1.邻接矩阵深度和广度遍历算法
#include "stdio.h"
#include "stdlib.h"
#include "math.h"
#include "time.h"
#define OK 1
#define ERROR 0
#define TRUE 1
#define FALSE 0
typedef int Status; /* Status是函数的类型,其值是函数结果状态代码,如OK等 */
typedef int Boolean; /* Boolean是布尔类型,其值是TRUE或FALSE */
typedef char VertexType; /* 顶点类型应由用户定义 */
typedef int EdgeType; /* 边上的权值类型应由用户定义 */
#define MAXSIZE 9 /* 存储空间初始分配量 */
#define MAXEDGE 15
#define MAXVEX 9
typedef struct
{
VertexType vexs[MAXVEX]; /* 顶点表 */
EdgeType arc[MAXVEX][MAXVEX];/* 邻接矩阵,可看作边表 */
int numVertexes, numEdges; /* 图中当前的顶点数和边数 */
}MGraph;
/* 用到的队列结构与函数********************************** */
/* 循环队列的顺序存储结构 */
typedef struct
{
int data[MAXSIZE];
int front; /* 头指针 */
int rear; /* 尾指针,若队列不空,指向队列尾元素的下一个位置 */
}Queue;
/* 初始化一个空队列Q */
Status InitQueue(Queue *Q)
{
Q->front=0;
Q->rear=0;
return OK;
}
/* 若队列Q为空队列,则返回TRUE,否则返回FALSE */
Status QueueEmpty(Queue Q)
{
if(Q.front==Q.rear) /* 队列空的标志 */
return TRUE;
else
return FALSE;
}
/* 若队列未满,则插入元素e为Q新的队尾元素 */
Status EnQueue(Queue *Q,int e)
{
if ((Q->rear+1)%MAXSIZE == Q->front) /* 队列满的判断 */
return ERROR;
Q->data[Q->rear]=e; /* 将元素e赋值给队尾 */
Q->rear=(Q->rear+1)%MAXSIZE;/* rear指针向后移一位置, */
/* 若到最后则转到数组头部 */
return OK;
}
/* 若队列不空,则删除Q中队头元素,用e返回其值 */
Status DeQueue(Queue *Q,int *e)
{
if (Q->front == Q->rear) /* 队列空的判断 */
return ERROR;
*e=Q->data[Q->front]; /* 将队头元素赋值给e */
Q->front=(Q->front+1)%MAXSIZE; /* front指针向后移一位置, */
/* 若到最后则转到数组头部 */
return OK;
}
/* ****************************************************** */
void CreateMGraph(MGraph *G)
{
int i, j;
G->numEdges=15;
G->numVertexes=9;
/* 读入顶点信息,建立顶点表 */
G->vexs[0]='A';
G->vexs[1]='B';
G->vexs[2]='C';
G->vexs[3]='D';
G->vexs[4]='E';
G->vexs[5]='F';
G->vexs[6]='G';
G->vexs[7]='H';
G->vexs[8]='I';
for (i = 0; i < G->numVertexes; i++)/* 初始化图 */
{
for ( j = 0; j < G->numVertexes; j++)
{
G->arc[i][j]=0;
}
}
G->arc[0][1]=1;
G->arc[0][5]=1;
G->arc[1][2]=1;
G->arc[1][8]=1;
G->arc[1][6]=1;
G->arc[2][3]=1;
G->arc[2][8]=1;
G->arc[3][4]=1;
G->arc[3][7]=1;
G->arc[3][6]=1;
G->arc[3][8]=1;
G->arc[4][5]=1;
G->arc[4][7]=1;
G->arc[5][6]=1;
G->arc[6][7]=1;
for(i = 0; i < G->numVertexes; i++)
{
for(j = i; j < G->numVertexes; j++)
{
G->arc[j][i] =G->arc[i][j];
}
}
}
Boolean visited[MAXVEX]; /* 访问标志的数组 */
/* 邻接矩阵的深度优先递归算法 */
void DFS(MGraph G, int i)
{
int j;
visited[i]=TRUE;
printf("%c",G.vexs[i]) ;
for(j=0;j<G.numVertexes;j++)
if(G.arc[i][j]==1&&!visited[j])
DFS(G,j);
}
/* 邻接矩阵的深度遍历操作 */
void DFSTraverse(MGraph G)
{
int i;
for(i=0;i<G.numVertexes;i++)
visited[i]=FALSE;
for(i=0;i<G.numVertexes;i++)
if(!visited[i])
DFS(G,i);
}
/* 邻接矩阵的广度遍历算法 */
void BFSTraverse(MGraph G)
{
int i,j;
