一、集合
0、集合
-
快捷键

-
ArraryList

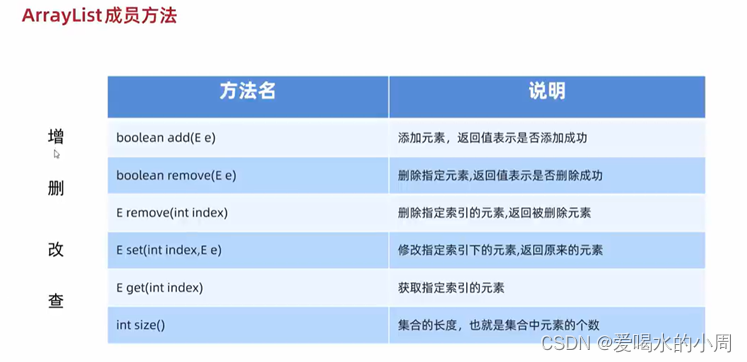
-
static


-
几个类

-
StringBuilder介绍


-
面向对象三大特征
-
封装
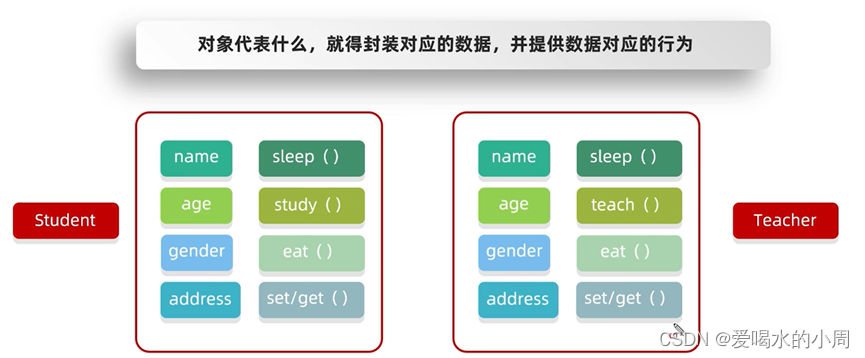
-
继承
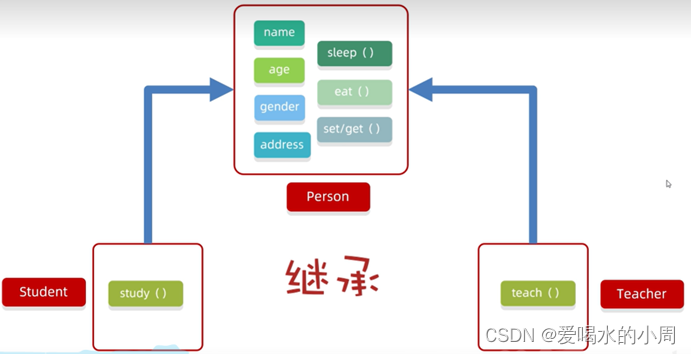




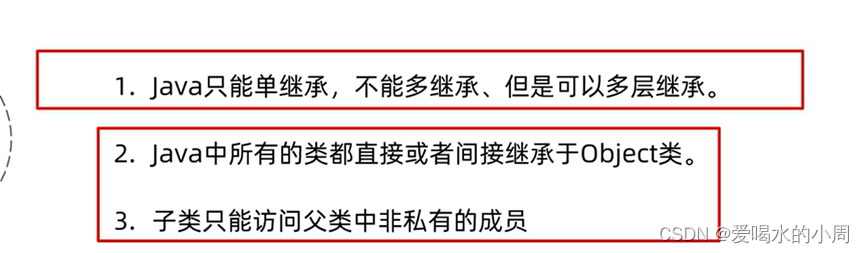

继承中成员变量的访问特点:就近原则:谁离我近,我就用谁
This找本类成员位置
Super找父类


继承中成员方法的访问特点: 就近原则:谁离我近,我就用谁


继承中构造方法的访问特点:

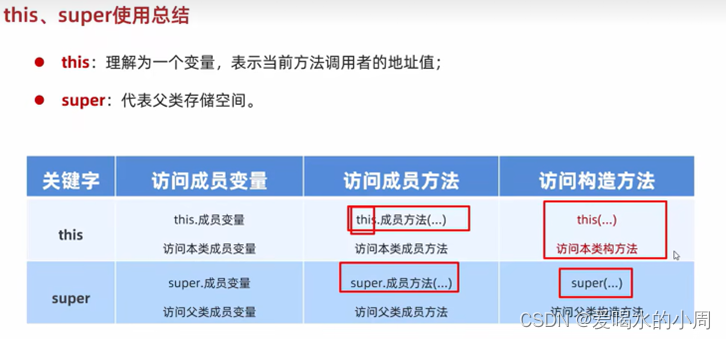
This、super使用 总结
-
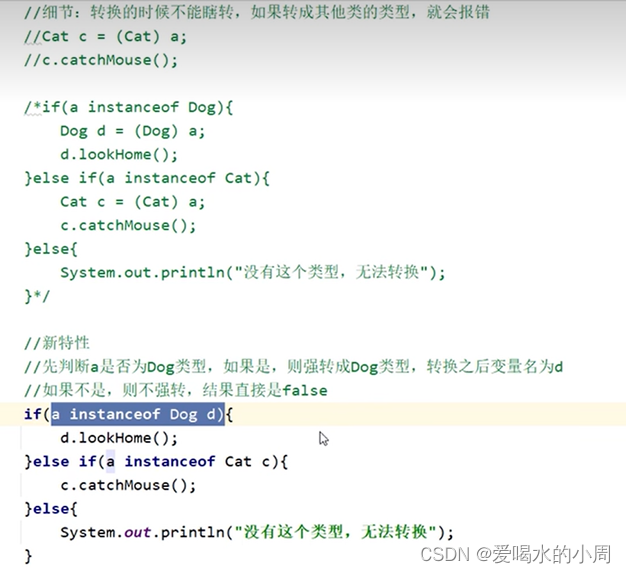
多态





