文末有福利领取哦~
👉一、Python所有方向的学习路线
Python所有方向的技术点做的整理,形成各个领域的知识点汇总,它的用处就在于,你可以按照上面的知识点去找对应的学习资源,保证自己学得较为全面。
👉二、Python必备开发工具
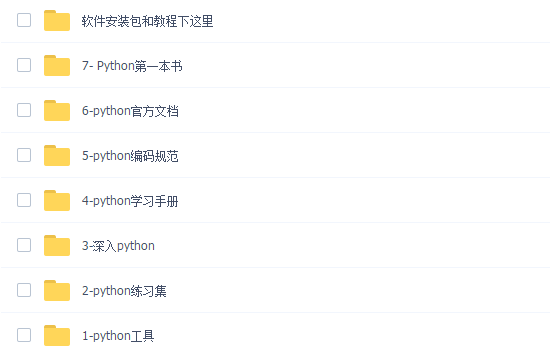
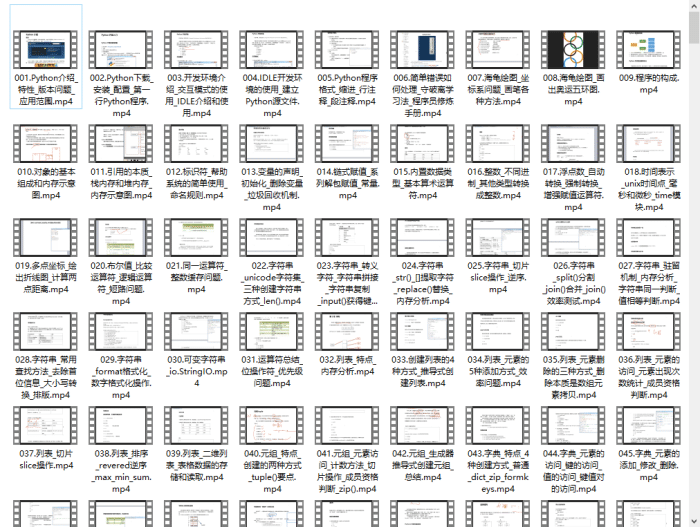
👉三、Python视频合集
观看零基础学习视频,看视频学习是最快捷也是最有效果的方式,跟着视频中老师的思路,从基础到深入,还是很容易入门的。
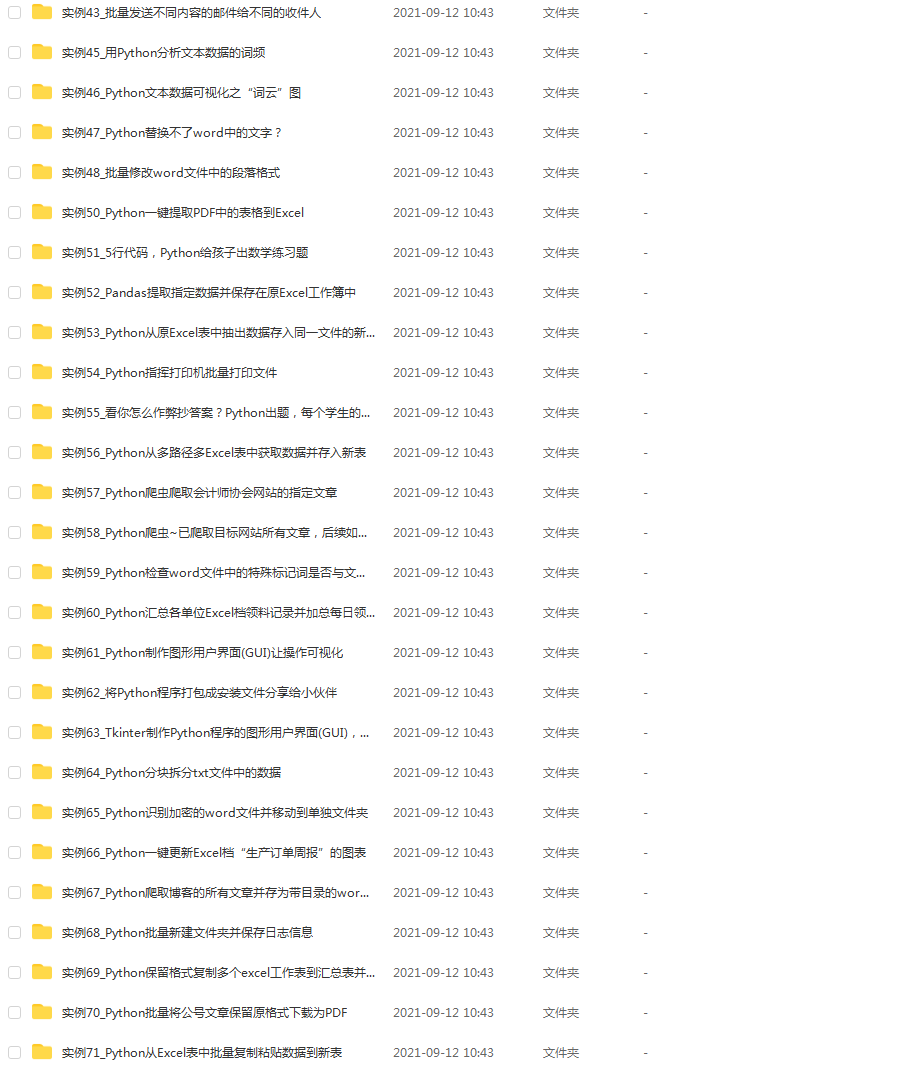
👉 四、实战案例
光学理论是没用的,要学会跟着一起敲,要动手实操,才能将自己的所学运用到实际当中去,这时候可以搞点实战案例来学习。(文末领读者福利)
👉五、Python练习题
检查学习结果。

