


既有适合小白学习的零基础资料,也有适合3年以上经验的小伙伴深入学习提升的进阶课程,涵盖了95%以上Go语言开发知识点,真正体系化!
由于文件比较多,这里只是将部分目录截图出来,全套包含大厂面经、学习笔记、源码讲义、实战项目、大纲路线、讲解视频,并且后续会持续更新
x5
array([0, 8, 5, 9, 2, 6, 2, 9, 4, 5, 1, 7])
**一维向量转行向量**
x7 = x5.reshape(1, x5.shape[0])
x7
array([[0, 8, 5, 9, 2, 6, 2, 9, 4, 5, 1, 7]])
x8 = x5[np.newaxis, :]
x8
array([[0, 8, 5, 9, 2, 6, 2, 9, 4, 5, 1, 7]])
**一维向量转列向量**
x7 = x5.reshape(x5.shape[0], 1)
x7
array([[0],
[8],
[5],
[9],
[2],
[6],
[2],
[9],
[4],
[5],
[1],
[7]])
x8 = x5[:, np.newaxis]
x8
array([[0],
[8],
[5],
[9],
[2],
[6],
[2],
[9],
[4],
[5],
[1],
[7]])
**多维向量转一维向量**
x6 = np.random.randint(0, 10, (3, 4))
x6
array([[3, 7, 6, 4],
[4, 5, 6, 3],
[7, 6, 2, 3]])
**flatten返回的是副本**
x9 = x6.flatten()
x9
array([3, 7, 6, 4, 4, 5, 6, 3, 7, 6, 2, 3])
x9[0]=0
x6
array([[3, 7, 6, 4],
[4, 5, 6, 3],
[7, 6, 2, 3]])
**ravel返回的是视图**
x10 = x6.ravel()
x10
array([3, 7, 6, 4, 4, 5, 6, 3, 7, 6, 2, 3])
x10[0]=0
x6
array([[0, 7, 6, 4],
[4, 5, 6, 3],
[7, 6, 2, 3]])
**reshape返回的是视图**
x11 = x6.reshape(-1)
x11
array([0, 7, 6, 4, 4, 5, 6, 3, 7, 6, 2, 3])
x11[0]=10
x6
array([[10, 7, 6, 4],
[ 4, 5, 6, 3],
[ 7, 6, 2, 3]])
#### 10.3.5 数组的拼接
x1 = np.array([[1, 2, 3],
[4, 5, 6]])
x2 = np.array([[7, 8, 9],
[0, 1, 2]])
**1、水平拼接——非视图**
* hstack()
* c\_
x3 = np.hstack([x1, x2])
x3
array([[1, 2, 3, 7, 8, 9],
[4, 5, 6, 0, 1, 2]])
x3[0][0] = 0
x1
array([[1, 2, 3],
[4, 5, 6]])
x4 = np.c_[x1, x2]
x4
array([[1, 2, 3, 7, 8, 9],
[4, 5, 6, 0, 1, 2]])
x4[0][0] = 0
x1
array([[1, 2, 3],
[4, 5, 6]])
**2、垂直拼接——非视图**
* vstack()
* r\_
x1 = np.array([[1, 2, 3],
[4, 5, 6]])
x2 = np.array([[7, 8, 9],
[0, 1, 2]])
x5 = np.vstack([x1, x2])
x5
array([[1, 2, 3],
[4, 5, 6],
[7, 8, 9],
[0, 1, 2]])
x6 = np.r_[x1, x2]
x6
array([[1, 2, 3],
[4, 5, 6],
[7, 8, 9],