-
包


-
final

-
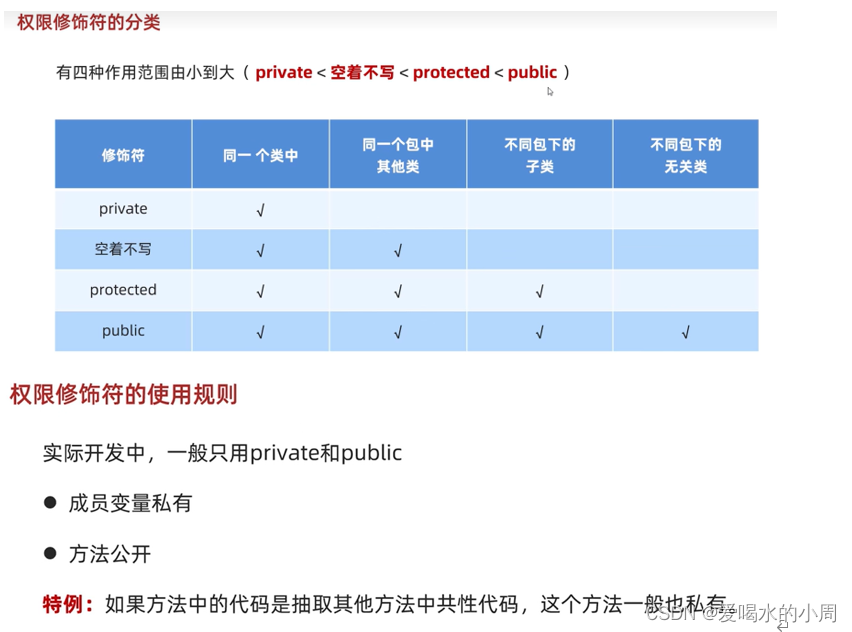
权限修饰符
-
抽象类


- 接口





- 内部类






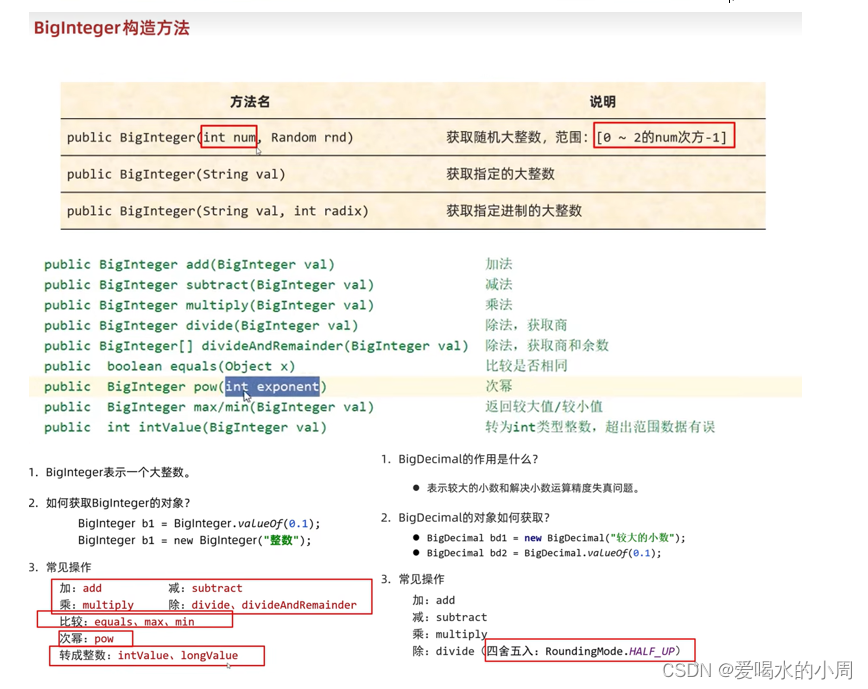
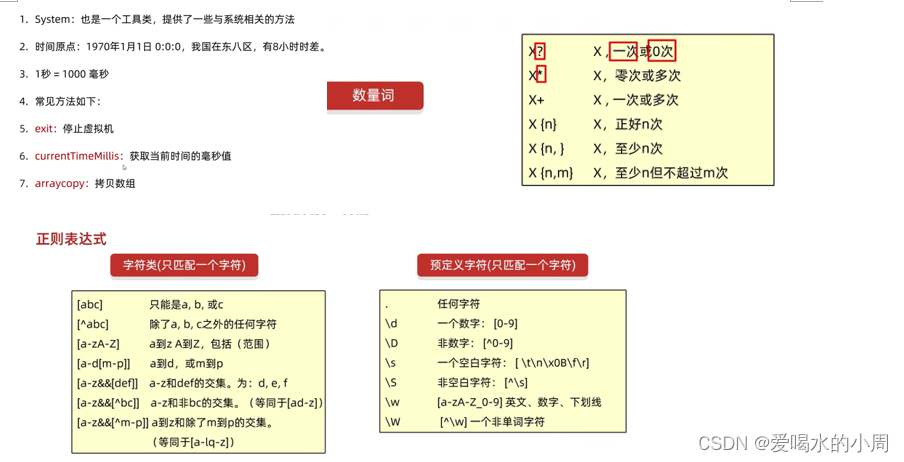
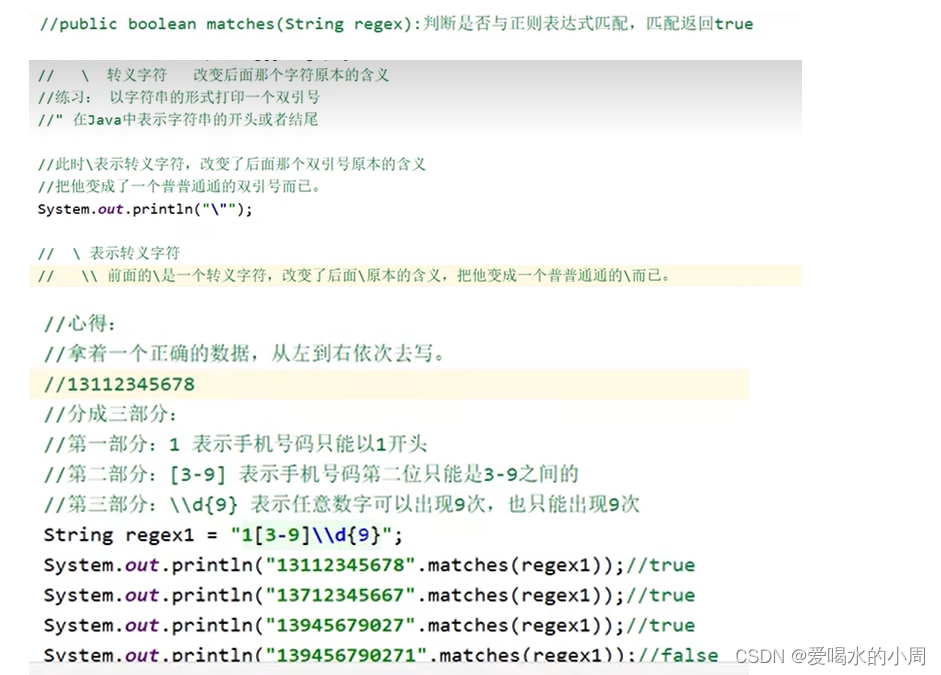