👉六、面试资料
我们学习Python必然是为了找到高薪的工作,下面这些面试题是来自阿里、腾讯、字节等一线互联网大厂最新的面试资料,并且有阿里大佬给出了权威的解答,刷完这一套面试资料相信大家都能找到满意的工作。
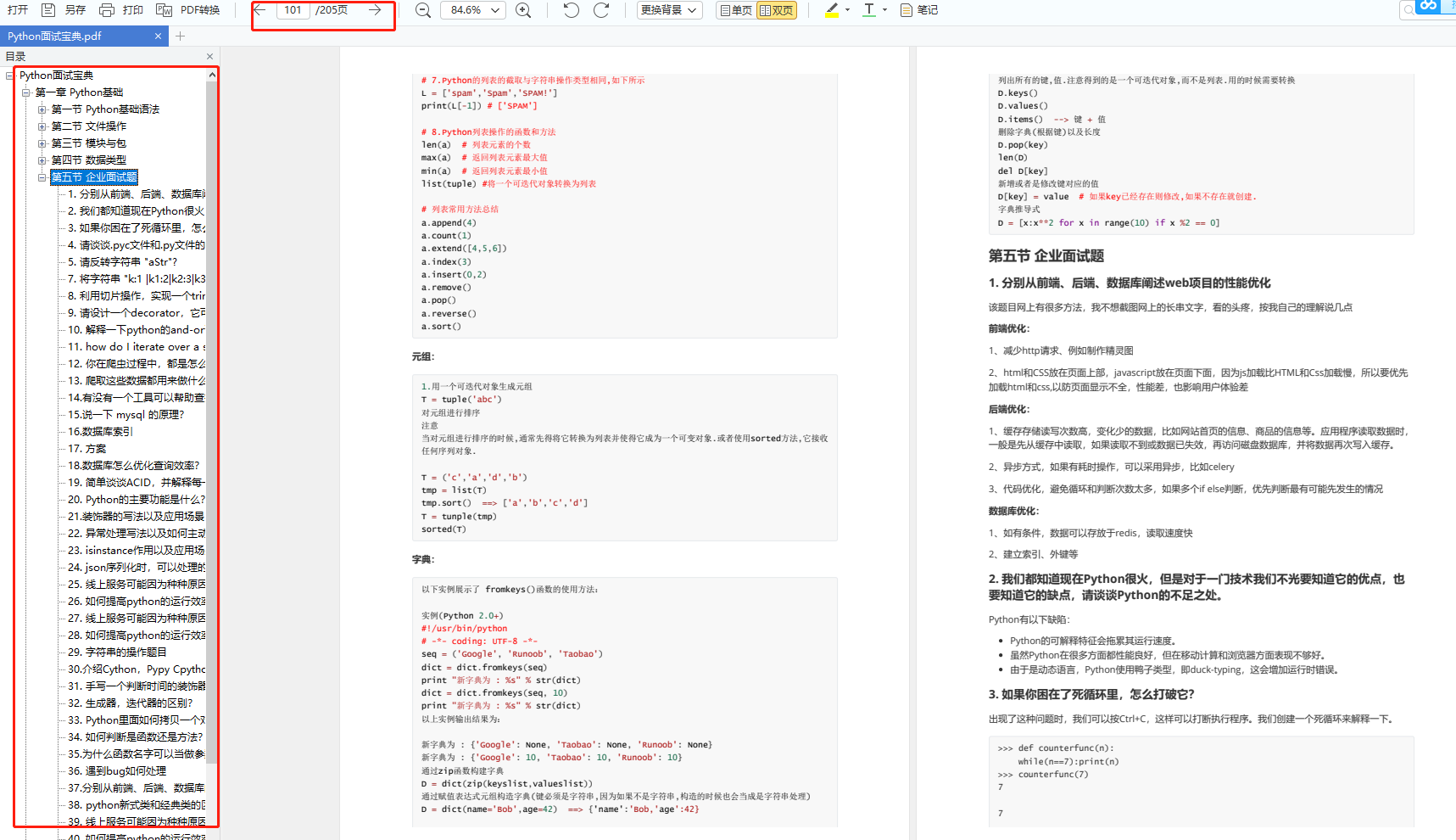
👉因篇幅有限,仅展示部分资料,这份完整版的Python全套学习资料已经上传
网上学习资料一大堆,但如果学到的知识不成体系,遇到问题时只是浅尝辄止,不再深入研究,那么很难做到真正的技术提升。
一个人可以走的很快,但一群人才能走的更远!不论你是正从事IT行业的老鸟或是对IT行业感兴趣的新人,都欢迎加入我们的的圈子(技术交流、学习资源、职场吐槽、大厂内推、面试辅导),让我们一起学习成长!
threads = []
for i in range(0, nloop):
t = myThread(i, 'thread' + str(i), hello, args=('thread' + str(i),))
threads.append(t)
for t in threads:
t.start()
for t in threads:
t.join()
主要是修改\_\_init\_\_函数和run函数,对参数和运行方式进行修改。调用方式差不多。

