基本的的层次遍历
思路:从上往下,从左往右遍历二叉树的每一个元素,每遍历到一个父节点,将其左右孩子压入队列,直到队列为空。具体代码如下
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.List;
public class TreeNode{
int val;
TreeNode left;
TreeNode right;
List<Integer> simpleLevelOrder(TreeNode root){
if (root == null)
return new ArrayList<Integer>();
List<Integer> res = new ArrayList<Integer>();//记录输出的数值
LinkedList<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<TreeNode>();//记录每层的节点
queue.add(root);
while (!queue.isEmpty()){
TreeNode t = queue.remove();
res.add(t.val);
if (t.left != null){
queue.add(t.left);
}
if (t.right != null){
queue.add(t.right);
}
}
return res;
}
}二叉树的层次遍历(自底向上)
思路:由于最后的结果是与上题相反的,所以用链表的形式比较好,因为这样使用头插法的时间复杂度较低
import sun.reflect.generics.tree.Tree;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Queue;
public class TreeNode{
int val;
TreeNode left;
TreeNode right;
public List<List<Integer>> simpleLevelOrder(TreeNode root){
if (root == null)
return new ArrayList<List<Integer>>();
List<List<Integer>> res = new LinkedList<List<Integer>>();
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<TreeNode>();
queue.offer(root);
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
int size = queue.size();
List<Integer> tmp = new ArrayList<Integer>();
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
TreeNode t = queue.poll();
tmp.add(t.val);
TreeNode left = t.left;
TreeNode right = t.right;
if (left != null) {
queue.offer(left);
}
if (right != null) {
queue.offer(right);
}
}
res.add(0,tmp);//插到头部
}
return res;
}
}二叉树的锯齿型遍历
思路:设置一个isLevelOrder来判断从左边还是右边进行遍历,因此还需要一个双端队列
public List<List<Integer>> zigzagLevelOrder(TreeNode root){
List<List<Integer>> ans = new LinkedList<List<Integer>>();
if (root == null)
return ans;
Deque<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<TreeNode>();
queue.offer(root);
boolean isOrderLeft = false;
while (!queue.isEmpty()){
Deque<Integer> temp = new LinkedList<Integer>();
int size = queue.size();
for (int i=0;i<size;i++){
TreeNode cur = queue.poll();
if (!isOrderLeft){
temp.addFirst(cur.val);
} else {
temp.addLast(cur.val);
}
if (cur.left != null) queue.offer(cur.left);
if (cur.right != null) queue.offer(cur.right);
}
ans.add(new LinkedList<Integer>(temp));
isOrderLeft = !isOrderLeft;
}
return ans;
}n叉树的层次遍历
思路:与上面的题的一个很大不同是需要将定义改一下,将左右孩子直接换成List<TreeNode> children。剩下的思路差不多
public List<List<Integer>> nLevelOrder(TreeNode root){
List<List<Integer>> ans = new LinkedList<List<Integer>>();
if (root == null)
return ans;
Deque<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<TreeNode>();
queue.offer(root);
while (!queue.isEmpty()){
Deque<TreeNode> next = new LinkedList<TreeNode>();
List<Integer> nd = new LinkedList<Integer>();
while (!queue.isEmpty()){
TreeNode t = queue.poll();
nd.add(t.val);
for (TreeNode chr : t.children){
if (chr != null)
nd.add(chr.val);
}
}
queue = next;
ans.add(nd);
}
return ans;
}在每个树行中找最大值
思路:用一个变量来记录最大值,其余思路大同小异
public List<Integer> largestValues(TreeNode root){
List<Integer> ans = new ArrayList<>();
Deque<TreeNode> de = new ArrayDeque<>();
if (root != null){
de.addLast(root);
}else {
return ans;
}
while (!de.isEmpty()){
int size = de.size();
int max = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
for (int i=0; i<size; i++){
TreeNode t = de.poll();
max = Math.max(t.val,max);
if (t.left != null) de.add(t.left);
if (t.right != null) de.add(t.right);
}
ans.add(max);
}
return ans;
}每行中找平均值
思路:跟之前的题一个区别是要先保存下来每行的值,求一下平均,即可
public List<Double> averageValues(TreeNode root){
List<Double> res = new ArrayList<>();
if (root == null) return null;
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.offer(root);
int sum =0;
while (!queue.isEmpty()){
double ave =0;
int size = queue.size();
for (int i=0;i < size;i++){
TreeNode t = queue.poll();
sum = sum + t.val;
if (t.left != null) queue.offer(t.left);
if (t.right != null) queue.offer(t.right);
}
ave = (double) sum / size;
res.add(ave);
}
return res;
}二叉树的右视图
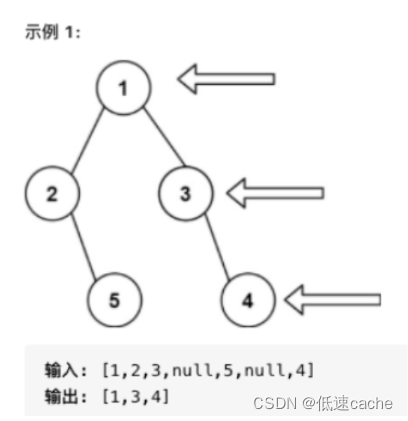
思路:与上一题几乎没什么不一样,只是做出记录每行最后一个节点这一个改动即可。
public List<Integer> averageValues(TreeNode root){
List<Integer> res = new ArrayList<>();
if (root == null) return null;
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.offer(root);
while (!queue.isEmpty()){
int size = queue.size();
for (int i=0;i < size;i++){
TreeNode t = queue.poll();
if (i == size - 1){
res.add(t.val);
}
if (t.left != null) queue.offer(t.left);
if (t.right != null) queue.offer(t.right);
}
}
return res;
}最底层最左边

思路:基于上一题的代码,我们知道queue队列的最后一个输出节点一定是每一行的右边的那个节点,所以我们在将节点输入queue的时候,可以先输入右边的节点
public int averageValues(TreeNode root){
if(root.left == null && root.right == null)
return root.val;
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();
TreeNode temp = new TreeNode();
queue.offer(root);
while (!queue.isEmpty()){
temp = queue.poll();
if (temp.left != null){
queue.offer(temp.left);
}
if (temp.right != null){
queue.offer(temp.right);
}
}
return temp.val;
}




















 103
103











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