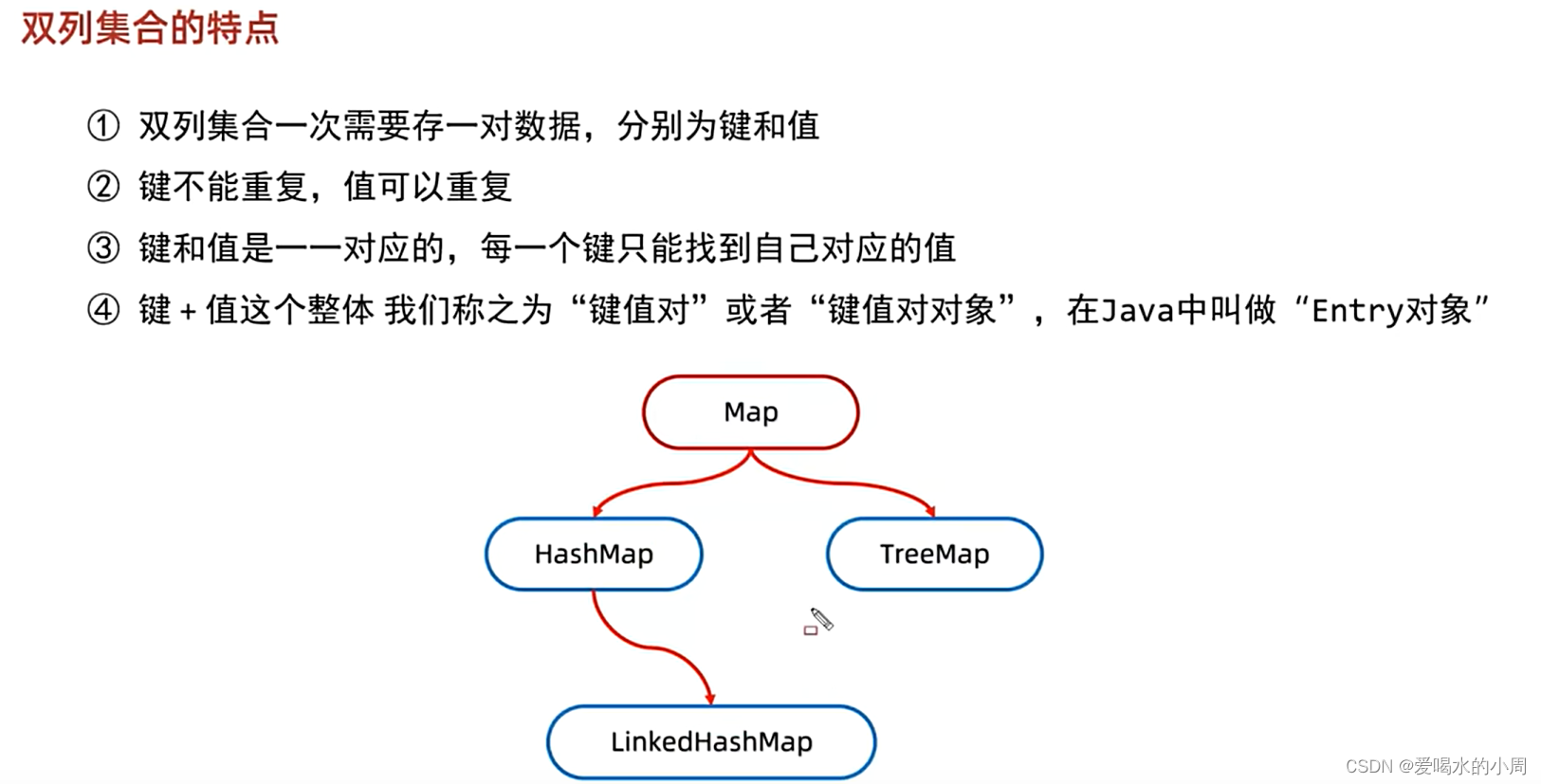
1、双列集合
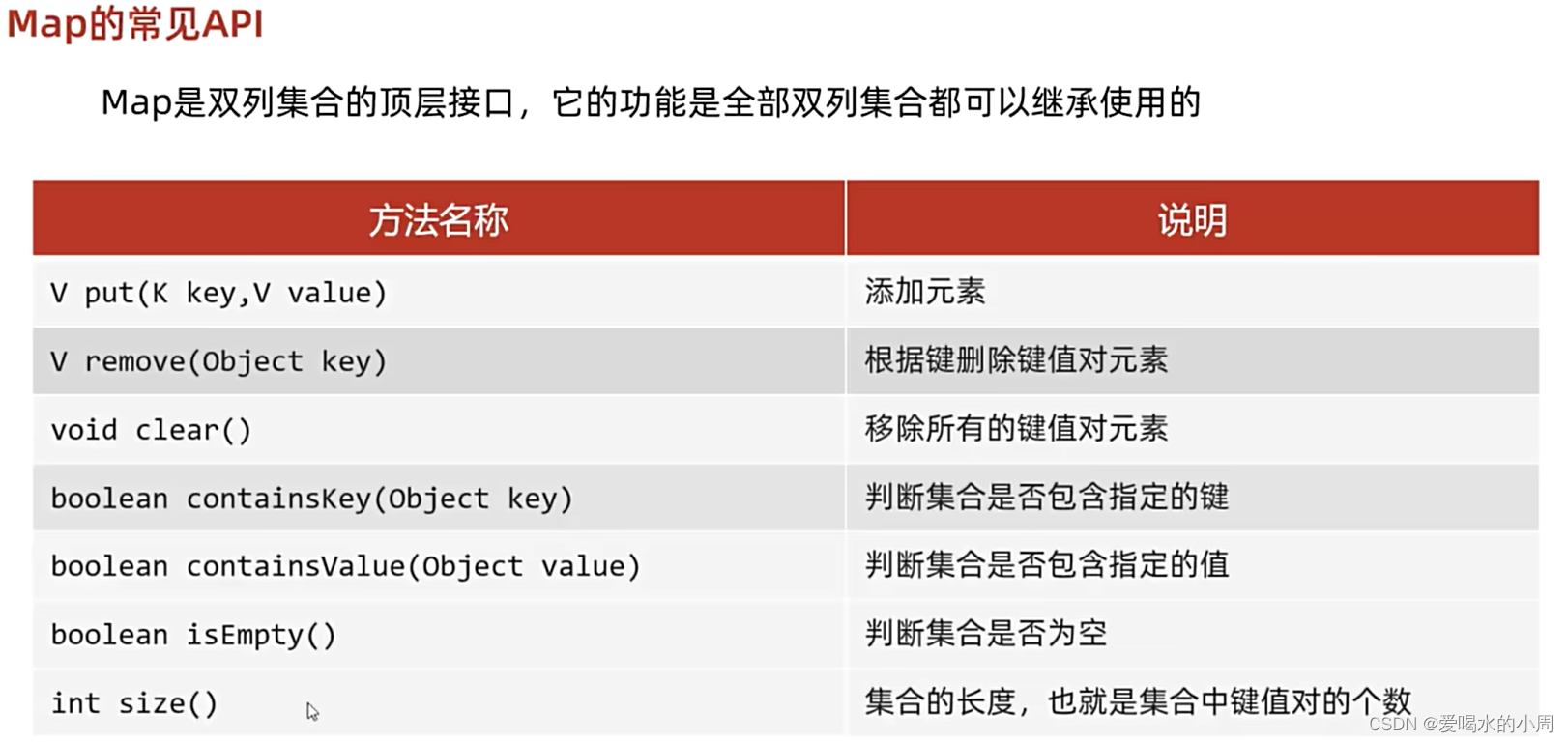