派生
### 多线程池
#### ThreadPoolExecutor
使用ThreadPoolExecutor
def thread_pool_executor_use():
nloop = 10
executor = ThreadPoolExecutor(4)
for i in range(nloop):
executor.submit(hello, ‘thread executor’ + str(i))

多线程池
### 线程同步
使用队列进行同步,先进先出。
线程同步-生产者,消费者
q = queue.Queue(maxsize=10)
生产者
def Producer(name):
count = 0
while True:
q.put(‘骨头%s’ % count)
print(‘%s生产了骨头’ % name, count)
count += 1
time.sleep(0.5)
if q.qsize() == q.maxsize:
exit(0)
消费者
def Consumer(name):
count = 6
while count:
count -= 1
print(‘%s吃了%s!’ % (name, q.get()))
time.sleep(1)
print(‘%s吃饱了!’ % name)
exit(0)
线程同步
def thread_synch():
p = Thread(target=Producer, args=(‘主人’,))
p.start()
c = Thread(target=Consumer, args=(‘二哈’,))
c.start()

生产者消费者
## 多进程编程
### Process类
和Thread类差不多,3.7有些优化,kill,close函数等。
#### 直接调用
直接实例化Process
def process_use():
nloop = 10
processes = []
for i in range(0, nloop):
p = Process(target=hello, args=('process' + str(i),))
processes.append(p)
for p in processes:
p.start()
for p in processes:
p.join()

Process类
#### 派生
同样是修改\_\_init\_\_函数和run函数,不做赘述。
### 多进程池
#### multiprocessing.pool
常用apply\_async和map函数
进程池
def process_pool_use():
nloop = 10
arg_list = []
with Pool(processes=4) as pool: # start 4 worker processes
for i in range(nloop):
pool.apply_async(hello, (‘process’+str(i),)) # evaluate “f(10)” asynchronously in a single process
arg_list.append(‘process’+str(i))
pool.map(hello, arg_list)
pool.close()
pool.join()

多进程池
#### ProcessPoolExecutor
使用ProcessPoolExecutor
def process_pool_executor_use():
nloop = 10
executor = ProcessPoolExecutor(4)
for i in range(nloop):
executor.submit(hello, ‘process executor’ + str(i))

