处理图像的步骤:
-
读取图像
-
用指定的大小去resize图像。
-
将图像转为数组
-
图像归一化
-
使用np_utils.to_categorical方法将标签转为onehot编码
具体做法详见代码:
def loadImageData():
imageList = []
listClasses = os.listdir(datapath)# 类别文件夹
print(listClasses)
for class_name in listClasses:
label_id = dicClass[class_name]
class_path=os.path.join(datapath,class_name)
image_names=os.listdir(class_path)
for image_name in image_names:
image_full_path = os.path.join(class_path, image_name)
labelList.append(label_id)
image = cv2.imdecode(np.fromfile(image_full_path, dtype=np.uint8), -1)
image = cv2.resize(image, (norm_size, norm_size), interpolation=cv2.INTER_LANCZOS4)
if image.shape[2] >3:
image=image[:,:,:3]
print(image.shape)
image = img_to_array(image)
imageList.append(image)
imageList = np.array(imageList) / 255.0
return imageList
print(“开始加载数据”)
imageArr = loadImageData()
print(type(imageArr))
labelList = np.array(labelList)
print(“加载数据完成”)
print(labelList)
labelList = np_utils.to_categorical(labelList, classnum)
print(labelList)
做好数据之后,我们需要切分训练集和测试集,一般按照4:1或者7:3的比例来切分。切分数据集使用train_test_split()方法,需要导入from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split 包。例:
trainX, valX, trainY, valY = train_test_split(imageArr, labelList, test_size=0.2, random_state=42)
ImageDataGenerator()是keras.preprocessing.image模块中的图片生成器,同时也可以在batch中对数据进行增强,扩充数据集大小,增强模型的泛化能力。比如进行旋转,变形,归一化等等。
keras.preprocessing.image.ImageDataGenerator(featurewise_center=False,samplewise_center
=False, featurewise_std_normalization=False, samplewise_std_normalization=False,zca_whitening=False,
zca_epsilon=1e-06, rotation_range=0.0, width_shift_range=0.0, height_shift_range=0.0,brightness_range=None, shear_range=0.0, zoom_range=0.0,channel_shift_range=0.0, fill_mode=‘nearest’, cval=0.0, horizontal_flip=False, vertical_flip=False, rescale=None, preprocessing_function=None,data_format=None,validation_split=0.0)
参数:
- featurewise_center: Boolean. 对输入的图片每个通道减去每个通道对应均值。
- samplewise_center: Boolan. 每张图片减去样本均值, 使得每个样本均值为0。
- featurewise_std_normalization(): Boolean()
- samplewise_std_normalization(): Boolean()
- zca_epsilon(): Default 12-6
- zca_whitening: Boolean. 去除样本之间的相关性
- rotation_range(): 旋转范围
- width_shift_range(): 水平平移范围
- height_shift_range(): 垂直平移范围
- shear_range(): float, 透视变换的范围
- zoom_range(): 缩放范围
- fill_mode: 填充模式, constant, nearest, reflect
- cval: fill_mode == 'constant’的时候填充值
- horizontal_flip(): 水平反转
- vertical_flip(): 垂直翻转
- preprocessing_function(): user提供的处理函数
- data_format(): channels_first或者channels_last
- validation_split(): 多少数据用于验证集
本例使用的图像增强代码如下:
from tensorflow.keras.preprocessing.image import ImageDataGenerator
