通常在内核rootkit 中,比较常见的hook:hook系统调用,hook /proc 接口,hook 中断向量表等等,如果系统调用表中的地址,proc接口和中断向量表中的某个地址没有在内核地址中,而是在内核模块地址中,那么该地址就很有可能被攻击了,内核rootkit都是通过内核模块的方式来加载。因为,系统调用表中的地址,proc接口和中断向量表中都是在内核地址中。
因此我们可以用该API来进行rootkit检测,来判断一个内核关键点是否被hook。
一、__module_address源码详解
1.1 struct module
struct module是内核模块在内核中最重要的一个结构体,每一个内核模块都有一个该结构体,用来描述该内核模块的基本信息。
struct module
{
enum module\_state state;
/\* Member of list of modules \*/
struct list\_head list;
/\* Unique handle for this module \*/
char name[MODULE_NAME_LEN];
......
/\* Startup function. \*/
int (\*init)(void);
/\* If this is non-NULL, vfree after init() returns \*/
void \*module_init;
/\* Here is the actual code + data, vfree'd on unload. \*/
void \*module_core;
/\* Here are the sizes of the init and core sections \*/
unsigned int init_size, core_size;
/\* The size of the executable code in each section. \*/
unsigned int init_text_size, core_text_size;
/\* Size of RO sections of the module (text+rodata) \*/
unsigned int init_ro_size, core_ro_size;
......
}
list是一个双向链表元素,有加载到内核中的模块都保存在一个双链表中。
module_init 是模块初始化部分的起始地址。
init_size是模块初始化部分的大小。
module_core是模块核心部分的起始地址。
core_size是模块核心部分的大小。
1.2 __module_address
// linux-3.10/kernel/module.c
// 所有加载到内核中的模块都保存在一个双链表中,modules是该内核模块链表head,一个全局的变量。
/\*
\* Mutex protects:
\* 1) List of modules (also safely readable with preempt\_disable),
\* 2) module\_use links,
\* 3) module\_addr\_min/module\_addr\_max.
\* (delete uses stop\_machine/add uses RCU list operations). \*/
DEFINE\_MUTEX(module_mutex);
EXPORT\_SYMBOL\_GPL(module_mutex);
static LIST\_HEAD(modules);
/\* Bounds of module allocation, for speeding \_\_module\_address.
\* Protected by module\_mutex. \*/
static unsigned long module_addr_min = -1UL, module_addr_max = 0;
/\*
\* \_\_module\_address - get the module which contains an address.
\* @addr: the address.
\*
\* Must be called with preempt disabled or module mutex held so that
\* module doesn't get freed during this.
\*/
struct module \*\_\_module\_address(unsigned long addr)
{
struct module \*mod;
if (addr < module_addr_min || addr > module_addr_max)
return NULL;
list\_for\_each\_entry\_rcu(mod, &modules, list) {
if (mod->state == MODULE_STATE_UNFORMED)
continue;
if (within\_module\_core(addr, mod)
|| within\_module\_init(addr, mod))
return mod;
}
return NULL;
}
EXPORT\_SYMBOL\_GPL(__module_address);
其中modules是一个全局变量,所有加载到内核中的模块都保存在一个双链表中,modules是该内核模块链表head。
// linux-3.10/include/linux/module.h
static inline int within\_module\_core(unsigned long addr, const struct module \*mod)
{
return (unsigned long)mod->module_core <= addr &&
addr < (unsigned long)mod->module_core + mod->core_size;
}
static inline int within\_module\_init(unsigned long addr, const struct module \*mod)
{
return (unsigned long)mod->module_init <= addr &&
addr < (unsigned long)mod->module_init + mod->init_size;
}
within_module_core判断地址addr是否在模块的module_core地址区间。
within_module_init判断地址addr是否在模块的module_init 地址区间。
// linux-3.10/include/linux/rculist.h
/\*\*
\* list\_for\_each\_entry\_rcu - iterate over rcu list of given type
\* @pos: the type \* to use as a loop cursor.
\* @head: the head for your list.
\* @member: the name of the list\_struct within the struct.
\*
\* This list-traversal primitive may safely run concurrently with
\* the \_rcu list-mutation primitives such as list\_add\_rcu()
\* as long as the traversal is guarded by rcu\_read\_lock().
\*/
#define list\_for\_each\_entry\_rcu(pos, head, member) \
for (pos = list\_entry\_rcu((head)->next, typeof(\*pos), member); \
&pos->member != (head); \
pos = list\_entry\_rcu(pos->member.next, typeof(\*pos), member))
该函数逻辑非常简单,遍历内核模块链表,如果给定的地址在一个内核模块的module_init和module_core的范围之间,则找到所在地址属于该模块。
为了防止模块被释放,使用该函数时必须禁止内核抢占,或者加锁访问。注意禁止内核抢占或加锁是保护的struct module结构体数据。
1.2 is_module_address
is_module_address是对__module_address函数的一个简单封装,用来判断一个地址是否在模块内。宏preempt_disable( )和preempt_enable( )分别用来实现禁止内核抢占和允许内核抢占。
/\*
\* is\_module\_address - is this address inside a module?
\* @addr: the address to check.
\*
\* See is\_module\_text\_address() if you simply want to see if the address
\* is code (not data).
\*/
bool is\_module\_address(unsigned long addr)
{
bool ret;
preempt\_disable();
ret = \_\_module\_address(addr) != NULL;
preempt\_enable();
return ret;
}
二、使用例程
# include <linux/init.h>
# include <linux/kernel.h>
# include <linux/module.h>
int test\_module(void)
{
return 0;
}
//内核模块初始化函数
static int __init lkm\_init(void)
{
struct module \*mod;
unsigned long addr = (unsigned long)test_module;
preempt\_disable();
mod = \_\_module\_address(addr);
preempt\_enable();
if(mod){
printk("module name = %s\n", mod->name);
printk("module core\_size = %d\n", mod->core_size);
printk("module refcount = %ld\n", module\_refcount(mod));
}
return 0;
}
//内核模块退出函数
static void __exit lkm\_exit(void)
{
}
module\_init(lkm_init);
module\_exit(lkm_exit);
MODULE\_LICENSE("GPL");
test_module函数的地址在该函数模块内,通过__module_address找到该模块,结果如下:
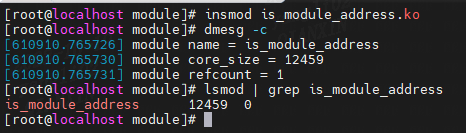
三、其它类似函数
3.1 __module_text_address
/\*
**网上学习资料一大堆,但如果学到的知识不成体系,遇到问题时只是浅尝辄止,不再深入研究,那么很难做到真正的技术提升。**
**[需要这份系统化的资料的朋友,可以点击这里获取!](https://bbs.csdn.net/topics/618542503)**
**一个人可以走的很快,但一群人才能走的更远!不论你是正从事IT行业的老鸟或是对IT行业感兴趣的新人,都欢迎加入我们的的圈子(技术交流、学习资源、职场吐槽、大厂内推、面试辅导),让我们一起学习成长!**






















 2997
2997











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








