目录
1.简介
它是从JDK8以后才有的一个新特性,是专业用于对集合或者数组进行便捷操作的。
2.简单案例介绍
案例需求:有一个List集合,元素有"张三丰","张无忌","周芷若","赵敏","张强",找出姓张,且是3个字的名字,存入到一个新集合中去。
List<String> names = new ArrayList<>();
Collections.addAll(names, "张三丰","张无忌","周芷若","赵敏","张强");
System.out.println(names);传统方法来做是这样的:
// 找出姓张,且是3个字的名字,存入到一个新集合中去。
List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
for (String name : names) {
if(name.startsWith("张") && name.length() == 3){
list.add(name);
}
}
System.out.println(list);用了Stream流之后:
List<String> list2 = names.stream().filter(s -> s.startsWith("张")).filter(a -> a.length()==3).collect(Collectors.toList());
System.out.println(list2);3.结构介绍
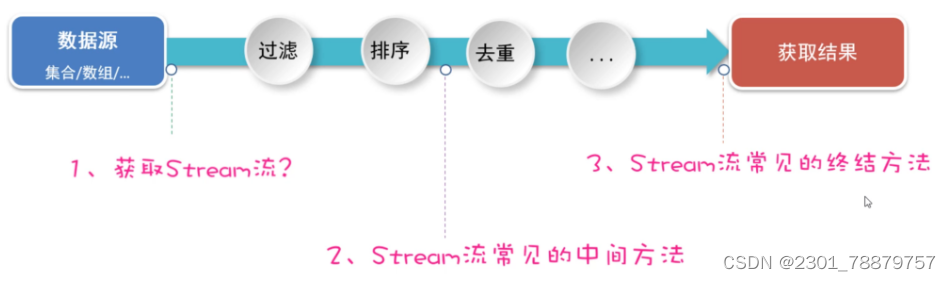
4.创建Stream流
/**
* 目标:掌握Stream流的创建。
*/
public class StreamTest2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 1、如何获取List集合的Stream流?
List<String> names = new ArrayList<>();
Collections.addAll(names, "张三丰","张无忌","周芷若","赵敏","张强");
Stream<String> stream = names.stream();
// 2、如何获取Set集合的Stream流?
Set<String> set = new HashSet<>();
Collections.addAll(set, "刘德华","张曼玉","蜘蛛精","马德","德玛西亚");
Stream<String> stream1 = set.stream();
stream1.filter(s -> s.contains("德")).forEach(s -> System.out.println(s));
// 3、如何获取Map集合的Stream流?
Map<String, Double> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("古力娜扎", 172.3);
map.put("迪丽热巴", 168.3);
map.put("马尔扎哈", 166.3);
map.put("卡尔扎巴", 168.3);
Set<String> keys = map.keySet();
Stream<String> ks = keys.stream();
Collection<Double> values = map.values();
Stream<Double> vs = values.stream();
Set<Map.Entry<String, Double>> entries = map.entrySet();
Stream<Map.Entry<String, Double>> kvs = entries.stream();
kvs.filter(e -> e.getKey().contains("巴"))
.forEach(e -> System.out.println(e.getKey()+ "-->" + e.getValue()));
// 4、如何获取数组的Stream流?
