int cport, cfd, max = MAX_ACCEPTS_PER_CALL;
char cip[NET_IP_STR_LEN];
UNUSED(el);
UNUSED(mask);
UNUSED(privdata);
//循环处理连接应答
while(max–) {
cfd = anetTcpAccept(server.neterr, fd, cip, sizeof(cip), &cport);
if (cfd == ANET_ERR) {
if (errno != EWOULDBLOCK)
serverLog(LL_WARNING,
“Accepting client connection: %s”, server.neterr);
return;
}
serverLog(LL_VERBOSE,“Accepted %s:%d”, cip, cport);
acceptCommonHandler(connCreateAcceptedSocket(cfd),0,cip);
}
}
连接应答处理器
在接收到客户端的连接后,触发链接应答处理器的acceptTcpHandler方法,这个方法里会创建客户端对于的client对象,它代表着连接到 Redis 客户端。
并且accept客户端的连接,然后把这个连接与命令处理器readQueryFromClient关联起来,服务器会将连接成功后的socket的AE_READABLE事件和命令请求处理器关联起来,命令请求处理器就可以从socket中读取数据了。
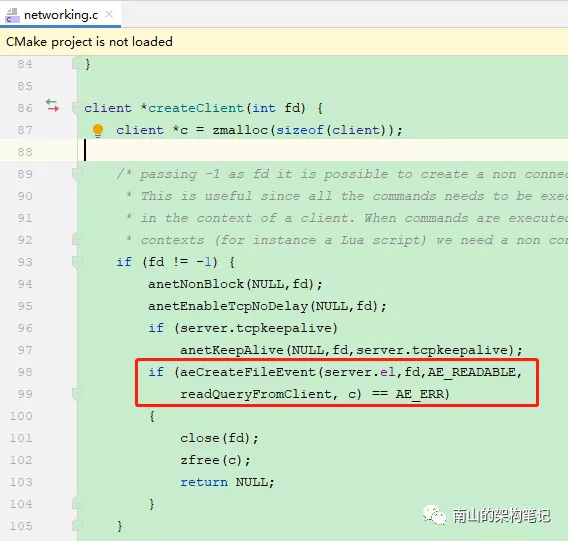
图3 建立连接后设置命令请求处理器
通过 networking.c中的readQueryFromClient方法,读取客户端发送的命令内容。
void readQueryFromClient(aeEventLoop *el, int fd, void *privdata, int mask) {
client c = (client) privdata;
int nread, readlen;
size_t qblen;
UNUSED(el);
UNUSED(mask);
readlen = PROTO_IOBUF_LEN;
/* If this is a multi bulk request, and we are processing a bulk reply
* that is large enough, try to maximize the probability that the query
* buffer contains exactly the SDS string representing the object, even
* at the risk of requiring more read(2) calls. This way the function
* processMultiBulkBuffer() can avoid copying buffers to create the
* Redis Object representing the argument. */
if (c->reqtype == PROTO_REQ_MULTIBULK && c->multibulklen && c->bulklen != -1
&& c->bulklen >= PROTO_MBULK_BIG_ARG)
{
ssize_t remaining = (size_t)(c->bulklen+2)-sdslen(c->querybuf);
/* Note that the ‘remaining’ variable may be zero in some edge case,
* for example once we resume a blocked client after CLIENT PAUSE. */
if (remaining > 0 && remaining < readlen) readlen = remaining;
}
qblen = sdslen(c->querybuf);
if (c->querybuf_peak < qblen) c->querybuf_peak = qblen;
c->querybuf = sdsMakeRoomFor(c->querybuf, readlen);
nread = read(fd, c->querybuf+qblen, readlen);
if (nread == -1) {
if (errno == EAGAIN) {
return;
} else {
serverLog(LL_VERBOSE, “Reading from client: %s”,strerror(errno));
freeClient©;
return;
}
} else if (nread == 0) {
serverLog(LL_VERBOSE, “Client closed connection”);
freeClient©;
return;
} else if (c->flags & CLIENT_MASTER) {
/* Append the query buffer to the pending (not applied) buffer
* of the master. We’ll use this buffer later in order to have a
* copy of the string applied by the last command executed. */
c->pending_querybuf = sdscatlen(c->pending_querybuf,
c->querybuf+qblen,nread);
}
sdsIncrLen(c->querybuf,nread);
c->lastinteraction = server.unixtime;
if (c->flags & CLIENT_MASTER) c->read_reploff += nread;
server.stat_net_input_bytes += nread;
if (sdslen(c->querybuf) > server.client_max_querybuf_len) {
sds ci = catClientInfoString(sdsempty(),c), bytes = sdsempty();
bytes = sdscatrepr(bytes,c->querybuf,64);
serverLog(LL_WARNING,“Closing client that reached max query buffer length: %s (qbuf initial bytes: %s)”, ci, bytes);
sdsfree(ci);
sdsfree(bytes);
freeClient©;
return;
}
/* Time to process the buffer. If the client is a master we need to
* compute the difference between the applied offset before and after
* processing the buffer, to understand how much of the replication stream
* was actually applied to the master state: this quantity, and its
* corresponding part of the replication stream, will be propagated to
* the sub-slaves and to the replication backlog. */
processInputBufferAndReplicate©;
}
void processInputBufferAndReplicate(client *c) {
if (!(c->flags & CLIENT_MASTER)) {
processInputBuffer©;
} else {
size_t prev_offset = c->reploff;
processInputBuffer©;
size_t applied = c->reploff - prev_offset;
if (applied) {
replicationFeedSlavesFromMasterStream(server.slaves,
c->pending_querybuf, applied);
sdsrange(c->pending_querybuf,applied,-1);
}
}
}
processInputBuffer主要是将输入缓冲区中的数据解析成对应的命令,根据命令类型是 PROTO_REQ_MULTIBULK 还是 PROTO_REQ_INLINE,来分别调用 processInlineBuffer 和 processMultibulkBuffer 方法来解析命令。
然后调用 processCommand 方法来执行命令,redis中有一个类似map的东西,会记录每条命令对应的handler,根据解析出来的命令执行对应的handler即可。
命令回复处理器
自我介绍一下,小编13年上海交大毕业,曾经在小公司待过,也去过华为、OPPO等大厂,18年进入阿里一直到现在。
深知大多数Java工程师,想要提升技能,往往是自己摸索成长或者是报班学习,但对于培训机构动则几千的学费,着实压力不小。自己不成体系的自学效果低效又漫长,而且极易碰到天花板技术停滞不前!
因此收集整理了一份《2024年Java开发全套学习资料》,初衷也很简单,就是希望能够帮助到想自学提升又不知道该从何学起的朋友,同时减轻大家的负担。

