先自我介绍一下,小编浙江大学毕业,去过华为、字节跳动等大厂,目前阿里P7
深知大多数程序员,想要提升技能,往往是自己摸索成长,但自己不成体系的自学效果低效又漫长,而且极易碰到天花板技术停滞不前!
因此收集整理了一份《2024年最新Linux运维全套学习资料》,初衷也很简单,就是希望能够帮助到想自学提升又不知道该从何学起的朋友。

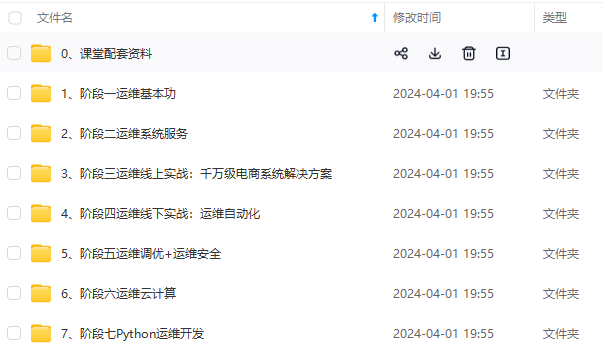
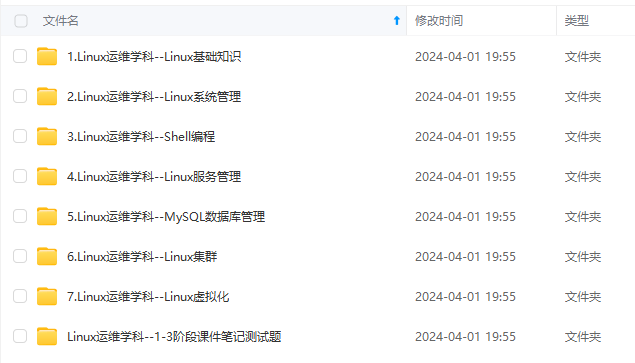
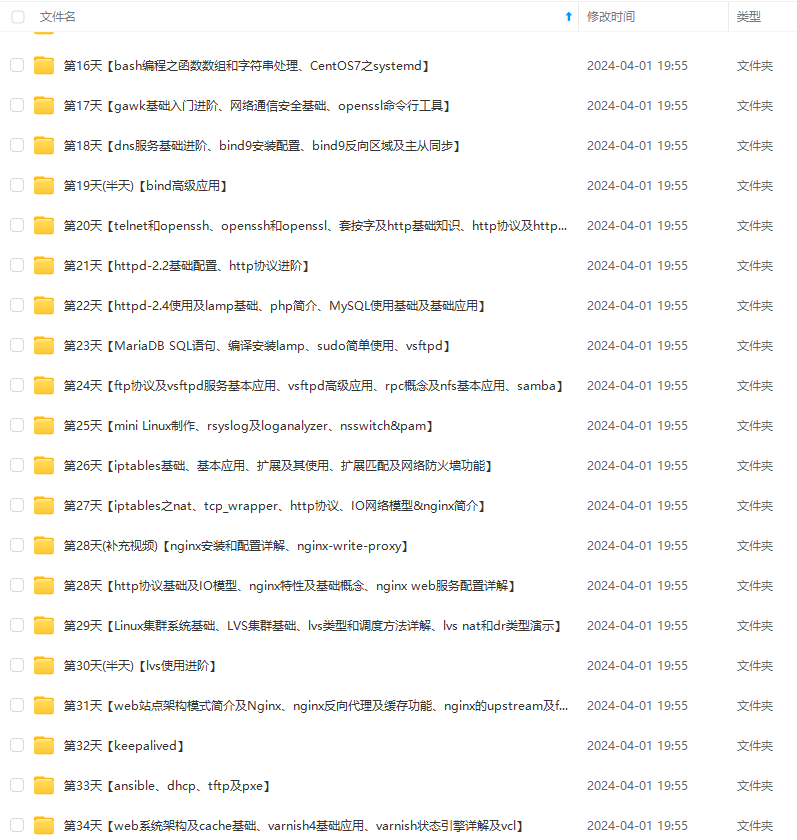
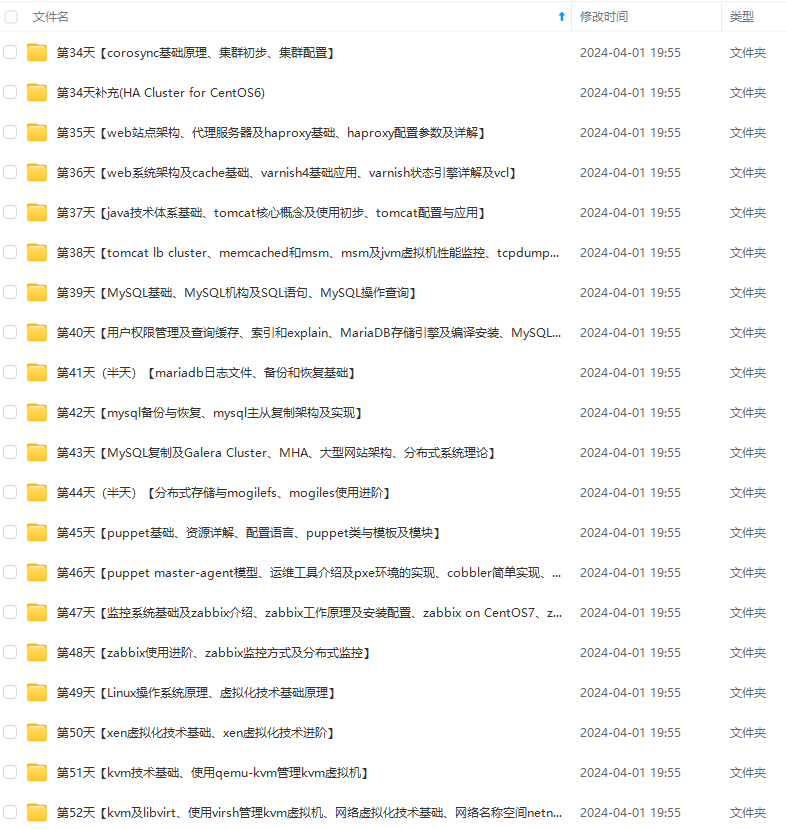
既有适合小白学习的零基础资料,也有适合3年以上经验的小伙伴深入学习提升的进阶课程,涵盖了95%以上运维知识点,真正体系化!
由于文件比较多,这里只是将部分目录截图出来,全套包含大厂面经、学习笔记、源码讲义、实战项目、大纲路线、讲解视频,并且后续会持续更新
如果你需要这些资料,可以添加V获取:vip1024b (备注运维)

正文
/dev/sdb6 29362180 33554436 2096128+ 83 Linux
/dev/sdb7 33556485 41943039 4193277+ 83 Linux
Command (m for help): d
Partition number (1-7, default 7):
Partition 7 is deleted
Command (m for help): d
Partition number (1-6, default 6):
Partition 6 is deleted
Command (m for help): d
Partition number (1-5, default 5):
Partition 5 is deleted
Command (m for help): d
Partition number (1-4, default 4):
Partition 4 is deleted
Command (m for help): d
Partition number (1-3, default 3):
Partition 3 is deleted
Command (m for help): d
Partition number (1,2, default 2):
Partition 2 is deleted
Command (m for help): d
Selected partition 1
Partition 1 is deleted
Command (m for help):
Command (m for help): p
Disk /dev/sdb: 21.5 GB, 21474836480 bytes, 41943040 sectors
Units = sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes
Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
Disk label type: dos
Disk identifier: 0x0ab2846a
Device Boot Start End Blocks Id System
Command (m for help):
脚本内容如下
注:下面的/dev/sdb务必要根据实际情况更换盘符信息,这玩意是不可逆的,搞错盘符可能会导致现有/dev/sdb盘的数据丢失。
[root@controll ccx]# cat disk.sh
#!/bin/bash
下面的/dev/sdb更改为你硬盘的实际盘符
fdisk /dev/sdb << EOF
n
p
1
2048
6289408
n
p
2
6289409
14678017
n
p
3
14678018
25163778
n
e
25163779
n
25165827
29360131
n
29362180
33554436
n
33556485
p
w
EOF
执行结果
成功,完美。
[root@controll ccx]# sh disk.sh
Welcome to fdisk (util-linux 2.23.2).
Changes will remain in memory only, until you decide to write them.
Be careful before using the write command.
