1.重定向 && 缓冲区
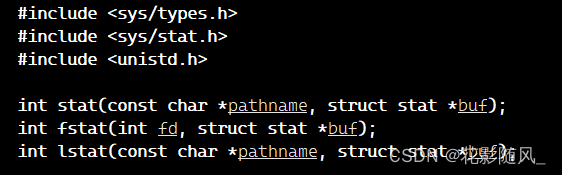
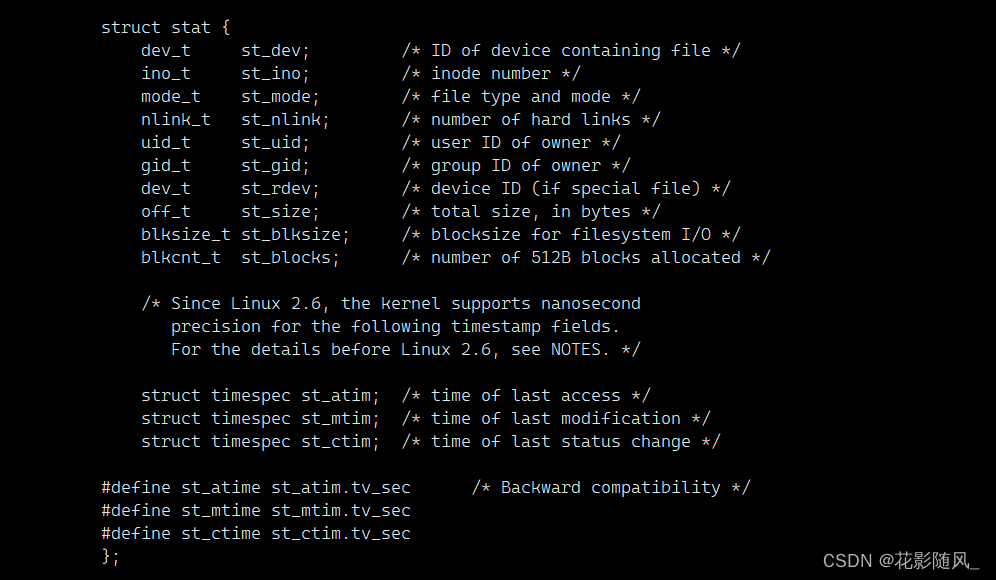
文件 = 内容 + 属性
而stat系列系统调用接口就是对文件:对内容的操作 + 对属性的操作。
文件描述符的分配规则:查自己的文件描述表,分配最小的没有被使用的fd。

FILE* -> stdin -> 0
FILE* -> stdout -> 1
FILE* -> stderr -> 2
我们学过的c语言中的printf是打印函数,那其实printf默认就是打印在显示器上,也就是stdout,我们如果使用sprintf传入stdout是两个函数的功能就完全相同的!!!
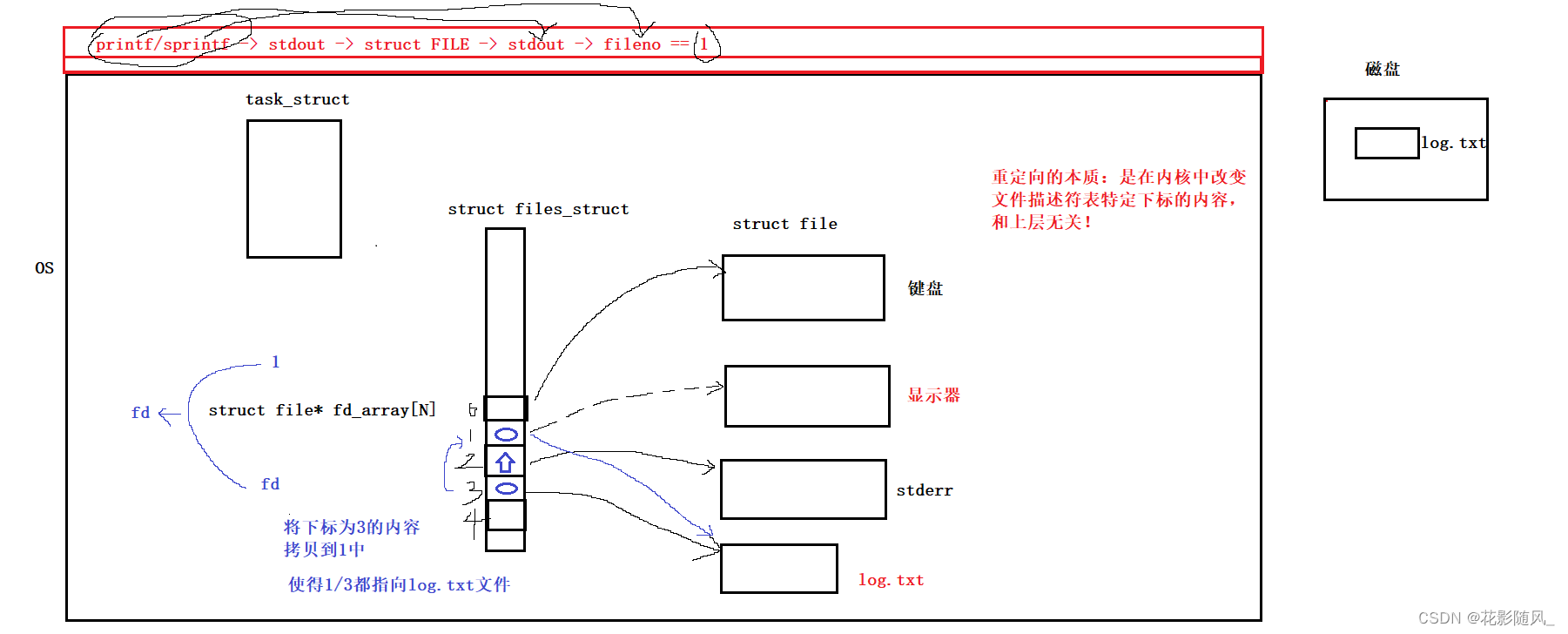

2.重定向的理解
![]()

dup2系统调用,本质是文件描述符下标对应的内容的拷贝!!!
log.txt -> fd
标准输出重定向,显示器打印 -> log.txt
dup2(fd, 1);将文件fd的文件描述符下标对应的内容拷贝到显示器对应的文件描述符下标为1中。
3.缓冲区的理解
用户级缓冲区
内核级缓冲区
为什么这样?
1.解耦
2.提高效率 -> 提高使用者的效率 -> 提高刷新IO的效率。
1,缓冲区是什么?
缓冲区就是一段内存空间
2.为什么?
给上层提供高效的IO体验,间接提高整体的效率
3.怎么办?
缓冲区刷新策略(用户层策略 -> 我们不用关心内核策略):
a.刷新策略
1.立即刷新(无缓冲)。fflush(stdout), int fsync(int fd), synchronize a file's in-core state with storage device.
2.行刷新。显示器, 照顾用户的查看习惯
3.全缓冲。缓冲区写满,才刷新,普通文件
b.特殊情况
进程退出,系统会自动刷新(强制)
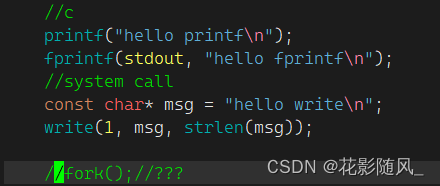
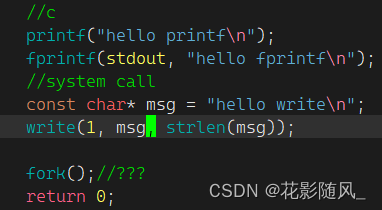
第一种运行结果
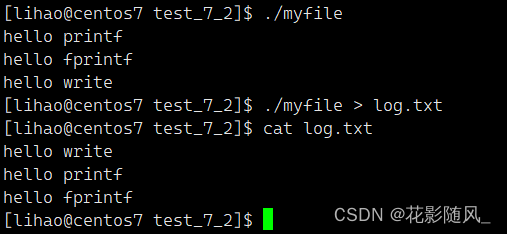
第二种加上fork后的运行结果
我们知道显示器文件stdout是行刷新
当我们向普通文件写时,刷新策略就发生了变化 -> 全缓冲。
stdout对应的缓冲区 -> 用户
fork会创建子进程,两个进程结束都会强制刷新一次,故出现了两次打印printf/fprintf
我们所说的都是用户级缓冲区。
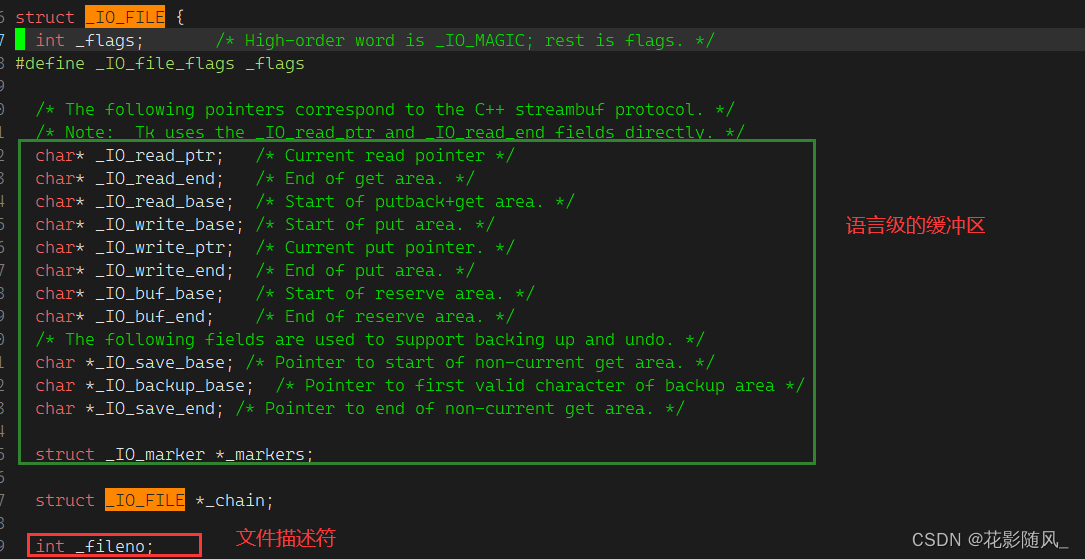
所以每一个文件都有自己的缓冲区,printf/scanf -> FILE*
4.自己的shell加入重定向
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<ctype.h>
#include<unistd.h>
#include<errno.h>
#include<sys/types.h>
#include<sys/wait.h>
#include<fcntl.h>
#define SIZE 512
#define ZERO '\0'
#define SEP " "
#define NUM 32
#define SkipPath(p) do{p += (strlen(p)-1);while(*p != '/')--p;}while(0)
