既有适合小白学习的零基础资料,也有适合3年以上经验的小伙伴深入学习提升的进阶课程,涵盖了95%以上大数据知识点,真正体系化!
由于文件比较多,这里只是将部分目录截图出来,全套包含大厂面经、学习笔记、源码讲义、实战项目、大纲路线、讲解视频,并且后续会持续更新
{
assert(ps);
assert(!StackEmpty(ps)); //这里判断是否为空栈如果为空栈就不能在进行出栈了
–ps->top; //只需要让top减一个就行了
}
#### 1.2.7栈顶的元素查看:
STDataType StackTop(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
assert(!StackEmpty(ps));
return ps->a[ps->top - 1]; //因为进行push后top++了一下,所以栈顶需要top-1
}
#### 1.2.7栈的元素个数:
int StackSize(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
return ps->top;
}
**栈还是比较容易实现的,如果熟练掌握顺序表我相信大家还是很容易就能把栈写出来。**
### **1.3栈实现的全部代码:**
#### 1.3.1 .c
#include “Stack.hpp”
void StackInit(STps)
{
assert(ps);
ps->a=NULL;
ps->top=ps->capicity=0;
}
void StackDestroy(STps)
{
assert(ps);
free(ps);
ps=NULL;
ps->top=0;
ps->capicity=0;
}
void StackPush(ST*ps,STDataType x)
{
assert(ps);
if(ps->top==ps->capicity)
{
int newcapicity=ps->capicity==0?4:(ps->capicity)*2;
STDataType* ptr = (STDataType*)realloc(ps->a, newcapicity*sizeof(STDataType));
if(ptr==NULL)
{
perror("StackPush");
exit(-1);
}
ps->a=ptr;
ps->capicity=newcapicity;
}
ps->a[ps->top]=x;
++ps->top;
}
bool StackEmpty(STps)
{
assert(ps);
return ps->top==0;
}
void StackPop(STps)
{
assert(ps);
assert(!StackEmpty(ps));
–ps->top;
}
STDataType StackTop(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
assert(!StackEmpty(ps));
return ps->a[ps->top - 1];
}
int StackSize(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
return ps->top;
}
#### 1.3.2 .h
#ifndef Stack_hpp
#define Stack_hpp
#include <stdio.h>
#include<assert.h>
#include<stdbool.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
typedef int STDataType;
typedef struct Stack{
STDataType* a;
STDataType top;
STDataType capicity;
}ST;
void StackInit(STps);
void StackDestroy(STps);
void StackPush(STps,STDataType x);
void StackPop(STps);
bool StackEmpty(STps);
STDataType StackTop(ST ps);
int StackSize(ST* ps);
#endif /* Stack_hpp */
#### **1.3.3 test**
**测试我这里是随便测试了一下,大家可以自己进行不同的测试就行不必和我一样**
#include “Stack.hpp”
void TestStack()
{
ST st;
StackInit(&st);
StackPush(&st, 1);
StackPush(&st, 2);
StackPush(&st, 3);
printf("%d “, StackTop(&st));
printf(”%d “,StackSize(&st));
StackPop(&st);
//printf(”%d ", StackTop(&st));
StackPop(&st);
StackPush(&st, 4);