train_datagen = ImageDataGenerator(
rotation_range=20,
width_shift_range=0.2,
height_shift_range=0.2,
horizontal_flip=True)
val_datagen = ImageDataGenerator() # 验证集不做图片增强
training_generator_mix = MixupGenerator(trainX, trainY, batch_size=batch_size, alpha=0.2, datagen=train_datagen)()
val_generator = val_datagen.flow(valX, valY, batch_size=batch_size, shuffle=True)
注意:只在训练集上做增强,不在验证集上做增强。
ModelCheckpoint:用来保存成绩最好的模型。
语法如下:
keras.callbacks.ModelCheckpoint(filepath, monitor=‘val_loss’, verbose=0, save_best_only=False, save_weights_only=False, mode=‘auto’, period=1)
该回调函数将在每个epoch后保存模型到filepath
filepath可以是格式化的字符串,里面的占位符将会被epoch值和传入on_epoch_end的logs关键字所填入
例如,filepath若为weights.{epoch:02d-{val_loss:.2f}}.hdf5,则会生成对应epoch和验证集loss的多个文件。
参数
- filename:字符串,保存模型的路径
- monitor:需要监视的值
- verbose:信息展示模式,0或1
- save_best_only:当设置为True时,将只保存在验证集上性能最好的模型
- mode:‘auto’,‘min’,‘max’之一,在save_best_only=True时决定性能最佳模型的评判准则,例如,当监测值为val_acc时,模式应为max,当检测值为val_loss时,模式应为min。在auto模式下,评价准则由被监测值的名字自动推断。
- save_weights_only:若设置为True,则只保存模型权重,否则将保存整个模型(包括模型结构,配置信息等)
- period:CheckPoint之间的间隔的epoch数
ReduceLROnPlateau:当评价指标不在提升时,减少学习率,语法如下:
keras.callbacks.ReduceLROnPlateau(monitor=‘val_loss’, factor=0.1, patience=10, verbose=0, mode=‘auto’, epsilon=0.0001, cooldown=0, min_lr=0)
当学习停滞时,减少2倍或10倍的学习率常常能获得较好的效果。该回调函数检测指标的情况,如果在patience个epoch中看不到模型性能提升,则减少学习率
参数
- monitor:被监测的量
- factor:每次减少学习率的因子,学习率将以lr = lr*factor的形式被减少
- patience:当patience个epoch过去而模型性能不提升时,学习率减少的动作会被触发
- mode:‘auto’,‘min’,‘max’之一,在min模式下,如果检测值触发学习率减少。在max模式下,当检测值不再上升则触发学习率减少。
- epsilon:阈值,用来确定是否进入检测值的“平原区”
- cooldown:学习率减少后,会经过cooldown个epoch才重新进行正常操作
- min_lr:学习率的下限
本例代码如下:
checkpointer = ModelCheckpoint(filepath=‘best_model.hdf5’,
monitor=‘val_accuracy’, verbose=1, save_best_only=True, mode=‘max’)
reduce = ReduceLROnPlateau(monitor=‘val_accuracy’, patience=10,
verbose=1,
factor=0.5,
min_lr=1e-6)
model = Sequential()
model.add(MobileNetV2(include_top=False, pooling=‘avg’, weights=‘imagenet’))
model.add(Dense(classnum, activation=‘softmax’))
model.summary()
optimizer = Adam(learning_rate=INIT_LR)
model.compile(optimizer=optimizer, loss=‘categorical_crossentropy’, metrics=[‘accuracy’])
history = model.fit(training_generator_mix,
steps_per_epoch=trainX.shape[0] / batch_size,
validation_data=val_generator,
epochs=EPOCHS,
validation_steps=valX.shape[0] / batch_size,
callbacks=[checkpointer, reduce])
model.save(‘my_model.h5’)
print(history)
运行结果:
随着训练次数的增加,准确率已经过达到了0.95。

loss_trend_graph_path = r"WW_loss.jpg"
acc_trend_graph_path = r"WW_acc.jpg"
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
print(“Now,we start drawing the loss and acc trends graph…”)