既有适合小白学习的零基础资料,也有适合3年以上经验的小伙伴深入学习提升的进阶课程,基本涵盖了95%以上Java开发知识点,真正体系化!
由于文件比较大,这里只是将部分目录截图出来,每个节点里面都包含大厂面经、学习笔记、源码讲义、实战项目、讲解视频,并且会持续更新!
如果你觉得这些内容对你有帮助,可以扫码获取!!(备注Java获取)

写在最后
还有一份JAVA核心知识点整理(PDF):JVM,JAVA集合,JAVA多线程并发,JAVA基础,Spring原理,微服务,Netty与RPC,网络,日志,Zookeeper,Kafka,RabbitMQ,Hbase,MongoDB,Cassandra,设计模式,负载均衡,数据库,一致性哈希,JAVA算法,数据结构,加密算法,分布式缓存,Hadoop,Spark,Storm,YARN,机器学习,云计算…

《互联网大厂面试真题解析、进阶开发核心学习笔记、全套讲解视频、实战项目源码讲义》点击传送门即可获取!
bitMQ,Hbase,MongoDB,Cassandra,设计模式,负载均衡,数据库,一致性哈希,JAVA算法,数据结构,加密算法,分布式缓存,Hadoop,Spark,Storm,YARN,机器学习,云计算…
[外链图片转存中…(img-OIQLpet0-1713428165866)]
《互联网大厂面试真题解析、进阶开发核心学习笔记、全套讲解视频、实战项目源码讲义》点击传送门即可获取!






















 519
519

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