Command (m for help): Partition type:
p primary (0 primary, 0 extended, 4 free)
e extended
Select (default p): Partition number (1-4, default 1): First sector (2048-41943039, default 2048): Last sector, +sectors or +size{K,M,G} (2048-41943039, default 41943039): Partition 1 of type Linux and of size 3 GiB is set
Command (m for help): Partition type:
p primary (1 primary, 0 extended, 3 free)
e extended
Select (default p): Partition number (2-4, default 2): First sector (6289409-41943039, default 6291456): Last sector, +sectors or +size{K,M,G} (6289409-41943039, default 41943039): Partition 2 of type Linux and of size 4 GiB is set
Command (m for help): Partition type:
p primary (2 primary, 0 extended, 2 free)
e extended
Select (default p): Partition number (3,4, default 3): First sector (14678018-41943039, default 14680064): Last sector, +sectors or +size{K,M,G} (14678018-41943039, default 41943039): Partition 3 of type Linux and of size 5 GiB is set
Command (m for help): Partition type:
p primary (3 primary, 0 extended, 1 free)
e extended
Select (default e): Selected partition 4
First sector (25163779-41943039, default 25165824): Last sector, +sectors or +size{K,M,G} (25163779-41943039, default 41943039): Using default value 41943039
Partition 4 of type Extended and of size 8 GiB is set
Command (m for help): All primary partitions are in use
Adding logical partition 5
First sector (25165827-41943039, default 25167872): Last sector, +sectors or +size{K,M,G} (25165827-41943039, default 41943039): Partition 5 of type Linux and of size 2 GiB is set
Command (m for help): All primary partitions are in use
Adding logical partition 6
First sector (29362180-41943039, default 29364224): Last sector, +sectors or +size{K,M,G} (29362180-41943039, default 41943039): Partition 6 of type Linux and of size 2 GiB is set
Command (m for help): All primary partitions are in use
Adding logical partition 7
First sector (33556485-41943039, default 33558528): Last sector, +sectors or +size{K,M,G} (33556485-41943039, default 41943039): Using default value 41943039
Partition 7 of type Linux and of size 4 GiB is set
Command (m for help):
Disk /dev/sdb: 21.5 GB, 21474836480 bytes, 41943040 sectors
Units = sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes
Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
Disk label type: dos
Disk identifier: 0x0ab2846a
Device Boot Start End Blocks Id System
/dev/sdb1 2048 6289408 3143680+ 83 Linux
/dev/sdb2 6289409 14678017 4194304+ 83 Linux
/dev/sdb3 14678018 25163778 5242880+ 83 Linux
/dev/sdb4 25163779 41943039 8389630+ 5 Extended
/dev/sdb5 25165827 29360131 2097152+ 83 Linux
/dev/sdb6 29362180 33554436 2096128+ 83 Linux
/dev/sdb7 33556485 41943039 4193277+ 83 Linux
Command (m for help): The partition table has been altered!
Calling ioctl() to re-read partition table.
Syncing disks.
[root@controll ccx]# partprobe
Warning: Unable to open /dev/sr0 read-write (Read-only file system). /dev/sr0 has been opened read-only.
[root@controll ccx]# lsblk
NAME MAJ:MIN RM SIZE RO TYPE MOUNTPOINT
sda 8:0 0 200G 0 disk
├─sda1 8:1 0 1G 0 part /boot
└─sda2 8:2 0 199G 0 part
├─centos-root 253:0 0 50G 0 lvm /
├─centos-swap 253:1 0 15.8G 0 lvm [SWAP]
└─centos-home 253:2 0 133.2G 0 lvm /home
sdb 8:16 0 20G 0 disk
├─sdb1 8:17 0 3G 0 part
├─sdb2 8:18 0 4G 0 part
├─sdb3 8:19 0 5G 0 part
├─sdb4 8:20 0 1K 0 part
├─sdb5 8:21 0 2G 0 part
├─sdb6 8:22 0 2G 0 part
└─sdb7 8:23 0 4G 0 part
sr0 11:0 1 4.3G 0 rom
[root@controll ccx]#
- 上面脚本仅仅是进行分区,需要加啥功能自己加在最后面即可,如我这新增分区的格式改为lvm,则我需要在脚本最后面加上这些代码即可【任何功能都应在分完区以后添加】
注:修改的时候扩展分区不能改格式的,应跳过【如我是第4个做的逻辑分区,则sdb4【4】不能改格式,应跳过】
增加功能后的代码如下
[root@controll ccx]# cat disk.sh
#!/bin/bash
fdisk /dev/sdb << EOF
n
p
1
2048
6289408
n
p
2
6289409
14678017
n
p
3
14678018
25163778
n
e
25163779
n
25165827
29360131
n
29362180
33554436
n
33556485
p
t
1
8e
t
2
8e
t
3
8e
t
5
8e
t
6
8e
t
7
8e
p
w
EOF
[root@controll ccx]#
执行结果
如果之前执行过,应先去删除已经创建的分区再执行。
[root@controll ccx]# sh disk.sh
Welcome to fdisk (util-linux 2.23.2).