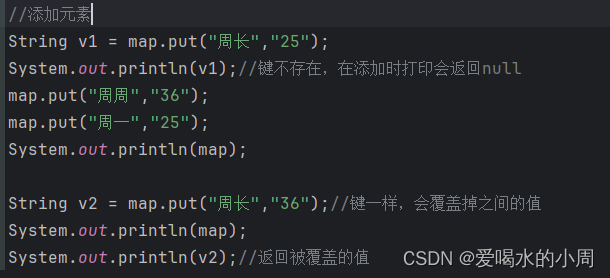



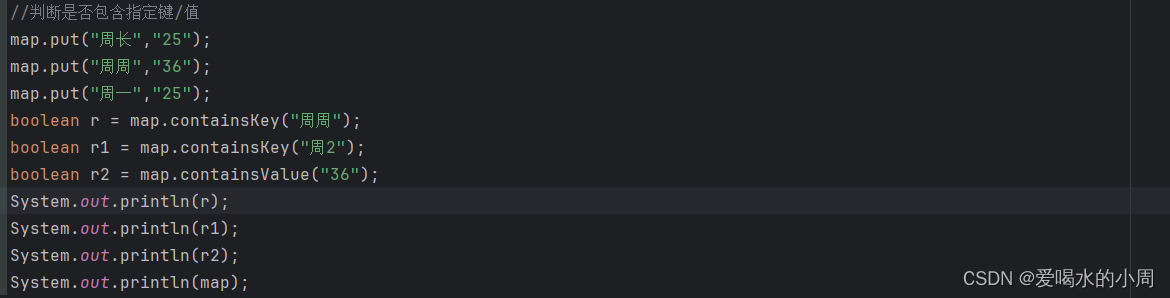

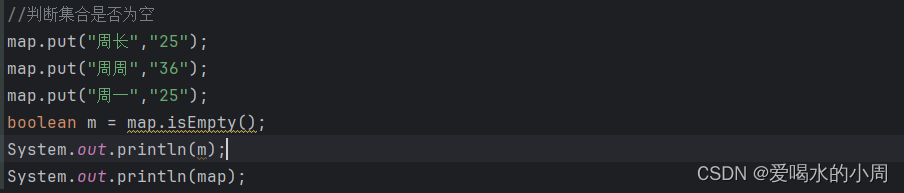
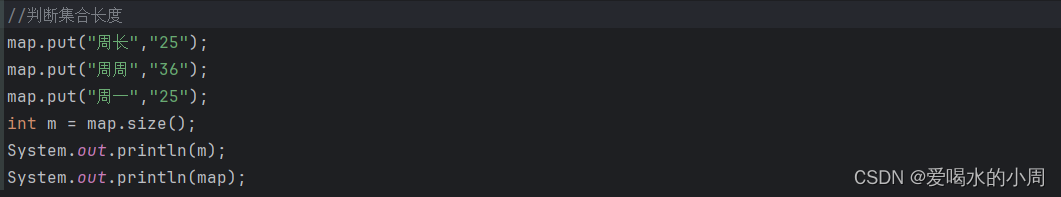