#define SkipSpace(cmd, pos) do{\
while(1){\
if(isspace(cmd[pos]))\
pos++;\
else break;\
}\
}while(0)
//ls -a -l > myfile.txt
#define None_Redir 0
#define In_Redir 1
#define Out_Redir 2
#define App_Redir 3
int redir_type = None_Redir;
char* filename = NULL;
char cwd[SIZE * 2];
char* gArgv[NUM];
int lastcode = 0;
void Die()
{
exit(1);
}
const char* GetHome()
{
const char* home = getenv("HOME");
if(home == NULL) return "None";
return home;
}
const char* GetUserName()
{
const char* username = getenv("USER");
if(username == NULL) return "None";
return username;
}
const char* GetHostName()
{
const char* hostname = getenv("HOSTNAME");
if(hostname == NULL) return "None";
return hostname;
}
const char* GetCwd()
{
const char* cwd = getenv("PWD");
if(cwd == NULL) return "None";
return cwd;
}
//commandline:output
void MakeCommandLineAndPrint()
{
char line[SIZE];
const char* username = GetUserName();
const char* hostname = GetHostName();
const char* cwd = GetCwd();
SkipPath(cwd);
snprintf(line, sizeof(line), "[%s@%s %s]>", username, hostname, strlen(cwd) == 1 ? "/" : cwd + 1);
printf("%s", line);
fflush(stdout);
}
int GetUserCommand(char command[], size_t n)
{
char* s = fgets(command, n, stdin);
if(s == NULL) return -1;
command[strlen(command) - 1] = ZERO;
return strlen(command);
}
void SplitCommand(char command[], size_t n)
{
(void)n;
//"ls -a -l" -> "ls", "-a", "-l"
gArgv[0] = strtok(command, SEP);
int index = 1;
while((gArgv[index] = strtok(NULL, SEP)))index++;// done, 故意写成=,表示先赋值,在判断,分割之后,strtok会返回NULL,刚好让gArgv最后一个元素是NULL,并且while判断结束