String[] names2 = {"张翠山", "东方不败", "唐大山", "独孤求败"};
Stream<String> s1 = Arrays.stream(names2);
Stream<String> s2 = Stream.of(names2);
}
}5.Stream流中间方法
中间方法指的是:调用完方法之后其结果是一个新的Stream流,于是可以继续调用方法,这样一来就可以支持链式编程(或者叫流式编程)。
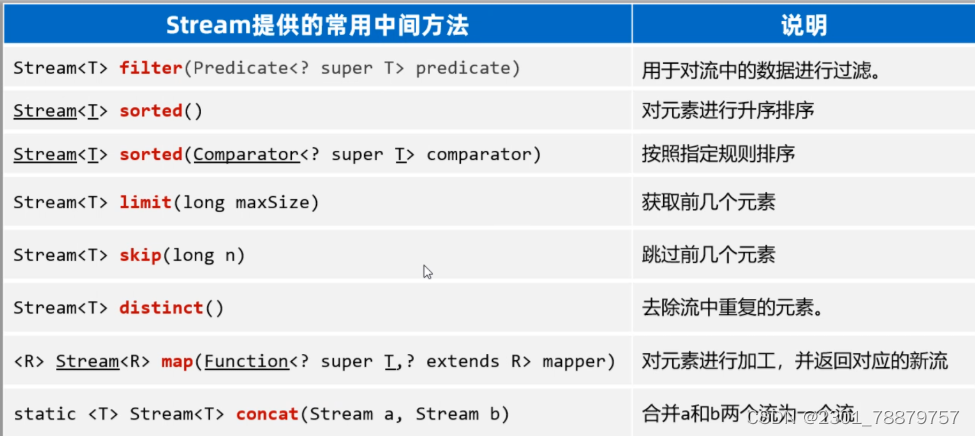
/**
* 目标:掌握Stream流提供的常见中间方法。
*/
public class StreamTest3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<Double> scores = new ArrayList<>();
Collections.addAll(scores, 88.5, 100.0, 60.0, 99.0, 9.5, 99.6, 25.0);
// 需求1:找出成绩大于等于60分的数据,并升序后,再输出。
scores.stream().filter(s -> s >= 60).sorted().forEach(s -> System.out.println(s));
List<Student> students = new ArrayList<>();
Student s1 = new Student("蜘蛛精", 26, 172.5);
Student s2 = new Student("蜘蛛精", 26, 172.5);
Student s3 = new Student("紫霞", 23, 167.6);
Student s4 = new Student("白晶晶", 25, 169.0);
Student s5 = new Student("牛魔王", 35, 183.3);
Student s6 = new Student("牛夫人", 34, 168.5);
Collections.addAll(students, s1, s2, s3, s4, s5, s6);
// 需求2:找出年龄大于等于23,且年龄小于等于30岁的学生,并按照年龄降序输出.
students.stream().filter(s -> s.getAge() >= 23 && s.getAge() <= 30)
.sorted((o1, o2) -> o2.getAge() - o1.getAge())
.forEach(s -> System.out.println(s));
// 需求3:取出身高最高的前3名学生,并输出。
students.stream().sorted((o1, o2) -> Double.compare(o2.getHeight(), o1.getHeight()))
.limit(3).forEach(System.out::println);
System.out.println("-----------------------------------------------");
// 需求4:取出身高倒数的2名学生,并输出。 s1 s2 s3 s4 s5 s6
students.stream().sorted((o1, o2) -> Double.compare(o2.getHeight(), o1.getHeight()))
.skip(students.size() - 2).forEach(System.out::println);
// 需求5:找出身高超过168的学生叫什么名字,要求去除重复的名字,再输出。
students.stream().filter(s -> s.getHeight() > 168).map(Student::getName)
.distinct().forEach(System.out::println);
// distinct去重复,自定义类型的对象(希望内容一样就认为重复,重写hashCode,equals)
students.stream().filter(s -> s.getHeight() > 168)
.distinct().forEach(System.out::println);
Stream<String> st1 = Stream.of("张三", "李四");
Stream<String> st2 = Stream.of("张三2", "李四2", "王五");
Stream<String> allSt = Stream.concat(st1, st2);
allSt.forEach(System.out::println);
}
}6.Stream流终结方法
最后,我们再学习Stream流的终结方法。这些方法的特点是,调用完方法之后,其结果就不再是Stream流了,所以不支持链式编程。
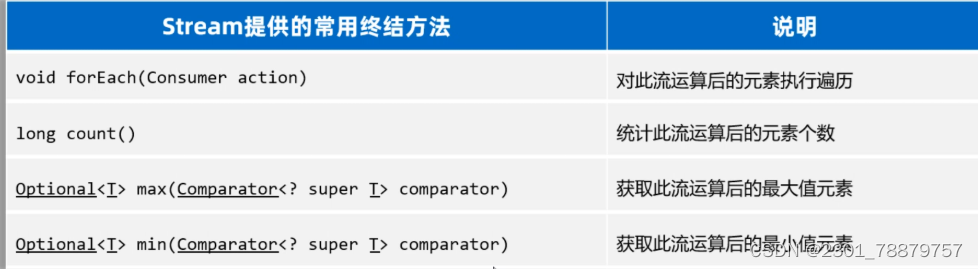
/**
* 目标:Stream流的终结方法
*/
public class StreamTest4 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<Student> students = new ArrayList<>();
Student s1 = new Student("蜘蛛精", 26, 172.5);
Student s2 = new Student("蜘蛛精", 26, 172.5);
Student s3 = new Student("紫霞", 23, 167.6);
Student s4 = new Student("白晶晶", 25, 169.0);
Student s5 = new Student("牛魔王", 35, 183.3);