Queue Q;
for(i=0;i<G.numVertexes;i++)
visited[i]=FALSE;
InitQueue(&Q);
for(i=0;i<G.numVertexes;i++)
{
if(!visited[i])
{
visited[i]=TRUE;
printf("%c",G.vexs[i]);
EnQueue(&Q,i);
while(!QueueEmpty(Q))
{
DeQueue(&Q,&i);
for(j=0;j<G.numVertexes;j++)
{
if(G.arc[i][j]==1&&!visited[j])
{
visited[j]=TRUE;
printf("%c",G.vexs[j]);
EnQueue(&Q,j);
}
}
}
}
}
}
int main(void)
{
MGraph G;
CreateMGraph(&G);
printf("\n深度遍历:");
DFSTraverse(G);
printf("\n广度遍历:");
BFSTraverse(G);
return 0;
}
2.邻接表深度和广度遍历
#include "stdio.h"
#include "stdlib.h"
#include "math.h"
#include "time.h"
#define OK 1
#define ERROR 0
#define TRUE 1
#define FALSE 0
#define MAXSIZE 9 /* 存储空间初始分配量 */
#define MAXEDGE 15
#define MAXVEX 9
typedef int Status; /* Status是函数的类型,其值是函数结果状态代码,如OK等 */
typedef int Boolean; /* Boolean是布尔类型,其值是TRUE或FALSE */
typedef char VertexType; /* 顶点类型应由用户定义 */
typedef int EdgeType; /* 边上的权值类型应由用户定义 */
/* 邻接矩阵结构 */
typedef struct
{
VertexType vexs[MAXVEX]; /* 顶点表 */
EdgeType arc[MAXVEX][MAXVEX];/* 邻接矩阵,可看作边表 */
int numVertexes, numEdges; /* 图中当前的顶点数和边数 */
}MGraph;
/* 邻接表结构****************** */
typedef struct EdgeNode /* 边表结点 */
{
int adjvex; /* 邻接点域,存储该顶点对应的下标 */
int weight; /* 用于存储权值,对于非网图可以不需要 */
struct EdgeNode *next; /* 链域,指向下一个邻接点 */
}EdgeNode;
typedef struct VertexNode /* 顶点表结点 */
{
int in; /* 顶点入度 */
char data; /* 顶点域,存储顶点信息 */
EdgeNode *firstedge;/* 边表头指针 */
}VertexNode, AdjList[MAXVEX];
typedef struct
{
AdjList adjList;
int numVertexes,numEdges; /* 图中当前顶点数和边数 */
}graphAdjList,*GraphAdjList;
/* **************************** */
/* 用到的队列结构与函数********************************** */
/* 循环队列的顺序存储结构 */
typedef struct
{
int data[MAXSIZE];
int front; /* 头指针 */
int rear; /* 尾指针,若队列不空,指向队列尾元素的下一个位置 */
}Queue;
/* 初始化一个空队列Q */
Status InitQueue(Queue *Q)
{
Q->front=0;
Q->rear=0;
return OK;
}
/* 若队列Q为空队列,则返回TRUE,否则返回FALSE */
Status QueueEmpty(Queue Q)
{
if(Q.front==Q.rear) /* 队列空的标志 */
return TRUE;
else
return FALSE;
}
/* 若队列未满,则插入元素e为Q新的队尾元素 */
Status EnQueue(Queue *Q,int e)
{
if ((Q->rear+1)%MAXSIZE == Q->front) /* 队列满的判断 */
return ERROR;
Q->data[Q->rear]=e; /* 将元素e赋值给队尾 */
Q->rear=(Q->rear+1)%MAXSIZE;/* rear指针向后移一位置, */
/* 若到最后则转到数组头部 */
return OK;
}
/* 若队列不空,则删除Q中队头元素,用e返回其值 */
Status DeQueue(Queue *Q,int *e)
{
if (Q->front == Q->rear) /* 队列空的判断 */
return ERROR;
*e=Q->data[Q->front]; /* 将队头元素赋值给e */
Q->front=(Q->front+1)%MAXSIZE; /* front指针向后移一位置, */
/* 若到最后则转到数组头部 */
return OK;
}
/* ****************************************************** */
void CreateMGraph(MGraph *G)
{
int i, j;
G->numEdges=15;
G->numVertexes=9;
/* 读入顶点信息,建立顶点表 */
G->vexs[0]='A';
G->vexs[1]='B';
G->vexs[2]='C';
G->vexs[3]='D';