2、Map的遍历方式
2.1 键找值
public class Map01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建Map集合的对象,map是一个接口,不能直接创建其对象,要创建其实现类的对象
Map<String,String> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("周周","25");
map.put("周一","26");
map.put("周二","27");
//通过键找值遍历
Set<String> keys = map.keySet();//获取所有的键,把这些键放到一个单列集合中
//遍历集合的到每个键
for (String key : keys) {
//利用键找值 get
String value = map.get(key);
System.out.println(key+" :"+value);
// 创建Map集合的对象
Map<String, String> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("周周", "25");
map.put("周一", "26");
map.put("周二", "27");
// 获取Map集合的entrySet视图,它包含了Map中的键值对
Set<Map.Entry<String, String>> entries = map.entrySet();
// 获取entrySet的迭代器
Iterator<Map.Entry<String, String>> iterator = entries.iterator();
// 使用迭代器遍历
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
// 获取下一个键值对
Map.Entry<String, String> entry = iterator.next();
// 输出键和值
System.out.println(entry.getKey() + " :" + entry.getValue());
}
// 创建Map集合的对象
Map<String, String> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("周周", "25");
map.put("周一", "26");
map.put("周二", "27");
// 使用forEach方法和lambda表达式遍历Map
map.forEach((key, value) -> {
System.out.println(key + " :" + value);
});
}
}
2.2 键值对
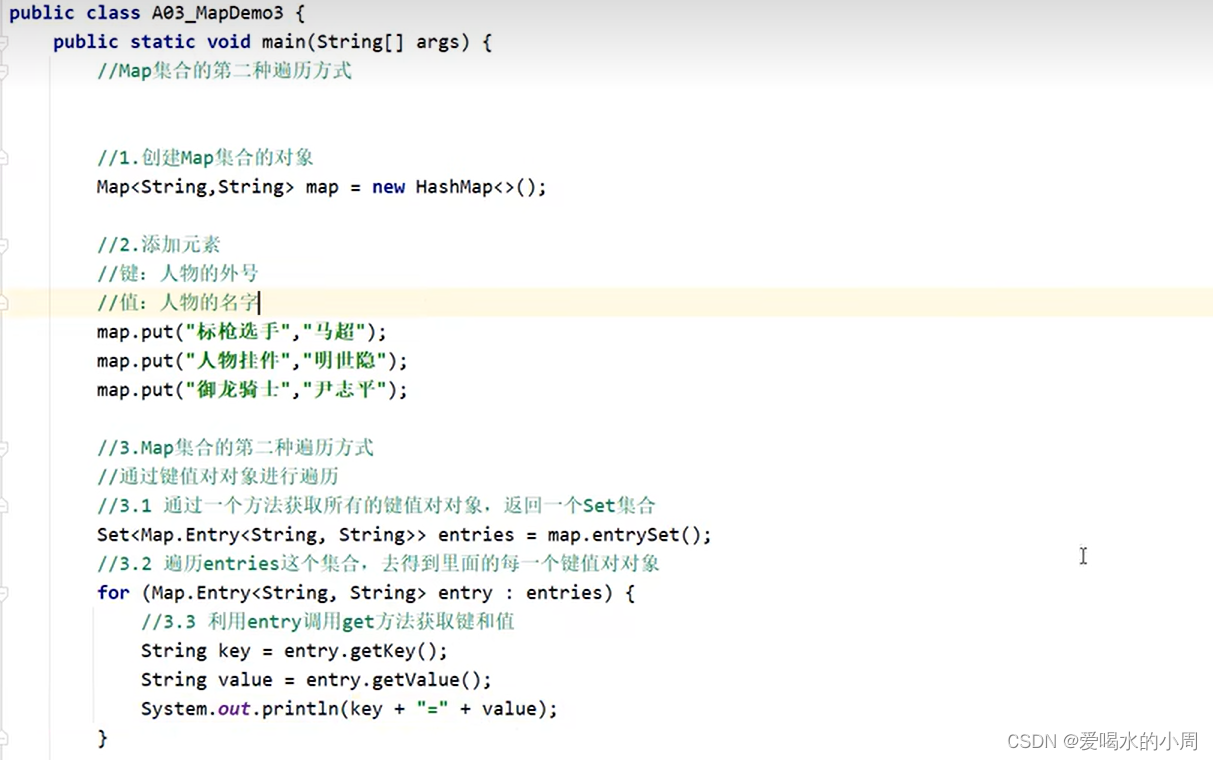

