链表的定义及相关的链表操作:
1、什么是链表?
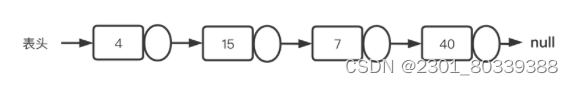
如上图这样的,将数据元素储存在内存中,通过指针使数据呈现“一对一”的逻辑关系,这样的链式储存结构的线性表称为链表。
2、为什么存在?
相比于数组,链表不需要一块连续的储存空间,它通过“指针”将一组连续的内存块(在链表中称为节点)串联起来使用。这样能避免数组创建时一次性申请过大的内存空间而导致有可能创建失败的问题。
3、怎么创建?(Java实现)
首先明确为什么选择创建头节点:不带头节点(虚拟节点)的单链表,在新节点要插入链表表头时,需要将新节点后继指针指向原来单链表的头一个节点,并且需要将头指针指向新节点,中间和表尾插入操作和带头节点的单链表相同,不带头节点会增加一个判断语句。
jvm怎么创建:

/**
* 在算法中最常用的链表定义方式
*/
public class ListNode {
public int val;
public ListNode next;
public ListNode(int x) {//构造方法中的 next = null 只是为了初始化节点对象,并没有直接指向下一个节点的地址。连接节点需要通过设置 next 属性来实现。
val = x;
next = null;
}4、怎么用?
遍历链表:
public static int getLength(Node head) {
int length = 0;
Node node = head;
while (node != null) {
length++;
node = node.next;
}
return length;
}插入:(注意中间插入更新节点的操作顺序)
public static Node insertNode(Node head, Node nodeInsert, int position) {
// 需要判空,否则后面可能会有空指针异常
if (head == null) {
return nodeInsert;
}
//越界判断
int size = getLength(head);
if (position > size + 1 || position < 1) {
System.out.println("位置参数越界");
return head;
}
//在链表开头插入
if (position == 1) {
nodeInsert.next = head;
// return nodeInsert;
//上面return还可以这么写:
head = nodeInsert;
return head;
}
Node pNode = head;
int count = 1;
while (count < position - 1) {
pNode = pNode.next;
count++;
}
nodeInsert.next = pNode.next;
pNode.next = nodeInsert;
return head;
}删除:
public static Node deleteNode(Node head, int position) {
if (head == null) {
return null;
}
int size = getLength(head);
//思考一下,这里为什么是size,而不是size+1
if (position > size || position <1) {
System.out.println("输入的参数有误");
return head;
}
if (position == 1) {
//curNode就是链表的新head
return head.next;
} else {
Node cur = head;
int count = 1;
while (count < position - 1) {
cur = cur.next;
count++;
}
Node curNode = cur.next;
cur.next = curNode.next;
}
return head;
}





















 425
425











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








