endl;
cout << s2.capacity() << endl;
cout << s2.size() << endl;运行结果为:
当利用进行缩容时,此时有两种情况:
,
,即缩容后的空间小于对象的最小存储,但是大于对象中字符串的长度:
cout << "进行缩容前" << endl;
cout << s2.capacity() << endl;
cout << s2.size() << endl;
s2.resize(12);
cout << "进行缩容后" << endl;
cout << s2.capacity() << endl;
cout << s2.size() << endl;
运行结果如下:
从结果可以看出,不影响的值。但是会改变
的值,并且还会用\0进行填充。
当 时,即:
cout << "进行缩容前" << endl;
cout << s2.capacity() << endl;
cout << s2.size() << endl;
s2.resize(8);
cout << "进行缩容后" << endl;
cout << s2.capacity() << endl;
cout << s2.size() << endl;
运行结果如下:

通过结果可以看出,此时的对于
都有影响,并且会删除对象中的内容,这一点可以从监视窗口进行确认:

6. 对于对象中内容的修改:
6.1 push_back:
使用_
可以在已有对象后方插入单个字符,例如:
string s4("hello");
s4.push_back('a');
cout << s4 << endl;打印结果如下:

6.2 append:
对于的使用有多种方式,例如:
string& append (const string& str);
string& append (const char* s)对于第一种,使用方法如下:
string s4("hello");
const string& s5 = "world";
s4.append(s5);
cout << s4 << endl;运行结果如下:
6.3 operator +=:
使用方式同样有许多种:
string& operator+= (const string& str);
string& operator+= (const char* s);
string& operator+= (char c);例如:
s6 += 'a';
cout << s6 << endl;
s6 += "ABCDE";
cout << s6 << endl;
s6 += s5;
cout << s6 << endl;运行结果如下: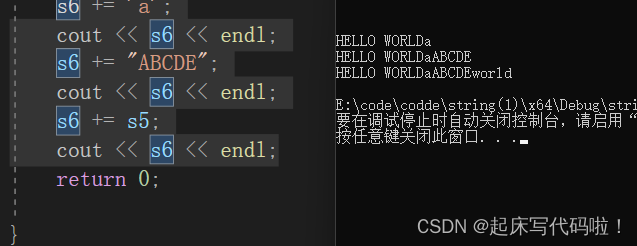
7. 勘误:
由于个人能力有限,书中难免出现汉字拼写错误、代码意义解释错误、内容逻辑以及理解错误等不同类型的错误。首先感谢各位大佬能花掉自己宝贵的时间阅读此文章,愿大佬们斧正,发现错误可以通过私信联系,本人不胜感激。






















 2184
2184











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










