在一维中求解非线性方程
1.课件02课后计算题
(1)
Consider the numerical solution of f
(
x
) =
x
3
= 0. How many iterations
does Newton take from the initial guess x
0
= 1 and stopping tolerance
tol = 10
−
6
? Use the graphical analysis method to estimate the order of
convergence.
方程为f(x) = x^3,初始猜测为x0=1,停止迭代的容许误差tol = 1e-6,求迭代次数
下边是colab代码
def myNewton(fnon, dfdx, x0, tol, maxk, *fnonargs):
# fnon - name of the nonlinear function f(x)
# dfdx - name of the derivative function df(x)
# x0 - initial guess for the solution x0
# tol - stopping tolerance for Newton's iteration
# maxk - maximum number of Newton iterations before stopping
# fnonargs - optional arguments that will be passed to the nonlinear function (useful for additional function parameters)
k = 0
x = x0
f = eval(fnon)(x,*fnonargs)
print(' k xk f(xk)')
# Main Newton loop
while (abs(f) > tol and k < maxk):
# Evaluate function derivative
d = eval(dfdx)(x,*fnonargs)
# Take Newton step
x = x - f/d
f = eval(fnon)(x,*fnonargs)
k += 1
print('{0:2.0f} {1:2.8f} {2:2.2e}'.format(k, x, abs(f)))
if (k == maxk):
print('Not converged')
else:
print('Converged')
#牛顿迭代法的方程
def squareRoot(x):
# Define function f(x) = x^3
return (x*x*x)
#原方程
def dSquareRoot(x):
# Define function df(x) = 3*x^2
return (3*x*x)
#原方程的导数
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
%matplotlib inline
x=np.arange(-2, 2, 0.05)
#x的取值范围
y=squareRoot(x)
fig=plt.figure()
ax=fig.add_axes([0,0,1,1])
ax.plot(x,y)
ax.plot(x,0*y)
ax.set_title('Function $f(x) = x^3$')
ax.set_xlabel('x')
ax.set_ylabel('f(x)')
#绘制图形
myNewton('squareRoot', 'dSquareRoot', 1, 1e-6, 100)
#运用牛顿迭代函数进行计算下边是运行的图片和结果
图片

结果 
(2)
Consider the numerical solution of f
(
x
) =
|
x
|
sin(
x
+
π
) = 0. (a) What is
the derivative f 0
(
x
) of this function? (b) Solve the problem numerically
with Newton’s method starting from x
0
= 1 and stopping tolerance
tol = 10
−
6
.
方程为f(x) =
|
x
|
sin(
x
+
π),初始猜测为x0=1,停止迭代的容许误差tol = 1e-6
(a)f'(x) = -|x|sin(x)
(b)下边为colab代码
#上部分与第一题中的牛顿迭代函数部分一致
def squareRoot(x):
# Define function f(x) = |x| * sin(x+π)
return (np.abs(x) * np.sin(x + np.pi))
#原函数
def dSquareRoot(x):
# Define function df(x) = -|x| * sin(x)
return (np.abs(x) * np.cos(x + np.pi) + np.sin(x + np.pi))
#原函数的导数
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
%matplotlib inline
x=np.arange(-2, 2, 0.05)
y=squareRoot(x)
fig=plt.figure()
ax=fig.add_axes([0,0,1,1])
ax.plot(x,y)
ax.plot(x,0*y)
ax.set_title('Function $f(x) = |x| * sin(x+π)$')
ax.set_xlabel('x')
ax.set_ylabel('f(x)')
#绘制图片
myNewton('squareRoot', 'dSquareRoot', 1, 1e-6, 100)
#使用牛顿迭代函数下边是运行的图片和结果
图片

结果

因为我没有正确答案,因此这道题是否正确我不是很确定,如果有错误麻烦大家帮我指出啦!!!十分感谢!!!![]()
(3)
A modifification of Newton’s method can be formulated: for an integer m
,
we defifine the iteration
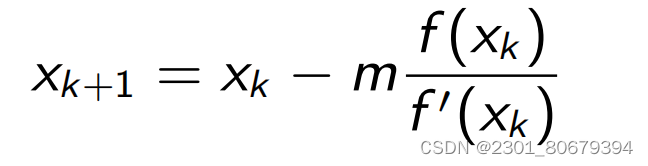
where m
should equal the
multiplicity
of the zero
x
∗
. Implement the
modifified Newton’s method and solve Problem 2 again for m
= 1
,
2
,
3
, . . .
.
Which value of m
is required to recover convergence of order 2?
这道题是在第二题的基础上进行编写
下边是利用python进行编写的代码
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# 定义函数 f(x) 和 f'(x)
def f(x):
return np.abs(x) * np.sin(x + np.pi)
def df(x):
return np.sign(x) * (np.abs(x) * np.cos(x + np.pi) + np.sin(x + np.pi))
def modified_newton_method(x0, tol, max_iter, m):
x = x0
k = 0
while k < max_iter:
fx = f(x)
dfx = df(x)
if np.abs(fx) < tol:
break
x = x - m * fx / dfx
k += 1
return x
# 初始参数
x0 = 1
tolerance = 1e-6
max_iterations = 100
# 尝试不同的 m 值
m_values = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
convergence_orders = []
# 对每个 m 进行数值求解
for m in m_values:
result = modified_newton_method(x0, tolerance, max_iterations, m)
convergence_order = np.log(np.abs(f(result)) / tolerance) / np.log(tolerance)
convergence_orders.append(convergence_order)
print(f"m = {m}: Numerical solution: {result}, Convergence order: {convergence_order}")
# 找到能够恢复到 2 阶收敛性的最佳 m 值
best_m_index = np.argmin(np.abs(np.array(convergence_orders) - 2))
best_m_value = m_values[best_m_index]
print(f"The value of m required to recover convergence of order 2 is: {best_m_value}")下边是运行结果

对于这道题,因为我不知道正确答案,因此我没办法确定编写是否正确,如果存在错误,也麻烦大家帮我指出啦!!!(・ω・)ノ
最后的最后,这是我根据老师的课程写出来的课后题,如果存在错误,请大家指出,十分感谢!!!
做题的思路来自于我亲爱的科学计算老师给的PPT







 本文介绍了如何使用牛顿迭代法求解一元非线性方程x^3=0和|x|sin(x+π)=0,通过实例计算迭代次数,并探讨了如何通过修改牛顿法来提高特定零点的收敛速度。
本文介绍了如何使用牛顿迭代法求解一元非线性方程x^3=0和|x|sin(x+π)=0,通过实例计算迭代次数,并探讨了如何通过修改牛顿法来提高特定零点的收敛速度。














 1968
1968

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