2.3 lambda遍历


2.4 集合的3种遍历方法
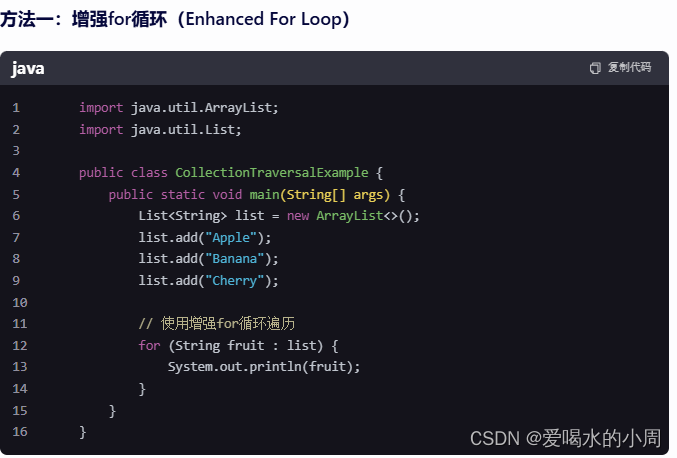
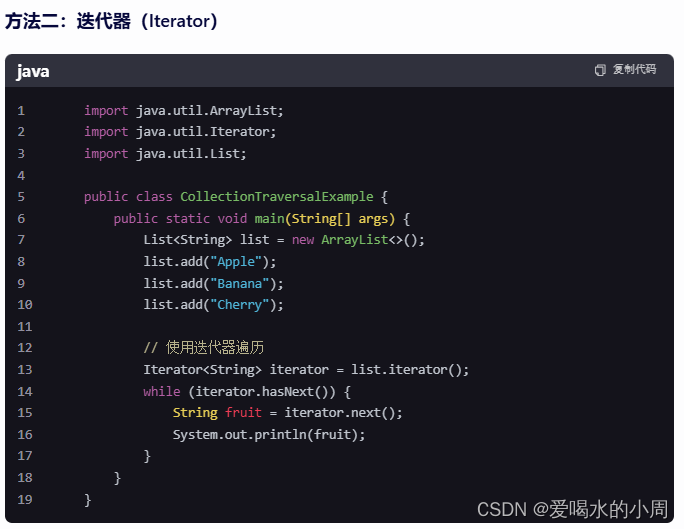
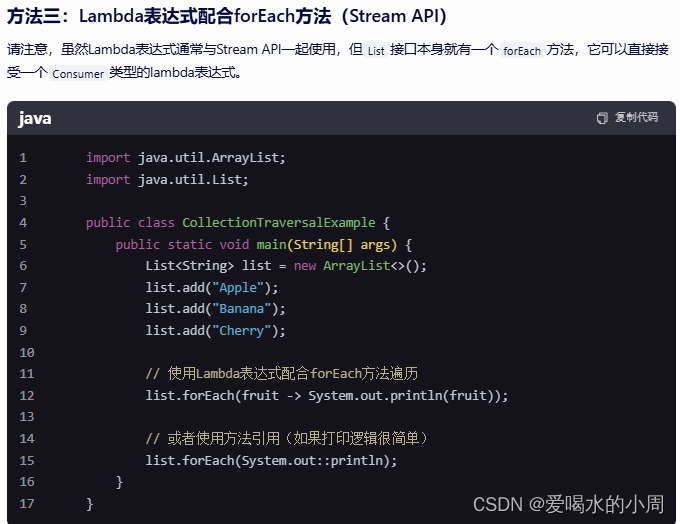
3、HashMap


3.1练习
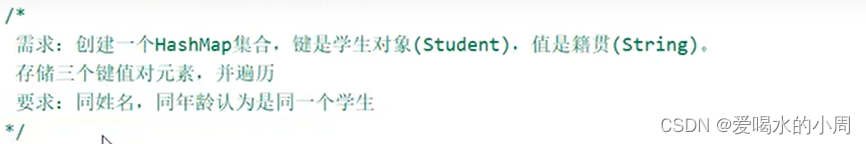
![]()
package com.fuyang.Map;
import java.util.Objects;
public class Student {
private String name;
private int age;
public Student() {
}
public Student(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
/**
* 获取
* @return name
*/
public String getName() {
return name;
}
/**
* 设置
* @param name
*/
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
/**
* 获取
* @return age
*/
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
/**
* 设置
* @param age
*/
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (this == o) return true;
if (o == null || getClass() != o.getClass()) return false;
Student student = (Student) o;
return age == student.age && Objects.equals(name, student.name);
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
return Objects.hash(name, age);
}
public String toString() {
return "Student{name = " + name + ", age = " + age + "}";
}
}
package com.fuyang.Map;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Set;
import java.util.function.BiConsumer;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建HashMap的对象
HashMap<Student,String> hashMap = new HashMap<>();
//创建对象
Student s1 = new Student("张三",23);
Student s2 = new Student("王五",25);
Student s3 = new Student("李四",28);
Student s4 = new Student("李四",28);
//添加
hashMap.put(s1,"江苏");
hashMap.put(s2,"安徽");
hashMap.put(s3,"山东");
hashMap.put(s4,"俄罗斯");
//遍历
Set<Student> keys = hashMap.keySet();//使用keySet()方法获取该映射中所有键的集合(Set)
for (Student key : keys) {
String value = hashMap.get(key);
System.out.println(key+"="+value);
}
System.out.println("~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~");
//遍历
Set<Map.Entry<Student,String>> entries = hashMap.entrySet();
for (Map.Entry<Student,String> entry:entries){
Student key = entry.getKey();
String value = entry.getValue();
System.out.println(key+"="+value);
}
System.out.println("~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~");
hashMap.forEach((student,s) -> System.out.println(student+"="+s));
}
}
3.2练习