}
void ExecuteCommand()
{
pid_t id = fork();
if(id < 0) Die();
else if(id == 0)
{
//重定向设置
if(filename != NULL)
{
if(redir_type == In_Redir)
{
int fd = open(filename, O_RDONLY);
dup2(fd, 0);
}
else if(redir_type == Out_Redir)
{
int fd = open(filename, O_WRONLY|O_CREAT|O_TRUNC, 0666);
dup2(fd, 1);
}
else if(redir_type == App_Redir)
{
int fd = open(filename, O_WRONLY|O_CREAT|O_APPEND, 0666);
dup2(fd, 2);
}
else
{}
}
//child
execvp(gArgv[0], gArgv);
exit(errno);
}
else
{
//father
int status = 0;
pid_t rid = waitpid(id, &status, 0);
if(rid > 0)
{
lastcode = WEXITSTATUS(status);
if(lastcode != 0) printf("%s:%s:%d\n", gArgv[0], strerror(lastcode), lastcode);
}
}
}
void Cd()
{
const char* path = gArgv[1];
if(path == NULL) path = GetHome();
//path一定存在
chdir(path);
//刷新环境变量
char temp[SIZE * 2];
getcwd(temp, sizeof(temp));
snprintf(cwd, sizeof(cwd), "PWD=%s", temp);
putenv(cwd);//ok
}
int CheckBuildin()
{
int yes = 0;
const char* enter_cmd = gArgv[0];
if(strcmp(enter_cmd, "cd") == 0)
{
yes = 1;
Cd();
}
else if(strcmp(enter_cmd, "echo") == 0 && strcmp(gArgv[1], "$?") == 0)
{
yes = 1;
printf("%d\n", lastcode);
lastcode = 0;
}
return yes;
}
void CheckRedir(char cmd[])
{
// > >> <
// ls -a -l > myfile.txt
int pos = 0;
int end = strlen(cmd);
while(pos < end)
{
if(cmd[pos] == '>')
{
if(cmd[pos+1] == '>')
{
cmd[pos++] = 0;
pos++;
redir_type = App_Redir;
SkipSpace(cmd, pos);
filename = cmd + pos;
}
else
{
cmd[pos++] = 0;
redir_type = Out_Redir;
SkipSpace(cmd, pos);
filename = cmd + pos;
}
}
else if(cmd[pos] == '<')