Changes will remain in memory only, until you decide to write them.
Be careful before using the write command.
Command (m for help): Partition type:
p primary (0 primary, 0 extended, 4 free)
e extended
Select (default p): Partition number (1-4, default 1): First sector (2048-41943039, default 2048): Last sector, +sectors or +size{K,M,G} (2048-41943039, default 41943039): Partition 1 of type Linux and of size 3 GiB is set
Command (m for help): Partition type:
p primary (1 primary, 0 extended, 3 free)
e extended
Select (default p): Partition number (2-4, default 2): First sector (6289409-41943039, default 6291456): Last sector, +sectors or +size{K,M,G} (6289409-41943039, default 41943039): Partition 2 of type Linux and of size 4 GiB is set
Command (m for help): Partition type:
p primary (2 primary, 0 extended, 2 free)
e extended
Select (default p): Partition number (3,4, default 3): First sector (14678018-41943039, default 14680064): Last sector, +sectors or +size{K,M,G} (14678018-41943039, default 41943039): Partition 3 of type Linux and of size 5 GiB is set
Command (m for help): Partition type:
p primary (3 primary, 0 extended, 1 free)
e extended
Select (default e): Selected partition 4
First sector (25163779-41943039, default 25165824): Last sector, +sectors or +size{K,M,G} (25163779-41943039, default 41943039): Using default value 41943039
Partition 4 of type Extended and of size 8 GiB is set
Command (m for help): All primary partitions are in use
Adding logical partition 5
First sector (25165827-41943039, default 25167872): Last sector, +sectors or +size{K,M,G} (25165827-41943039, default 41943039): Partition 5 of type Linux and of size 2 GiB is set
Command (m for help): All primary partitions are in use
Adding logical partition 6
First sector (29362180-41943039, default 29364224): Last sector, +sectors or +size{K,M,G} (29362180-41943039, default 41943039): Partition 6 of type Linux and of size 2 GiB is set
Command (m for help): All primary partitions are in use
Adding logical partition 7
First sector (33556485-41943039, default 33558528): Last sector, +sectors or +size{K,M,G} (33556485-41943039, default 41943039): Using default value 41943039
Partition 7 of type Linux and of size 4 GiB is set
Command (m for help):
Disk /dev/sdb: 21.5 GB, 21474836480 bytes, 41943040 sectors
Units = sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes
Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
Disk label type: dos
Disk identifier: 0x0ab2846a
Device Boot Start End Blocks Id System
/dev/sdb1 2048 6289408 3143680+ 83 Linux
/dev/sdb2 6289409 14678017 4194304+ 83 Linux
/dev/sdb3 14678018 25163778 5242880+ 83 Linux
/dev/sdb4 25163779 41943039 8389630+ 5 Extended
/dev/sdb5 25165827 29360131 2097152+ 83 Linux
/dev/sdb6 29362180 33554436 2096128+ 83 Linux
/dev/sdb7 33556485 41943039 4193277+ 83 Linux
Command (m for help): Partition number (1-7, default 7): Hex code (type L to list all codes): Changed type of partition ‘Linux’ to ‘Linux LVM’
Command (m for help): Partition number (1-7, default 7): Hex code (type L to list all codes): Changed type of partition ‘Linux’ to ‘Linux LVM’
Command (m for help): Partition number (1-7, default 7): Hex code (type L to list all codes): Changed type of partition ‘Linux’ to ‘Linux LVM’
Command (m for help): Partition number (1-7, default 7): Hex code (type L to list all codes):
You cannot change a partition into an extended one or vice versa.
Delete it first.