package com.fuyang.Map;
import java.util.*;
public class Test2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//1.投票
//定义一个数组
String[] arr = {"A","B","C","D"};
//利用随机数模拟80个同学的投票,并把投票结果保存起来
ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
Random r = new Random();
for (int i = 0; i < 80; i++) {
int index = r.nextInt(arr.length);
list.add(arr[index]);
}
//2、统计
//统计数据较多不易使用计数器
//使用map
//创建HashMap的对象
HashMap<String,Integer> hashMap = new HashMap<>();
for (String name : list){
//判断当前的景点在map集合中是否已经存在
if(hashMap.containsKey(name)){
//存在
//先获取当前经典的统计次数
int count = hashMap.get(name);
count++;
//把新的次数添加到集合中
hashMap.put(name,count);
}else {
//不存在
hashMap.put(name,1);
}
}
System.out.println(hashMap);
//求最大值
int max = 0;
//遍历
Set<Map.Entry<String,Integer>> entries=hashMap.entrySet();
for (Map.Entry<String,Integer> entry : entries){
int count = entry.getValue();
if(count > max){
max = count;
}
}
System.out.println(max);
//判断哪个景点是最大次数
for (Map.Entry<String,Integer> entry : entries){
int count = entry.getValue();
if(count == max){
System.out.println(entry.getKey());
}
}
}
}
4、LinkedHashMap

package com.fuyang.Map;
import java.util.LinkedHashMap;
public class Test3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建集合
LinkedHashMap<String,Integer> linkedHashMap = new LinkedHashMap<>();
//添加元素
linkedHashMap.put("b",456);
linkedHashMap.put("c",789);
linkedHashMap.put("a",213);
linkedHashMap.put("a",123);
//打印
System.out.println(linkedHashMap);
}
}
![]()
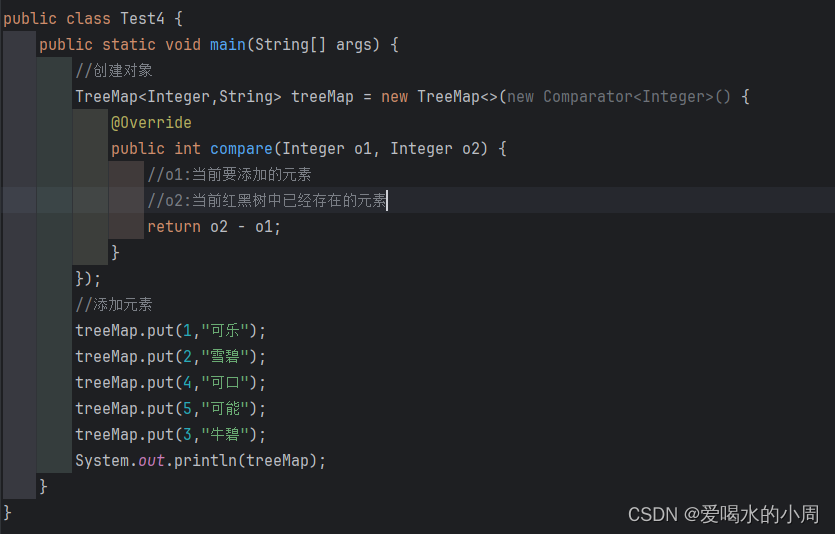
5、TreeMap


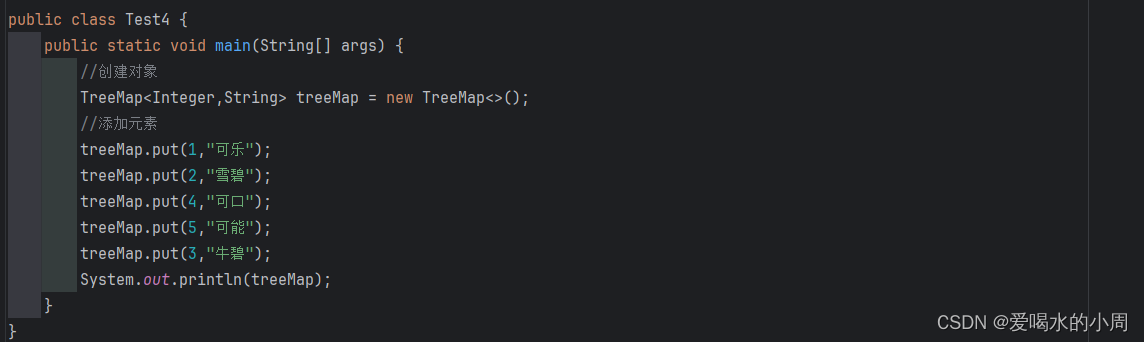
![]()
![]()






















 18万+
18万+











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