{
cmd[pos++] = 0;
redir_type = In_Redir;
SkipSpace(cmd, pos);
filename = cmd + pos;
}
else
{
pos++;
}
}
}
int main()
{
int quit = 0;
while(!quit)
{
//1.我们需要输出一个命令行
MakeCommandLineAndPrint();
//2.获取用户命令行字符串
char usercommand[SIZE];
int n = GetUserCommand(usercommand, sizeof(usercommand));
if(n <= 0) return 1;
//2.1 checkredir
CheckRedir(usercommand);
//debug
// printf("cmd:%s\n", usercommand);
// printf("redir_type:%d\n", redir_type);
// printf("filename:%s\n", filename);
//3.命令行字符串分割
SplitCommand(usercommand, sizeof(usercommand));
//4.检测命令是否是内键命令
n = CheckBuildin();
if(n) continue;
//5,执行命令
ExecuteCommand();
}
return 0;
}
5.封装一下简单的stdio.h库
mystdio.h文件
#pragma once
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#define LINE_SIZE 1024
#define FLUSH_NOW 1
#define FLUSH_LINE 2
#define FLUSH_FULL 4
struct _myFILE
{
unsigned int flags;
int fileno;
//缓冲区
char cache[LINE_SIZE];
int cap;
int pos;//下次写入的位置
};
typedef struct _myFILE myFILE;
myFILE* my_fopen(const char* path, const char* flag);
void my_fflush(myFILE* fp);
ssize_t my_fwrite(myFILE* fp, const char* data, int len);
void my_fclose(myFILE* fp); mystdio.c文件
#include"mystdio.h"
myFILE* my_fopen(const char* path, const char* flag)
{
int flag1 = 0;
int iscreate = 0;
mode_t mode = 0666;
if(strcmp(flag, "r") == 0)
{
flag1 = O_RDONLY;
}
else if(strcmp(flag, "w") == 0)
{
flag1 = O_WRONLY|O_CREAT|O_TRUNC;
iscreate = 1;
}
else if(strcmp(flag, "a") == 0)
{
flag1 = O_WRONLY|O_CREAT|O_APPEND;
iscreate = 1;
}
else
{}
int fd = 0;
if(iscreate)
fd = open(path, flag1, mode);