StackPush(&st, 5);
while (!StackEmpty(&st))
{
printf("%d ", StackTop(&st));
StackPop(&st);
}
printf("\n");
}
int main()
{
TestStack();
return 0;
}
## 二、数据结构队列:
### 2.1数列的概念和结构:
队列:只允许在一端进行插入数据操作,在另一端进行删除数据操作的特殊线性表,队列具有先进先出 FIFO(First In First Out) 入队列:进行插入操作的一端称为**队尾** 出队列:进行删除操作的一端称为**队头。** **队列和栈的区别就是先进的后出,就和排队买东西一样,先排队的先买,说白了就是先到先得。**
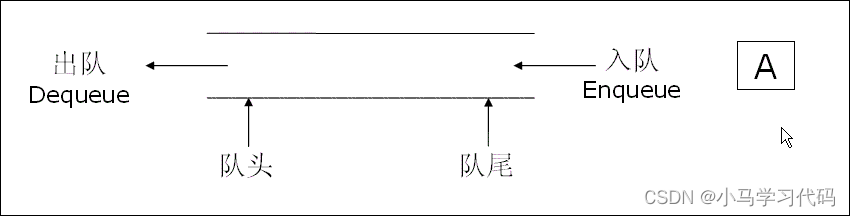
### 2.2队列的实现:
**队列要用到头删,因为第一个进入的要第一个删除,这样用数组就不太合适,因为数组的头删是0(n),时间复杂度比较大,这里我们用链表就是比较合适的选择。**
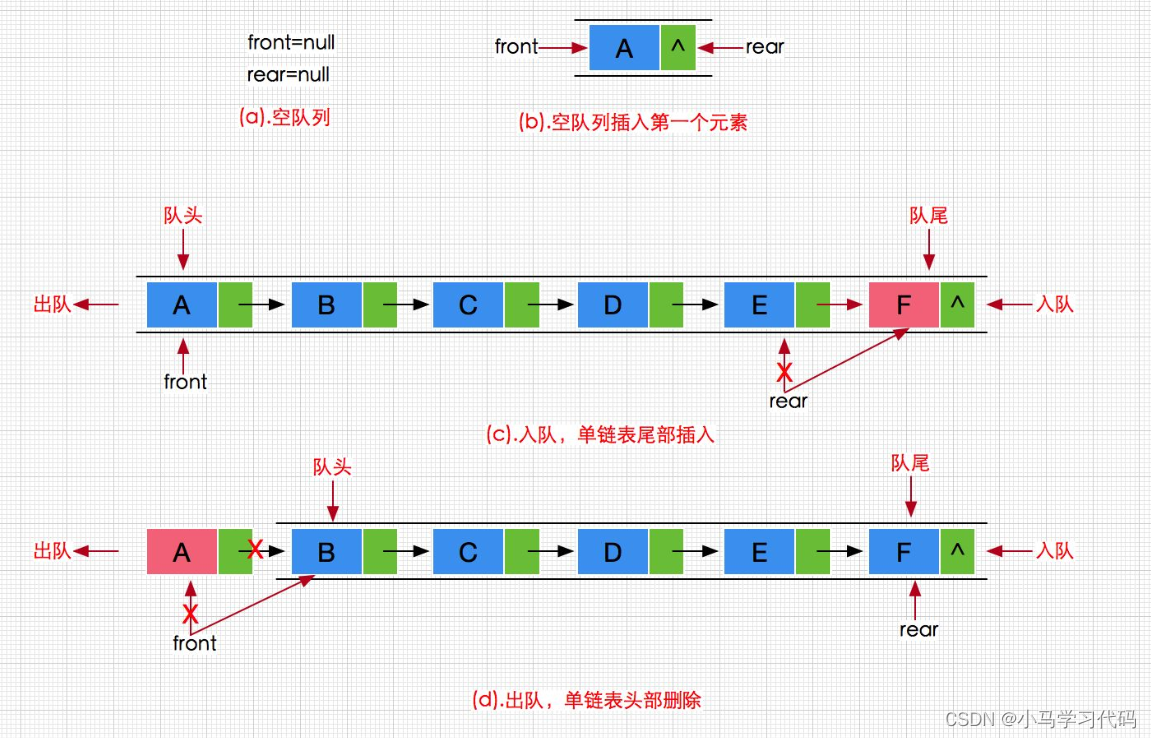
#### 2.2.1队列的定义:
typedef int QDataType;
typedef struct QueueNode
{
struct QueueNodenext;
QDataType data;
}QNode;
typedef struct Queue
{
QNode head; //队列要有一个头
QNode* rear; //队列要有一个尾
int size;
}Queue;
#### 2.2.2队列的初始化:
void QueueInit(Queue*pq)
{
assert(pq); //断言防止传入空指针
pq->head=NULL;
pq->rear=NULL;
pq->size=0;
}
#### 2.2.3队列的销毁:
void QueueDestroy(Queue*pq)
{
assert(pq);
QNode *cur=pq->head; //定一个节点进行遍历一个个销毁
while(cur)
{
QNode *del=cur;
free(cur);
cur=del->next;
}
pq->head=NULL;
pq->rear=NULL;
}
#### 2.2.4队列判断是否为空:
bool QueueEmpty(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
return pq->head == NULL && pq->rear == NULL;
}
#### 2.2.5队列插入(push):
void QueuePush(Queue* pq, QDataType x)
{
assert(pq);
QNodenewnode=(QNode)malloc(sizeof(QNode)); //插入前先创建一个节点
if(newnodeNULL) //这是判断是否申请成功
{
perror(“newnode”);
exit(-1);
}
else
{
newnode->data=x;
newnode->next=NULL;
}
if(pq->rearNULL) //两种情况这是尾节点位空的时候
{
pq->rear=pq->head=newnode;
}
else //这是尾节点不为空的时候
{
pq->rear->next=newnode;
pq->rear=newnode;
}
pq->size++;
}
#### 2.2.6队列出队(Pop):
void QueuePop(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
assert(!QueueEmpty(pq)); //判断队列是否为空
if(pq->head->next==NULL) //如果只有一个头节点情况
{
free(pq->head);
pq->head=pq->rear=NULL;
}
else //不止只有头节点的情况
{
QNode* del;
del=pq->head;
pq->head=pq->head->next;
free(del);
del=NULL;
}
pq->size–;
}
#### 2.2.7队头元素:
QDataType QueueFront(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
assert(!QueueEmpty(pq));
return pq->head->data;
}
#### 2.2.8队尾元素:
QDataType QueueBack(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
assert(!QueueEmpty(pq));
return pq->rear->data;
}
#### 2.2.9队的人员个数:
int QueueSize(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