G->vexs[4]='E';
G->vexs[5]='F';
G->vexs[6]='G';
G->vexs[7]='H';
G->vexs[8]='I';
for (i = 0; i < G->numVertexes; i++)/* 初始化图 */
{
for ( j = 0; j < G->numVertexes; j++)
{
G->arc[i][j]=0;
}
}
G->arc[0][1]=1;
G->arc[0][5]=1;
G->arc[1][2]=1;
G->arc[1][8]=1;
G->arc[1][6]=1;
G->arc[2][3]=1;
G->arc[2][8]=1;
G->arc[3][4]=1;
G->arc[3][7]=1;
G->arc[3][6]=1;
G->arc[3][8]=1;
G->arc[4][5]=1;
G->arc[4][7]=1;
G->arc[5][6]=1;
G->arc[6][7]=1;
for(i = 0; i < G->numVertexes; i++)
{
for(j = i; j < G->numVertexes; j++)
{
G->arc[j][i] =G->arc[i][j];
}
}
}
/* 利用邻接矩阵构建邻接表 */
void CreateALGraph(MGraph G,GraphAdjList *GL)
{
int i,j;
EdgeNode *e;
*GL = (GraphAdjList)malloc(sizeof(graphAdjList));
(*GL)->numVertexes=G.numVertexes;
(*GL)->numEdges=G.numEdges;
for(i= 0;i <G.numVertexes;i++) /* 读入顶点信息,建立顶点表 */
{
(*GL)->adjList[i].in=0;
(*GL)->adjList[i].data=G.vexs[i];
(*GL)->adjList[i].firstedge=NULL; /* 将边表置为空表 */
}
for(i=0;i<G.numVertexes;i++) /* 建立边表 */
{
for(j=G.numVertexes-1;j>=0;j--)
{
if (G.arc[i][j]==1)
{
e=(EdgeNode *)malloc(sizeof(EdgeNode));
//下面6句代码仅仅只是为了与图书中的206页图匹配,让生成的队列符合书中图示。
//实际构建无需这样,只需理解当前就是构建一个图结构的邻接表即可
if (i==1 && j==8)
e->adjvex=6;
else if (i==1 && j==6)
e->adjvex=8;
else
e->adjvex=j; /* 邻接序号为j */
//正常代码下如下
//e->adjvex=j; /* 邻接序号为j */
e->next=(*GL)->adjList[i].firstedge; /* 将当前顶点上的指向的结点指针赋值给e */
(*GL)->adjList[i].firstedge=e; /* 将当前顶点的指针指向e */
(*GL)->adjList[j].in++;
}
}
}
}
Boolean visited[MAXSIZE]; /* 访问标志的数组 */
/* 邻接表的深度优先递归算法 */
void DFS(GraphAdjList GL, int i)
{
EdgeNode *p;
visited[i]=TRUE;
printf("%c",GL->adjList[i].data);
p=GL->adjList[i].firstedge;
while(p)
{
if(!visited[p->adjvex])
DFS(GL,p->adjvex);
p=p->next;
}
}
/* 邻接表的深度遍历操作 */
void DFSTraverse(GraphAdjList GL)
{
int i;
for(i=0;i<GL->numVertexes;i++)
visited[i]=FALSE;
for(i=0;i<GL->numVertexes;i++)
if(!visited[i])
DFS(GL,i);
}
/* 邻接表的广度遍历算法 */
void BFSTraverse(GraphAdjList GL)
{
int i;
EdgeNode *p;
Queue Q;
for(i=0;i<GL->numVertexes;i++)
visited[i]=FALSE;
InitQueue(&Q);
for(i=0;i<GL->numVertexes;i++)
{
if(!visited[i])
{
visited[i]=TRUE;
printf("%c",GL->adjList[i].data);
EnQueue(&Q,i);
while(!QueueEmpty(Q))
{
DeQueue(&Q,&i);
p=GL->adjList[i].firstedge;
while(p)
{
if(!visited[p->adjvex])
{
visited[p->adjvex]=TRUE;
printf("%c",GL->adjList[p->adjvex].data);
EnQueue(&Q,p->adjvex);
}
p=p->next;
}
}
}
}
}
int main(void)
{
MGraph G;
GraphAdjList GL;
CreateMGraph(&G);
CreateALGraph(G,&GL);
printf("\n深度遍历:");
DFSTraverse(GL);
printf("\n广度遍历:");
BFSTraverse(GL);
return 0;
}
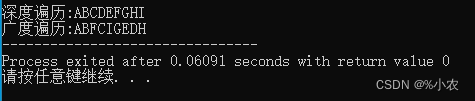
两者运行出来的结果是一样:






















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