[0, 1, 2]])
#### 10.3.6 数组的分裂
**1、split的用法**
x6 = np.arange(10)
x6
array([0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9])
x1, x2, x3 = np.split(x6, [2, 7]) #分裂点的位置,前向(从0开始)
print(x1, x2, x3)
[0 1] [2 3 4 5 6] [7 8 9]
**2、hsplit的用法**
x7 = np.arange(1, 26).reshape(5, 5)
x7
array([[ 1, 2, 3, 4, 5],
[ 6, 7, 8, 9, 10],
[11, 12, 13, 14, 15],
[16, 17, 18, 19, 20],
[21, 22, 23, 24, 25]])
left, middle, right = np.hsplit(x7, [2,4])
print(“left:\n”, left) # 第0~1列
print(“middle:\n”, middle) # 第2~3列
print(“right:\n”, right) # 第4列
left:
[[ 1 2]
[ 6 7]
[11 12]
[16 17]
[21 22]]
middle:
[[ 3 4]
[ 8 9]
[13 14]
[18 19]
[23 24]]
right:
[[ 5]
[10]
[15]
[20]
[25]]
**3、vsplit的用法**
x7 = np.arange(1, 26).reshape(5, 5)
x7
array([[ 1, 2, 3, 4, 5],
[ 6, 7, 8, 9, 10],
[11, 12, 13, 14, 15],
[16, 17, 18, 19, 20],
[21, 22, 23, 24, 25]])
upper, middle, lower = np.vsplit(x7, [2,4])
print(“upper:\n”, upper) # 第0~1行
print(“middle:\n”, middle) # 第2~3行
print(“lower:\n”, lower) # 第4行
upper:
[[ 1 2 3 4 5]
[ 6 7 8 9 10]]
middle:
[[11 12 13 14 15]
[16 17 18 19 20]]
lower:
[[21 22 23 24 25]]
### 10.4 Numpy四大运算
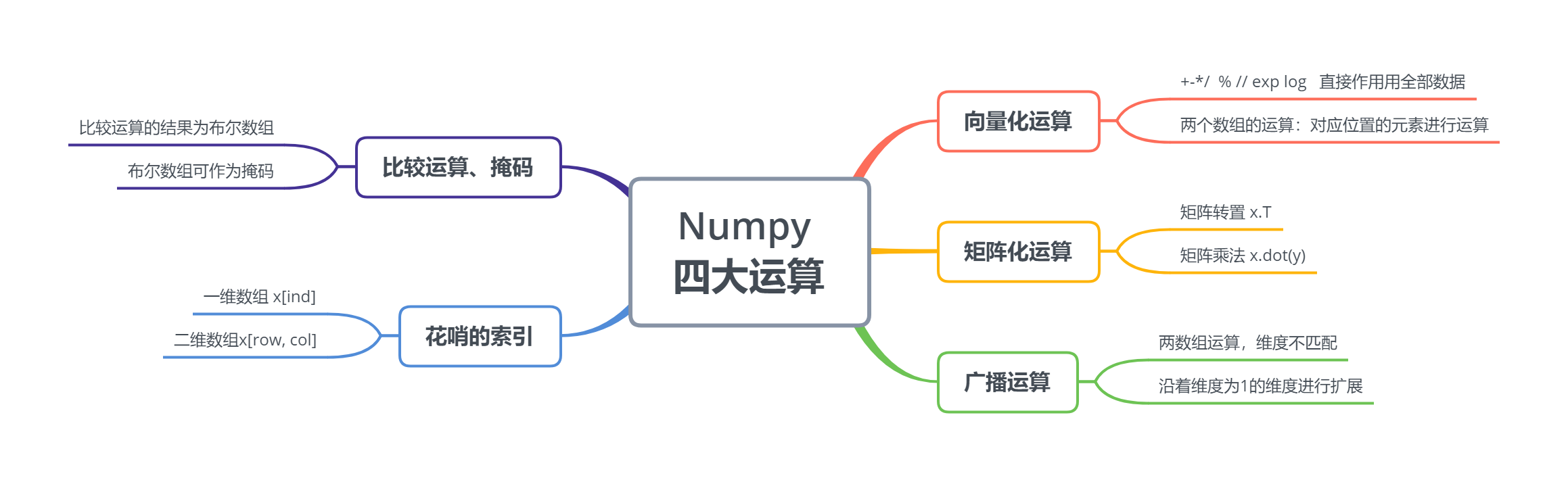
#### 10.4.1 向量化运算
**1、与数字的加减乘除等** 可见整体进行了向量化的运算
x1 = np.arange(1,6)
x1
array([1, 2, 3, 4, 5])
print(“x1+5”, x1+5)
print(“x1-5”, x1-5)
print(“x1*5”, x1*5)
print(“x1/5”, x1/5)
x1+5 [ 6 7 8 9 10]
x1-5 [-4 -3 -2 -1 0]
x1*5 [ 5 10 15 20 25]
x1/5 [0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1. ]
print(“-x1”, -x1)
print(“x1**2”, x1**2)
print(“x1//2”, x1//2)
print(“x1%2”, x1%2)
-x1 [-1 -2 -3 -4 -5]
x1**2 [ 1 4 9 16 25]
x1//2 [0 1 1 2 2]
x1%2 [1 0 1 0 1]
**2、绝对值、三角函数、指数、对数**
(1)绝对值
x2 = np.array([1, -1, 2, -2, 0])
x2
array([ 1, -1, 2, -2, 0])
abs(x2)
array([1, 1, 2, 2, 0])
np.abs(x2)
