代码随想录-暑假算法第五天(二叉树篇)
1.二叉树的前序遍历(opens new window)
题解
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public List<Integer> preorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
//前序遍历 中左右
ArrayList<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
preorder(list,root);
return list;
}
public void preorder(ArrayList<Integer> list,TreeNode node){
if(node == null){
return;
}
list.add(node.val);
preorder(list,node.left);
preorder(list,node.right);
}
}
2.二叉树的后序遍历(opens new window)
题解
import java.util.*;
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public List<Integer> postorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
ArrayList<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
post(list,root);
return list;
}
public void post(ArrayList<Integer> list ,TreeNode root){
if(root == null){
return;
}
post(list,root.left);
post(list,root.right);
list.add(root.val);
}
}
3.二叉树的中序遍历
题解
import java.util.*;
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public List<Integer> postorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
ArrayList<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
post(list,root);
return list;
}
public void post(ArrayList<Integer> list ,TreeNode root){
if(root == null){
return;
}
post(list,root.left);
(list,root.right);
post(list,root.right);
}
}
4.迭代法遍历
题解
// 前序遍历顺序:中-左-右,入栈顺序:中-右-左
class Solution {
public List<Integer> preorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> result = new ArrayList<>();
if (root == null){
return result;
}
Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>();
stack.push(root);
while (!stack.isEmpty()){
TreeNode node = stack.pop();
result.add(node.val);
if (node.right != null){
stack.push(node.right);
}
if (node.left != null){
stack.push(node.left);
}
}
return result;
}
}
// 中序遍历顺序: 左-中-右 入栈顺序: 左-右
class Solution {
public List<Integer> inorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> result = new ArrayList<>();
if (root == null){
return result;
}
Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>();
TreeNode cur = root;
while (cur != null || !stack.isEmpty()){
if (cur != null){
stack.push(cur);
cur = cur.left;
}else{
cur = stack.pop();
result.add(cur.val);
cur = cur.right;
}
}
return result;
}
}
// 后序遍历顺序 左-右-中 入栈顺序:中-左-右 出栈顺序:中-右-左, 最后翻转结果
class Solution {
public List<Integer> postorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> result = new ArrayList<>();
if (root == null){
return result;
}
Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>();
stack.push(root);
while (!stack.isEmpty()){
TreeNode node = stack.pop();
result.add(node.val);
if (node.left != null){
stack.push(node.left);
}
if (node.right != null){
stack.push(node.right);
}
}
Collections.reverse(result);
return result;
}
}
5.层序遍历
题解
import java.util.*;
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
List<List<Integer>> result = new ArrayList<List<Integer>>();
public List<List<Integer>> levelOrder(TreeNode root) {
//层序遍历
check(root);
return result;
}
public void check(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return;
}
//队列
LinkedList<TreeNode> linkedList = new LinkedList<TreeNode>();
//把根节点添加到队列里面
linkedList.add(root);
while (!linkedList.isEmpty()) {
//记录每一层的元素的个数
int count = linkedList.size();
//存储从队列里面出来的元素
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
while (count > 0) {
TreeNode node = linkedList.poll();
list.add(node.val);
if(node.left != null){
linkedList.offer(node.left);
}
if(node.right != null){
linkedList.offer(node.right);
}
count--;
}
//把list添加到result里面
result.add(list);
}
}
}
6. 翻转二叉树
给你一棵二叉树的根节点 root ,翻转这棵二叉树,并返回其根节点。
示例 1:
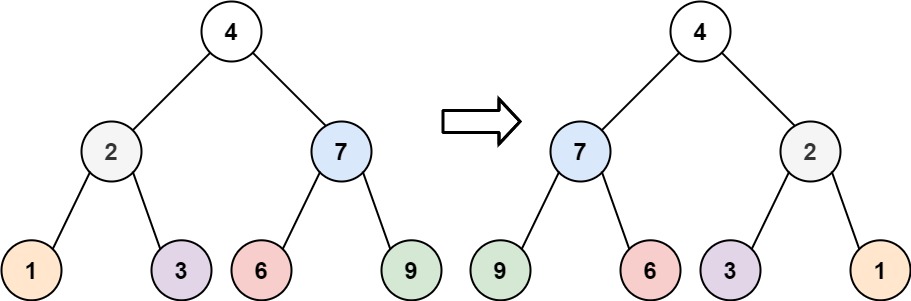
**输入:**root = [4,2,7,1,3,6,9]
输出:[4,7,2,9,6,3,1]
示例 2:

**输入:**root = [2,1,3]
输出:[2,3,1]
示例 3:
**输入:**root = []
输出:[]
题解
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public TreeNode invertTree(TreeNode root) {
//使用前序或者后序遍历的方式
if(root == null){
return null;
}
swap(root.left,root.right);
invertTree(root.left);
invertTree(root.right);
return root;
}
public void swap(TreeNode left,TreeNode right){
TreeNode t = left;
left = right;
right = t;
}
}
7.二叉树的最大深度
给定一个二叉树,找出其最大深度。
二叉树的深度为根节点到最远叶子节点的最长路径上的节点数。
说明: 叶子节点是指没有子节点的节点。
示例: 给定二叉树 [3,9,20,null,null,15,7],

返回它的最大深度 3 。
题解
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public int maxDepth(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null){
return 0;
}
int leftH = maxDepth(root.left);
int rightH = maxDepth(root.right);
int max = Math.max(leftH,rightH) + 1;
return max;
}
}
8. 对称二叉树
给定一个二叉树,检查它是否是镜像对称的。

题解
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public boolean isSymmetric(TreeNode root) {
return compare(root.left,root.right);
}
public boolean compare(TreeNode left,TreeNode right){
//递归的出口
if(left ==null && right!=null){
return false;
}
if(left!= null && right == null){
return false;
}
if(left == null && right ==null){
return true;
}
if(left.val != right.val){
return false;
}
boolean b1 = compare(left.left,right.right);
boolean b2 = compare(left.right,right.left);
boolean result = b1&&b2;
return result;
}
}
9.二叉树的最小深度
给定一个二叉树,找出其最小深度。
最小深度是从根节点到最近叶子节点的最短路径上的节点数量。
说明: 叶子节点是指没有子节点的节点。
示例:
给定二叉树 [3,9,20,null,null,15,7],

返回它的最小深度 2
题解
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public int minDepth(TreeNode root) {
//2. 递归的终止条件
if (root == null) {
return 0;
}
//分别找到左右子树的深度
int minLeft = minDepth(root.left);
int minRight = minDepth(root.right);
int min = Math.min(minLeft, minRight) + 1;
//特殊情况
//当有一个子树为null时,最小深度不能是它
if (minLeft == 0) {
min = minRight + 1;
}
if( minRight == 0){
min = minLeft + 1;
}
return min;
}
}
222.完全二叉树的节点个数
给出一个完全二叉树,求出该树的节点个数。
示例 1:
- 输入:root = [1,2,3,4,5,6]
- 输出:6
示例 2:
- 输入:root = []
- 输出:0
示例 3:
- 输入:root = [1]
- 输出:1
提示:
- 树中节点的数目范围是[0, 5 * 10^4]
- 0 <= Node.val <= 5 * 10^4
- 题目数据保证输入的树是 完全二叉树
题解
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public int countNodes(TreeNode root) {
//递归的终止条件
if(root == null){
return 0;
}
//单层的逻辑
int leftCount = countNodes(root.left);
int rightCount = countNodes(root.right);
return leftCount+rightCount+1;
}
}
110.平衡二叉树
给定一个二叉树,判断它是否是高度平衡的二叉树。
本题中,一棵高度平衡二叉树定义为:一个二叉树每个节点 的左右两个子树的高度差的绝对值不超过1。
示例 1:
给定二叉树 [3,9,20,null,null,15,7]

返回 true 。
示例 2:
给定二叉树 [1,2,2,3,3,null,null,4,4]

返回 false
题解
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public boolean isBalanced(TreeNode root) {
int result = getHeight(root);
if(result == -1){
return false;
}else{
return true;
}
}
//递归函数
public int getHeight(TreeNode node){
if(node == null){
return 0;
}
int leftH = getHeight(node.left);
if(leftH == -1){
return -1;
}
int rightH = getHeight(node.right);
if(rightH == -1){
return -1;
}
if(Math.abs(leftH-rightH) > 1) {
return -1;
}else{
return Math.max(leftH,rightH) +1;
}
}
}
404.左叶子之和
计算给定二叉树的所有左叶子之和。
示例:

题解1
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public int sumOfLeftLeaves(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null){
return 0;
}
int leftSum = 0;
if (root.left != null && root.left.left == null && root.left.right == null) {
leftSum = root.left.val;
}
int i = sumOfLeftLeaves(root.left);
int j = sumOfLeftLeaves(root.right);
return leftSum + i + j;
}
}
题解2
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
//存储叶子节点的总和
ArrayList<Integer> listResult = new ArrayList<>();
public int sumOfLeftLeaves(TreeNode root) {
cengxu(root);
int sum = 0;
for (Integer i : listResult) {
sum = sum + i;
}
return sum;
}
public void cengxu(TreeNode root) {
//队列
LinkedList<TreeNode> linkedList = new LinkedList<>();
if (root == null) {
return;
}
linkedList.add(root);
while (!linkedList.isEmpty()) {
//记录每一层有几个元素
int size = linkedList.size();
while (size > 0) {
TreeNode poll = linkedList.poll();
//判断是否是叶子节点
if(poll.left!=null && poll.left.left==null && poll.left.right == null){
listResult.add(poll.left.val);
}
//加入进栈
if(poll.left != null){
linkedList.add(poll.left);
}
if(poll.right != null){
linkedList.add(poll.right);
}
//元素减减
size--;
}
}
}
}
513.找树左下角的值
给定一个二叉树,在树的最后一行找到最左边的值。
示例 1:

示例 2:

题解
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public int findBottomLeftValue(TreeNode root) {
//使用层序遍历 (迭代法)
//队列 存储每一层的元素
LinkedList<TreeNode> linkedList = new LinkedList<>();
//存储结果
int result = 0;
linkedList.add(root);
while (!linkedList.isEmpty()) {
//记录每一层的元素的个数
int count = linkedList.size();
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
//最左边第一个元素的值
TreeNode node = linkedList.poll();
if(i == 0){
result = node.val;
}
if(node.left != null){
linkedList.add(node.left);
}
if(node.right != null){
linkedList.add(node.right);
}
}
}
return result;
}
}
112. 路径总和
给定一个二叉树和一个目标和,判断该树中是否存在根节点到叶子节点的路径,这条路径上所有节点值相加等于目标和。
说明: 叶子节点是指没有子节点的节点。
示例: 给定如下二叉树,以及目标和 sum = 22,
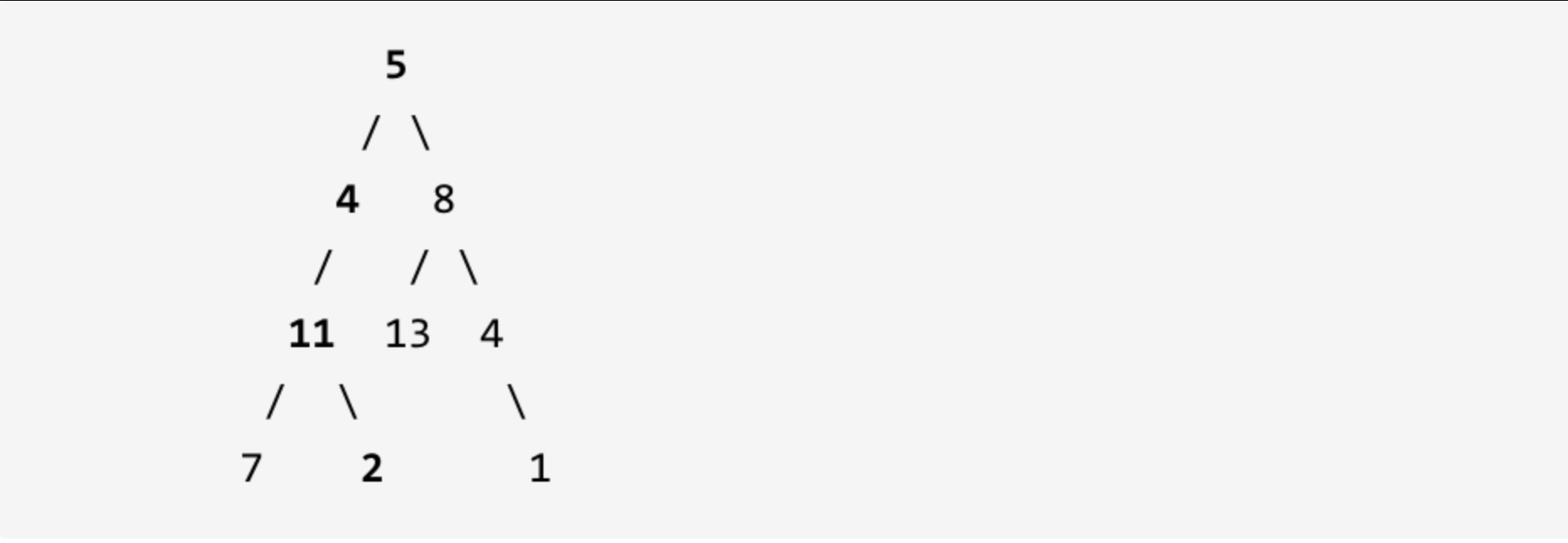
返回 true, 因为存在目标和为 22 的根节点到叶子节点的路径 5->4->11->2
题解
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public boolean hasPathSum(TreeNode root, int targetSum) {
//使用递归法
if(root == null){
return false;
}
targetSum = targetSum - root.val;
//不用回溯也可以
//判断是否是叶子节点
if(root.left == null && root.right == null){
//判断是否为0
if(targetSum == 0){
return true;
}
}
//左递归
boolean left = hasPathSum(root.left,targetSum);
if(left){
return true;
}
//右递归
boolean right = hasPathSum(root.right,targetSum);
if(right){
return true;
}
return false;
}
}
106.从中序与后序遍历序列构造二叉树
根据一棵树的中序遍历与后序遍历构造二叉树。
注意: 你可以假设树中没有重复的元素。
例如,给出
- 中序遍历 inorder = [9,3,15,20,7]
- 后序遍历 postorder = [9,15,7,20,3] 返回如下的二叉树:

题解
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public TreeNode buildTree(int[] inorder, int[] postorder) {
//递归的终止条件
if(inorder.length == 0 || postorder.length == 0){
return null;
}
//根节点
int rootValue = postorder[postorder.length - 1];
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(rootValue);
for (int i = 0; i < inorder.length; i++) {
if(inorder[i] == rootValue){
//包左不包右
//1. 把中序数值进行切分 切分为左右
int[] inorderLeft = Arrays.copyOfRange(inorder, 0, i);
int[] inorderRight = Arrays.copyOfRange(inorder, i+1, inorder.length);
//2. 把后序数值进行切分 切分为左右
int[] postorderLeft = Arrays.copyOfRange(postorder, 0, i);
int[] postorderRight = Arrays.copyOfRange(postorder, i,postorder.length-1);
//进行递归
root.left = buildTree(inorderLeft,postorderLeft);
root.right = buildTree(inorderRight,postorderRight);
break;
}
}
return root;
}
}
654.最大二叉树
给定一个不含重复元素的整数数组。一个以此数组构建的最大二叉树定义如下:
- 二叉树的根是数组中的最大元素。
- 左子树是通过数组中最大值左边部分构造出的最大二叉树。
- 右子树是通过数组中最大值右边部分构造出的最大二叉树。
通过给定的数组构建最大二叉树,并且输出这个树的根节点。
示例 :

提示:
给定的数组的大小在 [1, 1000] 之间。
题解
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }1
*/
class Solution {
public TreeNode constructMaximumBinaryTree(int[] nums) {
//使用前序遍历 中左右构造二叉树
//递归的终止条件
if(nums.length == 1){
return new TreeNode(nums[0]);
}
//存储数值的最大值
int maxValue = 0;
//存储最大值的下标
int maxIndex = 0;
for(int i = 0;i< nums.length;i++){
if(nums[i] > maxValue){
maxValue = nums[i];
maxIndex = i;
}
}
//根据最大值 构造根节点
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(maxValue);
//切分数值 进行递归
if(maxIndex > 0){
int[] leftArr;
leftArr = Arrays.copyOfRange(nums, 0, maxIndex);//包左不包右
//向左递归
root.left = constructMaximumBinaryTree(leftArr);
}
if(maxIndex < nums.length-1){
int[] rightArr;
rightArr = Arrays.copyOfRange(nums, maxIndex + 1, nums.length);
//向右递归
root.right = constructMaximumBinaryTree(rightArr);
}
//返回
return root;
}
}
617.合并二叉树
给定两个二叉树,想象当你将它们中的一个覆盖到另一个上时,两个二叉树的一些节点便会重叠。
你需要将他们合并为一个新的二叉树。合并的规则是如果两个节点重叠,那么将他们的值相加作为节点合并后的新值,否则不为 NULL 的节点将直接作为新二叉树的节点。
示例 1:

注意: 合并必须从两个树的根节点开始。
题解
class Solution {
//1. 递归的返回值和参数
public TreeNode mergeTrees(TreeNode root1, TreeNode root2) {
//使用前序遍历 构造二叉树
//2. 递归的终止条件
if(root1 == null && root2 == null){
return null;
}
//这2步需要好好琢磨
if(root1 == null){
return root2;
}
if(root2 == null){
return root1;
}
//单层递归逻ji 1和2都不为空的情况
int value = root1.val + root2.val;
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(value);
//向左进行递归
root.left = mergeTrees(root1.left,root2.left);
root.right = mergeTrees(root1.right ,root2.right);
//返回
return root;
}
}
700.二叉搜索树中的搜索
给定二叉搜索树(BST)的根节点和一个值。 你需要在BST中找到节点值等于给定值的节点。 返回以该节点为根的子树。 如果节点不存在,则返回 NULL。
例如,

在上述示例中,如果要找的值是 5,但因为没有节点值为 5,我们应该返回 NULL
题解
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public TreeNode searchBST(TreeNode root, int val) {
if(root == null){
return null;
}
if(root.val == val){
return root;
}
if(root.val > val){
//zai 左边
return searchBST(root.left,val);
}else{
return searchBST(root.right,val);
}
}
}
98.验证二叉搜索树
给定一个二叉树,判断其是否是一个有效的二叉搜索树。
假设一个二叉搜索树具有如下特征:
- 节点的左子树只包含小于当前节点的数。
- 节点的右子树只包含大于当前节点的数。
- 所有左子树和右子树自身必须也是二叉搜索树。

题解
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
//记录前一个节点
TreeNode pre = null;
public boolean isValidBST(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null){
return true;
}
//向左递归
boolean left = isValidBST(root.left);
if(pre != null && pre.val >= root.val){
return false;
}
pre = root;
//向右递归
boolean right = isValidBST(root.right);
return left && right;
}
}
530.二叉搜索树的最小绝对差
给你一棵所有节点为非负值的二叉搜索树,请你计算树中任意两节点的差的绝对值的最小值。
示例:

提示:树中至少有 2 个节点
题解
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
// 使用双指针法(但在这里我们实际上只需要一个指针来跟踪前一个访问的节点)
TreeNode pre = null;
// 初始化一个很大的数作为最小差值的初始值
int result = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
public int getMinimumDifference(TreeNode root) {
// 直接开始中序遍历,不需要在这里进行任何特殊的初始化
digui(root);
// 返回找到的最小差值
return result;
}
public void digui(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return;
}
// 向左进行递归
digui(root.left);
// 如果pre不为null,说明之前已经访问过一个节点,计算差值并更新result
if (pre != null) {
result = Math.min(result, Math.abs(pre.val - root.val));
}
// 移动指针
pre = root;
// 向右进行递归
digui(root.right);
}
}
450.删除二叉搜索树中的节点
给定一个二叉搜索树的根节点 root 和一个值 key,删除二叉搜索树中的 key 对应的节点,并保证二叉搜索树的性质不变。返回二叉搜索树(有可能被更新)的根节点的引用。
一般来说,删除节点可分为两个步骤:
首先找到需要删除的节点; 如果找到了,删除它。 说明: 要求算法时间复杂度为 O ( h ) O(h) O(h),h 为树的高度。
示例:

题解
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public TreeNode deleteNode(TreeNode root, int key) {
if(root == null){
return null;
}
if(root.val == key){
//叶子节点
if(root.left == null && root.right == null){
return null;
}
//左为空 右不为空
else if(root.left == null && root.right!= null){
return root.right;
}
else if(root.left != null && root.right == null){
return root.left;
}else{
TreeNode cur = root.right;
while(cur.left != null){
cur = cur.left;
}
cur.left = root.left;
return root.right;
}
}
if(root.val > key){
root.left = deleteNode(root.left,key);
}
if(root.val < key){
root.right = deleteNode(root.right,key);
}
return root;
}
}
669. 修剪二叉搜索树
给定一个二叉搜索树,同时给定最小边界L 和最大边界 R。通过修剪二叉搜索树,使得所有节点的值在[L, R]中 (R>=L) 。你可能需要改变树的根节点,所以结果应当返回修剪好的二叉搜索树的新的根节点。


题解
class Solution {
public TreeNode trimBST(TreeNode root, int low, int high) {
if (root == null) {
return null;
}
if (root.val < low) {
return trimBST(root.right, low, high);
}
if (root.val > high) {
return trimBST(root.left, low, high);
}
// root在[low,high]范围内
root.left = trimBST(root.left, low, high);
root.right = trimBST(root.right, low, high);
return root;
}
}





















 570
570

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