Type of partition 4 is unchanged: Extended
Command (m for help): Partition number (1-7, default 7): Hex code (type L to list all codes): Changed type of partition ‘Linux’ to ‘Linux LVM’
Command (m for help): Partition number (1-7, default 7): Hex code (type L to list all codes): Changed type of partition ‘Linux’ to ‘Linux LVM’
Command (m for help): Partition number (1-7, default 7): Hex code (type L to list all codes): Changed type of partition ‘Linux’ to ‘Linux LVM’
Command (m for help):
Disk /dev/sdb: 21.5 GB, 21474836480 bytes, 41943040 sectors
Units = sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes
Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
Disk label type: dos
Disk identifier: 0x0ab2846a
Device Boot Start End Blocks Id System
/dev/sdb1 2048 6289408 3143680+ 8e Linux LVM
/dev/sdb2 6289409 14678017 4194304+ 8e Linux LVM
/dev/sdb3 14678018 25163778 5242880+ 8e Linux LVM
/dev/sdb4 25163779 41943039 8389630+ 5 Extended
/dev/sdb5 25165827 29360131 2097152+ 8e Linux LVM
/dev/sdb6 29362180 33554436 2096128+ 8e Linux LVM
/dev/sdb7 33556485 41943039 4193277+ 8e Linux LVM
Command (m for help): The partition table has been altered!
Calling ioctl() to re-read partition table.
Syncing disks.
[root@controll ccx]#
功能修改后的效果展示
功能修改后的效果就是下图这样的【如果要划lv,这格式必须改为这个】

==========================================================================
-
4个条件
-
必须是同一批服务器【或确保网络互通即可】
-
/dev/sdb这种名称必须相同
-
硬盘大小必须一致
-
必须是新硬盘
-
如果上述不确定的,先跑个批量脚本查看每台主机的该硬盘的大小和是否为新硬盘。
-
脚本执行后,该操作是不可逆的,务必要确定上面信息。
-
如,跑的脚本是/dev/sdb,如果某台服务器上的/dev/sdb是正在使用中的硬盘,可能会导致该服务器上的/dev/sdb中的硬盘丢失
说明
-
下面功能代码和遍历执行代码均放一个服务器上的同一目录中,分2个文件存放。
-
可以先手动执行功能代码,没报错以后,再执行遍历执行代码。
功能代码
-
这里面放的是分区的代码【代码最后面其实还可以放做lv的代码】【做lv流程是纯代码,过于简单,这就不做演示了】
-
注:如果想看分区过程,将下面代码中的
fdisk $diskname << EOF>/dev/null改为:fdisk $diskname << EOF
[root@controll ccx]# pwd
/ccx
[root@controll ccx]# cat disk.sh
#!/bin/bash
diskname=/dev/sdb
fdisk $diskname << EOF > /dev/null
n
p
1
2048
6289408
n
p
2
6289409
14678017
n
p
3
14678018
25163778
n
e
25163779
n
25165827
29360131
n
29362180
33554436
n
33556485
p
t
1
8e
t
2
8e
t
3
8e
t
4
8e
t
5
8e
t
6
8e
t
7
8e
p
w
EOF
partprobe
lsblk|grep sdb
[root@controll ccx]#
遍历执行代码
-
这批服务器是没有免密登陆的,所以ip存放文件中的格式为:
ip 密码 -
这个执行流程如下:
-
登陆
-
scp拷贝功能脚本到当前服务器
-
查看是否拷贝成功
-
执行功能代码
-
删除功能代码文件
-
退出登陆
[root@controll ccx]# cat disk_send.sh
#/bin/bash
file=/ccx/iplist.txt
cat $file | while read ip ; do
ippaswd=($ip)
/usr/bin/expect<<EOF
spawn ssh root@${ippaswd[0]}
expect {
“*yes/no” { send “yes\r”; exp_continue}
“*assword:” { send “${ippaswd[1]}\r” }
}
expect “#”
下面为功能代码存放ip和路径
send “scp 192.168.59.133:/ccx/disk.sh /root\r”
expect {
“*yes/no” { send “yes\r”; exp_continue}
“*assword:” { send “${ippaswd[1]}\r” }
}
expect “#”
send “ls /root | grep disk\r”
send “sh /root/disk.sh\r”
send “rm -rf /root/disk.sh\r”
send “exit\r”
expect eof
EOF
done
[root@controll ccx]#
[root@controll ccx]# cat iplist.txt
192.168.59.128 root
192.168.59.129 root
192.168.59.130 root
[root@controll ccx]#
-
注意看执行结果是否所有sdb都创建成功【如果创建失败的看下发创建失败处理过程】
-
执行的是遍历执行代码
执行方式:sh disk_send.sh
[root@controll ccx]# sh disk_send.sh
spawn ssh root@192.168.59.128
root@192.168.59.128’s password:
Last login: Thu Jun 10 20:51:38 2021 from 192.168.59.133
[root@centso76_1 ~]# scp 192.168.59.133:/ccx/disk.sh /root
The authenticity of host ‘192.168.59.133 (192.168.59.133)’ can’t be established.