Student s6 = new Student("牛夫人", 34, 168.5);
Collections.addAll(students, s1, s2, s3, s4, s5, s6);
// 需求1:请计算出身高超过168的学生有几人。
long size = students.stream().filter(s -> s.getHeight() > 168).count();
System.out.println(size);
// 需求2:请找出身高最高的学生对象,并输出。
Student s = students.stream().max((o1, o2) -> Double.compare(o1.getHeight(), o2.getHeight())).get();
System.out.println(s);
// 需求3:请找出身高最矮的学生对象,并输出。
Student ss = students.stream().min((o1, o2) -> Double.compare(o1.getHeight(), o2.getHeight())).get();
System.out.println(ss);
// 需求4:请找出身高超过170的学生对象,并放到一个新集合中去返回。
// 流只能收集一次。
List<Student> students1 = students.stream().filter(a -> a.getHeight() > 170).collect(Collectors.toList());
System.out.println(students1);
Set<Student> students2 = students.stream().filter(a -> a.getHeight() > 170).collect(Collectors.toSet());
System.out.println(students2);
// 需求5:请找出身高超过170的学生对象,并把学生对象的名字和身高,存入到一个Map集合返回。
Map<String, Double> map =
students.stream().filter(a -> a.getHeight() > 170)
.distinct().collect(Collectors.toMap(a -> a.getName(), a -> a.getHeight()));
System.out.println(map);
// Object[] arr = students.stream().filter(a -> a.getHeight() > 170).toArray();
Student[] arr = students.stream().filter(a -> a.getHeight() > 170).toArray(len -> new Student[len]);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr));
}
}7.关于Strem流实现list转Map集合
需求:List TO Map
List Stream 转换 Map时向collect()方法中传递Collector对象,对象由Collectors.toMap()方法返回。
List<GroupBrandCateBO> list = new ArrayList<>(
Arrays.asList(
new GroupBrandCateBO("v1", "g1", "b1"),
new GroupBrandCateBO("v1", "g1", "b1"),
new GroupBrandCateBO("v3", "g3", "b3")
)
);
Map<String, String> map = list.stream().collect(Collectors.toMap(item -> item.getVersion(), item -> item.getGroupCode(), (oldVal, currVal) -> oldVal, LinkedHashMap::new));
System.out.println(map.getClass());
Map<String, String> map0 = list.stream().collect(Collectors.toMap(item -> item.getVersion(), item -> item.getGroupCode(), (oldVal, currVal) -> oldVal));
System.out.println(map0.getClass());
System.out.println(map0.toString());
Map<String, String> map1 = list.stream().collect(Collectors.toMap(GroupBrandCateBO::getVersion, GroupBrandCateBO::getGroupCode));
System.out.println(map1.toString());
Console
class java.util.LinkedHashMap
class java.util.HashMap
{v1=g1, v3=g3}
Exception in thread “main” java.lang.IllegalStateException: Duplicate key g1
at java.util.stream.Collectors.lambda$throwingMerger$0(Collectors.java:133)
…
对问题分析一下:
toMap()函数重载:
未指定合并函数mergeFunction情况下,传入throwingMerger()返回BinaryOperator对象,当出现key重复时,调用合并函数!