return pq->size;
}
### **2.3队列实现的全部代码:**
#### 2.3.1 .c
#include"Queue.h"
void QueueInit(Queuepq)
{
assert(pq);
pq->head=NULL;
pq->rear=NULL;
pq->size=0;
}
void QueueDestroy(Queuepq)
{
assert(pq);
QNode *cur=pq->head;
while(cur)
{
QNode *del=cur;
free(cur);
cur=del->next;
}
pq->head=NULL;
pq->rear=NULL;
}
void QueuePush(Queue* pq, QDataType x)
{
assert(pq);
QNodenewnode=(QNode)malloc(sizeof(QNode));
if(newnodeNULL)
{
perror(“newnode”);
exit(-1);
}
else
{
newnode->data=x;
newnode->next=NULL;
}
if(pq->rearNULL)
{
pq->rear=pq->head=newnode;
}
else
{
pq->rear->next=newnode;
pq->rear=newnode;
}
pq->size++;
}
void QueuePop(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
assert(!QueueEmpty(pq));
if(pq->head->next==NULL)
{
free(pq->head);
pq->head=pq->rear=NULL;
}
else{
QNode* del;
del=pq->head;
pq->head=pq->head->next;
free(del);
del=NULL;
}
pq->size–;
}
bool QueueEmpty(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
return pq->head == NULL && pq->rear == NULL;
}
QDataType QueueFront(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
assert(!QueueEmpty(pq));
return pq->head->data;
}
QDataType QueueBack(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
assert(!QueueEmpty(pq));
return pq->rear->data;
}
int QueueSize(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
return pq->size;
}
#### 2.3.2 .h
#ifndef Queue_h
#define Queue_h
#include <stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<stdbool.h>
#include<assert.h>
typedef int QDataType;
typedef struct QueueNode
{
struct QueueNode*next;
QDataType data;
网上学习资料一大堆,但如果学到的知识不成体系,遇到问题时只是浅尝辄止,不再深入研究,那么很难做到真正的技术提升。
一个人可以走的很快,但一群人才能走的更远!不论你是正从事IT行业的老鸟或是对IT行业感兴趣的新人,都欢迎加入我们的的圈子(技术交流、学习资源、职场吐槽、大厂内推、面试辅导),让我们一起学习成长!
ude <stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<stdbool.h>
#include<assert.h>
typedef int QDataType;
typedef struct QueueNode
{
struct QueueNode*next;
QDataType data;
[外链图片转存中…(img-Zkgml6gm-1714915774649)]
[外链图片转存中…(img-c4PjvxO2-1714915774649)]
网上学习资料一大堆,但如果学到的知识不成体系,遇到问题时只是浅尝辄止,不再深入研究,那么很难做到真正的技术提升。
一个人可以走的很快,但一群人才能走的更远!不论你是正从事IT行业的老鸟或是对IT行业感兴趣的新人,都欢迎加入我们的的圈子(技术交流、学习资源、职场吐槽、大厂内推、面试辅导),让我们一起学习成长!






















 746
746











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