ECDSA key fingerprint is SHA256:ulUqmZhBWg273m620MpAzoq6iPZEDU2ULoPjfiXTGDc.
ECDSA key fingerprint is MD5:ca:60:fa:17:0c:09:5d:4b:39:c5:95:7d:20:54:c5:49.
Are you sure you want to continue connecting (yes/no)? yes
Warning: Permanently added ‘192.168.59.133’ (ECDSA) to the list of known hosts.
Password:
disk.sh 100% 281 265.0KB/s 00:00
[root@centso76_1 ~]# ls /root | grep disk
disk.sh
[root@centso76_1 ~]# sh /root/disk.sh
sdb 8:16 0 20G 0 disk
├─sdb1 8:17 0 3G 0 part
├─sdb2 8:18 0 4G 0 part
├─sdb3 8:19 0 5G 0 part
├─sdb4 8:20 0 1K 0 part
├─sdb5 8:21 0 2G 0 part
├─sdb6 8:22 0 2G 0 part
└─sdb7 8:23 0 4G 0 part
[root@centso76_1 ~]# rm -rf /root/disk.sh
[root@centso76_1 ~]# exit
登出
Connection to 192.168.59.128 closed.
spawn ssh root@192.168.59.129
root@192.168.59.129’s password:
Last login: Thu Jun 10 08:56:58 2021 from 192.168.59.133
[root@centos76_2 ~]# scp 192.168.59.133:/ccx/disk.sh /root
The authenticity of host ‘192.168.59.133 (192.168.59.133)’ can’t be established.
ED25519 key fingerprint is SHA256:0uTcB4pn/p0X72gZrtG4b7MrgLJJL9Q8Gr1TrDNFThA.
This key is not known by any other names
Are you sure you want to continue connecting (yes/no/[fingerprint])? yes
Warning: Permanently added ‘192.168.59.133’ (ED25519) to the list of known hosts.
(root@192.168.59.133) Password:
disk.sh 100% 281 226.4KB/s 00:00
[root@centos76_2 ~]# ls /root | grep disk
disk.sh
[root@centos76_2 ~]# sh /root/disk.sh
sdb 8:16 0 20G 0 disk
├─sdb1 8:17 0 3G 0 part
├─sdb2 8:18 0 4G 0 part
├─sdb3 8:19 0 5G 0 part
├─sdb4 8:20 0 1K 0 part
├─sdb5 8:21 0 2G 0 part
├─sdb6 8:22 0 2G 0 part
└─sdb7 8:23 0 4G 0 part
[root@centos76_2 ~]# rm -rf /root/disk.sh
[root@centos76_2 ~]# exit
logout
Connection to 192.168.59.129 closed.
spawn ssh root@192.168.59.130
(root@192.168.59.130) Password:
Last login: Thu Jun 10 20:52:08 2021 from 192.168.59.133
[root@centos76_3 ~]# scp 192.168.59.133:/ccx/disk.sh /root
The authenticity of host ‘192.168.59.133 (192.168.59.133)’ can’t be established.
ECDSA key fingerprint is SHA256:ulUqmZhBWg273m620MpAzoq6iPZEDU2ULoPjfiXTGDc.
Are you sure you want to continue connecting (yes/no/[fingerprint])? yes
Warning: Permanently added ‘192.168.59.133’ (ECDSA) to the list of known hosts.
Password:
disk.sh 100% 281 181.3KB/s 00:00
[root@centos76_3 ~]# ls /root | grep disk
disk.sh
[root@centos76_3 ~]# sh /root/disk.sh
Do you really want to quit? sdb 8:16 0 20G 0 disk
├─sdb1 8:17 0 3G 0 part
├─sdb2 8:18 0 4G 0 part
├─sdb3 8:19 0 5G 0 part
├─sdb4 8:20 0 1K 0 part
└─sdb5 8:21 0 2G 0 part
[root@centos76_3 ~]# rm -rf /root/disk.sh
[root@centos76_3 ~]# exit
logout
Connection to 192.168.59.130 closed.
