栈是只允许在一端进行插入或删除的线性表,遵循先入后出的原则
以下是栈的基本功能:
typedef int STDataType;
typedef struct Stack
{
STDataType* a;
int capacity;
int top;
} ST;
//初始化
void STInit(ST* ps);
//销毁
void STDestroy(ST* ps);
//插入
void STPush(ST* ps, STDataType x);
//删除
void STPop(ST* ps);
//判空
bool STEmpty(ST* ps);
//数据个数
int STSize(ST* ps);
//返回栈顶元素
STDataType STTop(ST* ps);要说明一点,本篇栈的实现是采取顺序存储,并且栈顶元素位置初始化为0
初始化:
void STInit(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
ps->a = NULL;
ps->capacity = 0;
ps->top = 0;
}销毁:
void STDestroy(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
free(ps->a);
ps->a = NULL;
ps->capacity = 0;
ps->top = 0;
}插入元素:
void STPush(ST* ps, STDataType x)
{
assert(ps);
if (ps->capacity == ps->top) {
int newcapacity = ps->capacity == 0 ? 4 : 2 * ps->capacity;
STDataType* tem = (STDataType*)realloc(ps->a, sizeof(STDataType) * newcapacity);
if (tem == NULL)
{
perror("realloc fail");
return;
}
ps->a = tem;
ps->capacity = newcapacity;
}
ps->a[ps->top] = x;
ps->top++;
}删除元素:
void STPop(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
assert(!STEmpty(ps));
ps->top--;
}判定栈是否为空:
bool STEmpty(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
return ps->top == 0;
}返回栈的数据个数:
int STSize(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
return ps->top;
}返回栈顶元素:
STDataType STTop(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
assert(!STEmpty(ps));
return ps->a[ps->top - 1];
}在主函数中打印元素:
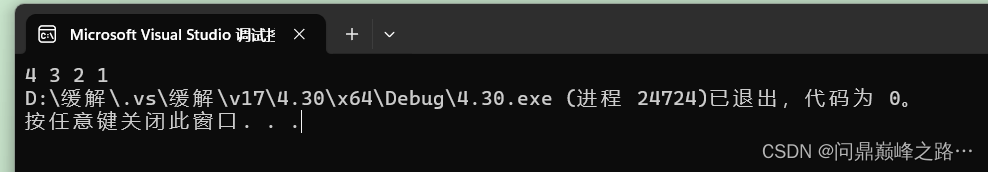
int main()
{
ST ps;
STInit(&ps);
STPush(&ps, 1);
STPush(&ps, 2);
STPush(&ps, 3);
STPush(&ps, 4);
while (!STEmpty(&ps))
{
printf("%d ", STTop(&ps));
STPop(&ps);
}
STDestroy(&ps);
return 0;
}







 本文详细介绍了使用C语言实现的栈数据结构,包括栈的初始化、销毁、插入、删除、判断空栈、获取栈大小和返回栈顶元素的方法。通过顺序存储方式,展示了栈的典型操作过程。
本文详细介绍了使用C语言实现的栈数据结构,包括栈的初始化、销毁、插入、删除、判断空栈、获取栈大小和返回栈顶元素的方法。通过顺序存储方式,展示了栈的典型操作过程。














 1466
1466











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