ProcessPoolExecutor
## 全部代码
“”"
–coding:utf-8–
@File: multithreading.py
@Author:frank yu
@DateTime: 2020.07.21 18:32
@Contact: frankyu112058@gmail.com
“”"
from threading import Thread
from concurrent.futures import ThreadPoolExecutor, ProcessPoolExecutor
from multiprocessing import Process, Pool
import queue
import time
简单的输出函数
def hello(con):
print(‘hello,’ + con)
派生Thread
class myThread(Thread):
def init(self, threadID, name, func, args):
Thread.init(self)
self.threadID = threadID
self.name = name
self.func = func
self.args = args
def run(self):
print("开始线程:" + self.name)
try:
if self.func:
self.func(*self.args)
finally:
del self.func, self.args
print("退出线程:" + self.name)
直接实例化Thread
def thread_use():
nloop = 10
threads = []
for i in range(0, nloop):
t = Thread(target=hello, args=('thread' + str(i),))
threads.append(t)
for t in threads:
t.start()
for t in threads:
t.join()
使用派生线程类
def mythread_use():
nloop = 10
threads = []
for i in range(0, nloop):
t = myThread(i, 'thread' + str(i), hello, args=('thread' + str(i),))
threads.append(t)
for t in threads:
t.start()
for t in threads:
t.join()
使用ThreadPoolExecutor
def thread_pool_executor_use():
nloop = 10
executor = ThreadPoolExecutor(4)
for i in range(nloop):
executor.submit(hello, ‘thread executor’ + str(i))
线程同步-生产者,消费者
q = queue.Queue(maxsize=10)
生产者
def Producer(name):
count = 0
while True:
q.put(‘骨头%s’ % count)
print(‘%s生产了骨头’ % name, count)
count += 1
time.sleep(0.5)
if q.qsize() == q.maxsize:
exit(0)
消费者
def Consumer(name):
count = 6
while count:
count -= 1
print(‘%s吃了%s!’ % (name, q.get()))
time.sleep(1)
print(‘%s吃饱了!’ % name)
exit(0)
线程同步
def thread_synch():
p = Thread(target=Producer, args=(‘主人’,))
p.start()
c = Thread(target=Consumer, args=(‘二哈’,))
c.start()
直接实例化Process
def process_use():
nloop = 10
processes = []
for i in range(0, nloop):
p = Process(target=hello, args=('process' + str(i),))
processes.append(p)
for p in processes:
p.start()
for p in processes:
p.join()
进程池
def process_pool_use():
nloop = 10
arg_list = []
with Pool(processes=4) as pool: # start 4 worker processes
for i in range(nloop):
pool.apply_async(hello, (‘process’ + str(i),)) # evaluate “f(10)” asynchronously in a single process
arg_list.append(‘process’ + str(i))
pool.map(hello, arg_list)
pool.close()
pool.join()
使用ProcessPoolExecutor
def process_pool_executor_use():
nloop = 10
executor = ProcessPoolExecutor(4)
for i in range(nloop):
executor.submit(hello, ‘process executor’ + str(i))
if name == “main”:
# thread_use()
# mythread_use()
# thread_pool_executor_use()
thread_synch()
# process_use()
# process_pool_use()
# process_pool_executor_use()
## 参考
python 3.7官方文档:[threading-基于线程的并行](https://bbs.csdn.net/topics/618317507)
python 3.7官方文档:[processing-基于进程的并行](https://bbs.csdn.net/topics/618317507)
python 3.7官方文档:[concurrent.futures--- 启动并行任务](https://bbs.csdn.net/topics/618317507)
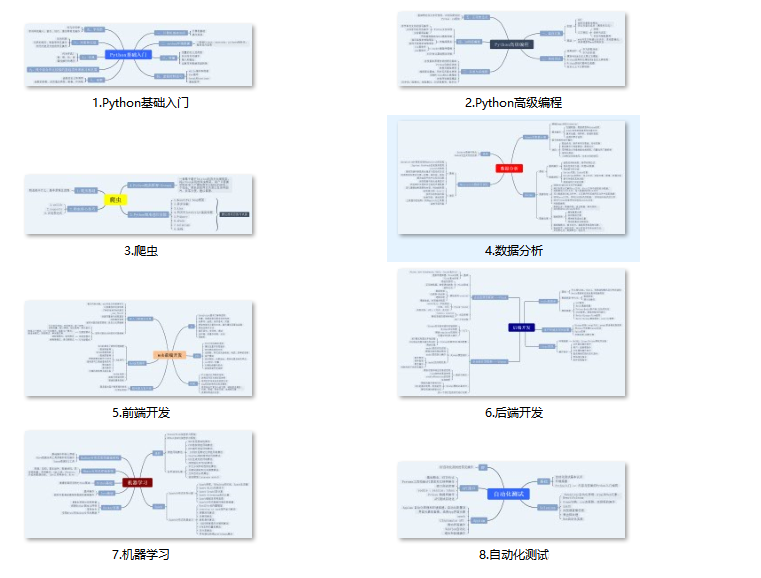
### 一、Python所有方向的学习路线
Python所有方向路线就是把Python常用的技术点做整理,形成各个领域的知识点汇总,它的用处就在于,你可以按照上面的知识点去找对应的学习资源,保证自己学得较为全面。
### 二、学习软件
工欲善其事必先利其器。学习Python常用的开发软件都在这里了,给大家节省了很多时间。
### 三、入门学习视频
我们在看视频学习的时候,不能光动眼动脑不动手,比较科学的学习方法是在理解之后运用它们,这时候练手项目就很适合了。
**网上学习资料一大堆,但如果学到的知识不成体系,遇到问题时只是浅尝辄止,不再深入研究,那么很难做到真正的技术提升。**
**[需要这份系统化学习资料的朋友,可以戳这里获取](https://bbs.csdn.net/topics/618317507)**
**一个人可以走的很快,但一群人才能走的更远!不论你是正从事IT行业的老鸟或是对IT行业感兴趣的新人,都欢迎加入我们的的圈子(技术交流、学习资源、职场吐槽、大厂内推、面试辅导),让我们一起学习成长!**






















 2026
2026











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