[root@controll ccx]#
批量中某一台创建失败处理方法
-
注:我把执行过程给放到/dev/null里面了,仅展示了sdb的结果,否则执行过程中内容会非常长,所以就需要看结果是否均正常就可以了,就如上面的最后一台主机名是centos76_3的虚机,结果就不对劲,sdb6和sdb7没有创建成功;
-
处理方法
-
登陆到该主机
-
手动删除已经分区的内容
-
拷贝上面的“功能代码“过来
-
将
fdisk $diskname << EOF>/dev/null改为:fdisk $diskname << EOF【为了看过程】 -
手动执行该脚本
-
删除已分区的内容
[root@centos76_3 ccx]# fdisk /dev/sdb #删除已经配置完成的
Welcome to fdisk (util-linux 2.23.2).
最后的话
最近很多小伙伴找我要Linux学习资料,于是我翻箱倒柜,整理了一些优质资源,涵盖视频、电子书、PPT等共享给大家!
资料预览
给大家整理的视频资料:
给大家整理的电子书资料:

如果本文对你有帮助,欢迎点赞、收藏、转发给朋友,让我有持续创作的动力!
网上学习资料一大堆,但如果学到的知识不成体系,遇到问题时只是浅尝辄止,不再深入研究,那么很难做到真正的技术提升。
需要这份系统化的资料的朋友,可以添加V获取:vip1024b (备注运维)

一个人可以走的很快,但一群人才能走的更远!不论你是正从事IT行业的老鸟或是对IT行业感兴趣的新人,都欢迎加入我们的的圈子(技术交流、学习资源、职场吐槽、大厂内推、面试辅导),让我们一起学习成长!
8 0 4G 0 part
├─sdb3 8:19 0 5G 0 part
├─sdb4 8:20 0 1K 0 part
└─sdb5 8:21 0 2G 0 part
[root@centos76_3 ~]# rm -rf /root/disk.sh
[root@centos76_3 ~]# exit
logout
Connection to 192.168.59.130 closed.
[root@controll ccx]#
批量中某一台创建失败处理方法
-
注:我把执行过程给放到/dev/null里面了,仅展示了sdb的结果,否则执行过程中内容会非常长,所以就需要看结果是否均正常就可以了,就如上面的最后一台主机名是centos76_3的虚机,结果就不对劲,sdb6和sdb7没有创建成功;
-
处理方法
-
登陆到该主机
-
手动删除已经分区的内容
-
拷贝上面的“功能代码“过来
-
将
fdisk $diskname << EOF>/dev/null改为:fdisk $diskname << EOF【为了看过程】 -
手动执行该脚本
-
删除已分区的内容
[root@centos76_3 ccx]# fdisk /dev/sdb #删除已经配置完成的
Welcome to fdisk (util-linux 2.23.2).
最后的话
最近很多小伙伴找我要Linux学习资料,于是我翻箱倒柜,整理了一些优质资源,涵盖视频、电子书、PPT等共享给大家!
资料预览
给大家整理的视频资料:
[外链图片转存中…(img-neVQetXF-1713158642894)]
给大家整理的电子书资料:
[外链图片转存中…(img-JAN3Lmvv-1713158642894)]
如果本文对你有帮助,欢迎点赞、收藏、转发给朋友,让我有持续创作的动力!
网上学习资料一大堆,但如果学到的知识不成体系,遇到问题时只是浅尝辄止,不再深入研究,那么很难做到真正的技术提升。
需要这份系统化的资料的朋友,可以添加V获取:vip1024b (备注运维)
[外链图片转存中…(img-vrUDwgIM-1713158642894)]
一个人可以走的很快,但一群人才能走的更远!不论你是正从事IT行业的老鸟或是对IT行业感兴趣的新人,都欢迎加入我们的的圈子(技术交流、学习资源、职场吐槽、大厂内推、面试辅导),让我们一起学习成长!






















 8644
8644











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