未指定Supplier实例情况下,默认生成HashMap实例。
public static <T, K, U>
Collector<T, ?, Map<K,U>> toMap(Function<? super T, ? extends K> keyMapper,
Function<? super T, ? extends U> valueMapper) {
return toMap(keyMapper, valueMapper, throwingMerger(), HashMap::new);
}
public static <T, K, U>
Collector<T, ?, Map<K,U>> toMap(Function<? super T, ? extends K> keyMapper,
Function<? super T, ? extends U> valueMapper,
BinaryOperator<U> mergeFunction) {
return toMap(keyMapper, valueMapper, mergeFunction, HashMap::new);
}
public static <T, K, U, M extends Map<K, U>>
Collector<T, ?, M> toMap(Function<? super T, ? extends K> keyMapper,
Function<? super T, ? extends U> valueMapper,
BinaryOperator<U> mergeFunction,
Supplier<M> mapSupplier) {
BiConsumer<M, T> accumulator
= (map, element) -> map.merge(keyMapper.apply(element),
valueMapper.apply(element), mergeFunction);
return new CollectorImpl<>(mapSupplier, accumulator, mapMerger(mergeFunction), CH_ID);
}
private static <T> BinaryOperator<T> throwingMerger() {
return (u,v) -> { throw new IllegalStateException(String.format("Duplicate key %s", u)); };
}
补充一下:
关于合并函数
List<GroupBrandCateBO> list = new ArrayList<>(
Arrays.asList(
new GroupBrandCateBO("v1", "g1", "b1"),
new GroupBrandCateBO("v1", "g2", "b2"),
new GroupBrandCateBO("v1", "g2", "b2"),
new GroupBrandCateBO("v3", "g3", "b3")
)
);
Map<String, String> map00 = list.stream().collect(Collectors.toMap(item -> item.getVersion(), item -> item.getGroupCode(), (oldVal, currVal) -> currVal));
Map<String, String> map01 = list.stream().collect(Collectors.toMap(item -> item.getVersion(), item -> item.getGroupCode(), (oldVal, currVal) -> oldVal + currVal));
System.out.println(map00.toString());
System.out.println(map01.toString());
Console
{v1=g2, v3=g3}
{v1=g1g2g2, v3=g3}
传入Lambda表达式将转化为BinaryOperator<U> mergeFunction对象,合并处理value,非Key!!!
比如:
(oldVal, currVal) -> currVal) // key相同时当前值替换原始值
(oldVal, currVal) -> oldVal + currVal //key相同时保留原始值和当前值
————————————————
版权声明:本文第7小节为CSDN博主「OxygenBling」的原创文章,遵循CC 4.0 BY-SA版权协议,转载请附上原文出处链接及本声明。
原文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/xiaolulululululu/article/details/86636203
8.重要!转换对象,并收集到新的集合中
1.需求:已有A对象的集合aList,把集合元素中 对象A 转为对象 B,返回新集合bList
//aList : 泛型<A>
//bList : 泛型<B> 实现方法如下:
List<B> bList= aList.stream().map((a) ->{
//~~~~
//业务逻辑书写
//~~~~
return b;
}).collect(Collectors.toList());2.需求:已有A对象的集合aList,把集合元素中 对象A的id属性作为key,对象A作为value,存入并返回Map中
//假设id属性的类型为Long
Map<Long, A> map = aList.stream().collect(Collectors.toMap((b) -> {
return b.getId();
}, (b) -> {
return b;
}));




















 1121
1121











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