summarize history for accuracy
fig = plt.figure(1)
plt.plot(history.history[“accuracy”])
plt.plot(history.history[“val_accuracy”])
plt.title(“Model accuracy”)
plt.ylabel(“accuracy”)
plt.xlabel(“epoch”)
plt.legend([“train”, “test”], loc=“upper left”)
plt.savefig(acc_trend_graph_path)
plt.close(1)
summarize history for loss
fig = plt.figure(2)
plt.plot(history.history[“loss”])
plt.plot(history.history[“val_loss”])
plt.title(“Model loss”)
plt.ylabel(“loss”)
plt.xlabel(“epoch”)
plt.legend([“train”, “test”], loc=“upper left”)
plt.savefig(loss_trend_graph_path)
plt.close(2)
print(“We are done, everything seems OK…”)
#windows系统设置10关机
#os.system(“shutdown -s -t 10”)
结果:


===============================================================
1、导入依赖
import cv2
import numpy as np
from tensorflow.keras.preprocessing.image import img_to_array
from tensorflow.keras.models import load_model
import time
2、设置全局参数
这里注意,字典的顺序和训练时的顺序保持一致
norm_size=224
imagelist=[]
emotion_labels = {
0: ‘Black-grass’,
1: ‘Charlock’,
2: ‘Cleavers’,
3: ‘Common Chickweed’,
4: ‘Common wheat’,
5: ‘Fat Hen’,
6: ‘Loose Silky-bent’,
7: ‘Maize’,
8: ‘Scentless Mayweed’,
9: ‘Shepherds Purse’,
10: ‘Small-flowered Cranesbill’,
11: ‘Sugar beet’,
}
3、加载模型
emotion_classifier=load_model(“best_model.hdf5”)
t1=time.time()
4、处理图片
处理图片的逻辑和训练集也类似,步骤:
-
读取图片
-
将图片resize为norm_size×norm_size大小。
-
将图片转为数组。
-
放到imagelist中。
-
imagelist整体除以255,把数值缩放到0到1之间。
image = cv2.imdecode(np.fromfile(‘data/test/0a64e3e6c.png’, dtype=np.uint8), -1)
load the image, pre-process it, and store it in the data list
image = cv2.resize(image, (norm_size, norm_size), interpolation=cv2.INTER_LANCZOS4)
image = img_to_array(image)
imagelist.append(image)
imageList = np.array(imagelist, dtype=“float”) / 255.0
5、预测类别
预测类别,并获取最高类别的index。
out=emotion_classifier.predict(imageList)
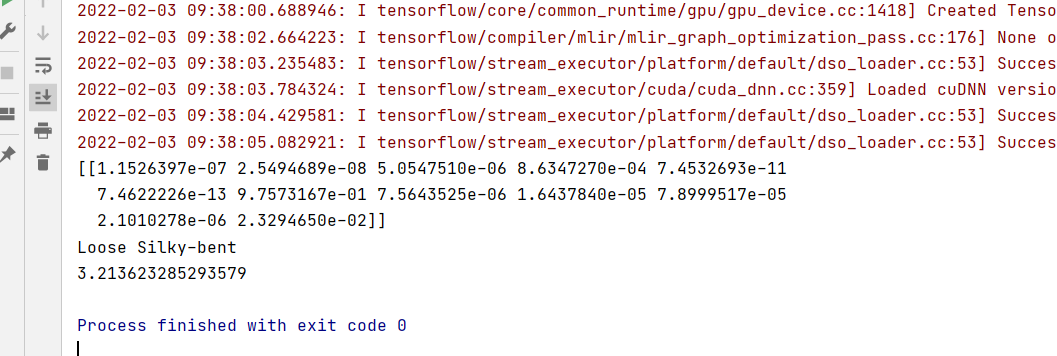
print(out)
pre=np.argmax(out)
emotion = emotion_labels[pre]
t2=time.time()
print(emotion)
t3=t2-t1
print(t3)
运行结果:
一、Python所有方向的学习路线
Python所有方向的技术点做的整理,形成各个领域的知识点汇总,它的用处就在于,你可以按照下面的知识点去找对应的学习资源,保证自己学得较为全面。
二、Python必备开发工具
工具都帮大家整理好了,安装就可直接上手!
三、最新Python学习笔记
当我学到一定基础,有自己的理解能力的时候,会去阅读一些前辈整理的书籍或者手写的笔记资料,这些笔记详细记载了他们对一些技术点的理解,这些理解是比较独到,可以学到不一样的思路。
四、Python视频合集
观看全面零基础学习视频,看视频学习是最快捷也是最有效果的方式,跟着视频中老师的思路,从基础到深入,还是很容易入门的。
五、实战案例
纸上得来终觉浅,要学会跟着视频一起敲,要动手实操,才能将自己的所学运用到实际当中去,这时候可以搞点实战案例来学习。
六、面试宝典
简历模板
网上学习资料一大堆,但如果学到的知识不成体系,遇到问题时只是浅尝辄止,不再深入研究,那么很难做到真正的技术提升。
一个人可以走的很快,但一群人才能走的更远!不论你是正从事IT行业的老鸟或是对IT行业感兴趣的新人,都欢迎加入我们的的圈子(技术交流、学习资源、职场吐槽、大厂内推、面试辅导),让我们一起学习成长!






















 2527
2527

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