else
fd = open(path, flag1);
if(fd < 0) return NULL;
myFILE* fp = (myFILE*)malloc(sizeof(myFILE));
if(!fp) return NULL;
fp->fileno = fd;
fp->flags = FLUSH_LINE;
fp->cap = LINE_SIZE;
fp->pos = 0;
return fp;
}
void my_fflush(myFILE* fp)
{
write(fp->fileno, fp->cache, fp->pos);
fp->pos = 0;
}
ssize_t my_fwrite(myFILE* fp, const char* data, int len)
{
//写入操作本质是拷贝,如果条件允许就刷新,否则就不刷新
memcpy(fp->cache + fp->pos, data, len);//肯定要考虑越界,扩容
fp->pos += len;
if((fp->flags & FLUSH_LINE) && fp->cache[fp->pos - 1] == '\n')
{
my_fflush(fp);
}
return len;
}
void my_fclose(myFILE* fp)
{
my_fflush(fp);
close(fp->fileno);
free(fp);
}
testfile.c文件
#include "mystdio.h"
#include <string.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#define FILE_NAME "log.txt"
int main()
{
myFILE* fp = my_fopen(FILE_NAME, "w");
if(fp == NULL) return 1;
const char* str = "hello bit";
int cnt = 10;
char buffer[128];
while(cnt)
{
sprintf(buffer, "%s - %d", str, cnt);
my_fwrite(fp, buffer, strlen(buffer));//strlen(buffer) + 1 不需要
cnt--;
sleep(1);
my_fflush(fp);
}
my_fclose(fp);
return 0;
} 总结:c语言为什么要在FILE中提供用户级缓冲区 -- 为了减少底层调用系统调用的次数,让使用
c IO函数(printf/fpriintf)效率更高
6.0/1/2 -> 2 stdrr的理解
为什么有0,1,2?--> 我们写的程序,本质:都是对数据在进行处理(计算,存储...)
那数据从哪里来,数据去哪里,用户要不要看到这个过程。(历史原因导致)

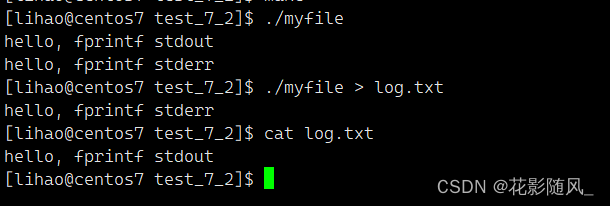
> :标准输出重定向,更改1号fd里面的内容
思考,为什么1正确,2错误
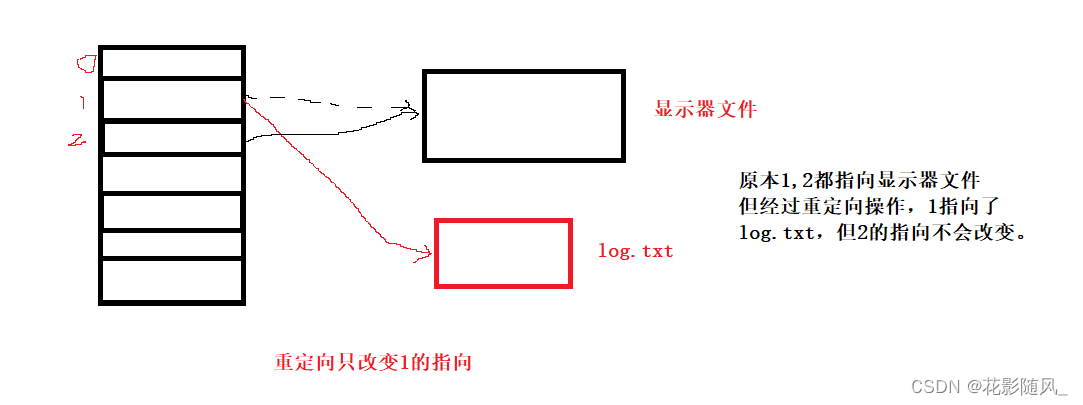

再有
我们学习c语言写过perror函数 perror(“open”);本质是向2打印,printf本质是向1打印























 1219
1219

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