array([1, 1, 2, 2, 0])
(2)三角函数
theta = np.linspace(0, np.pi, 3)
theta
array([0. , 1.57079633, 3.14159265])
print(“sin(theta)”, np.sin(theta))
print(“con(theta)”, np.cos(theta))
print(“tan(theta)”, np.tan(theta))
sin(theta) [0.0000000e+00 1.0000000e+00 1.2246468e-16]
con(theta) [ 1.000000e+00 6.123234e-17 -1.000000e+00]
tan(theta) [ 0.00000000e+00 1.63312394e+16 -1.22464680e-16]
x = [1, 0 ,-1]
print(“arcsin(x)”, np.arcsin(x))
print(“arccon(x)”, np.arccos(x))
print(“arctan(x)”, np.arctan(x))
arcsin(x) [ 1.57079633 0. -1.57079633]
arccon(x) [0. 1.57079633 3.14159265]
arctan(x) [ 0.78539816 0. -0.78539816]
(3)指数运算
x = np.arange(3)
x
array([0, 1, 2])
np.exp(x)
array([1. , 2.71828183, 7.3890561 ])
(4)对数运算
x = np.array([1, 2, 4, 8 ,10])
print(“ln(x)”, np.log(x))
print(“log2(x)”, np.log2(x))
print(“log10(x)”, np.log10(x))
ln(x) [0. 0.69314718 1.38629436 2.07944154 2.30258509]
log2(x) [0. 1. 2. 3. 3.32192809]
log10(x) [0. 0.30103 0.60205999 0.90308999 1. ]
**3、两个数组的运算**
x1 = np.arange(1,6)
x1
array([1, 2, 3, 4, 5])
x2 = np.arange(6,11)
x2
array([ 6, 7, 8, 9, 10])
print(“x1+x2:”, x1+x2)
print(“x1-x2:”, x1-x2)
print(“x1*x2:”, x1*x2)
print(“x1/x2:”, x1/x2)
x1+x2: [ 7 9 11 13 15]
x1-x2: [-5 -5 -5 -5 -5]
x1*x2: [ 6 14 24 36 50]
x1/x2: [0.16666667 0.28571429 0.375 0.44444444 0.5 ]
#### 10.4.2 矩阵运算
x = np.arange(9).reshape(3, 3)
x
array([[0, 1, 2],
[3, 4, 5],
[6, 7, 8]])
* 矩阵的转置
y = x.T
y
array([[0, 3, 6],
[1, 4, 7],
[2, 5, 8]])
* 矩阵乘法
x = np.array([[1, 0],
[1, 1]])
y = np.array([[0, 1],
[1, 1]])
x.dot(y)
array([[0, 1],
[1, 2]])
np.dot(x, y)
array([[0, 1],
[1, 2]])
y.dot(x)
array([[1, 1],
[2, 1]])
np.dot(y, x)
array([[1, 1],
[2, 1]])
**注意跟x\*y的区别**,x\*y只是对应位置相乘
x*y
array([[0, 0],
[1, 1]])
#### 10.4.3 广播运算
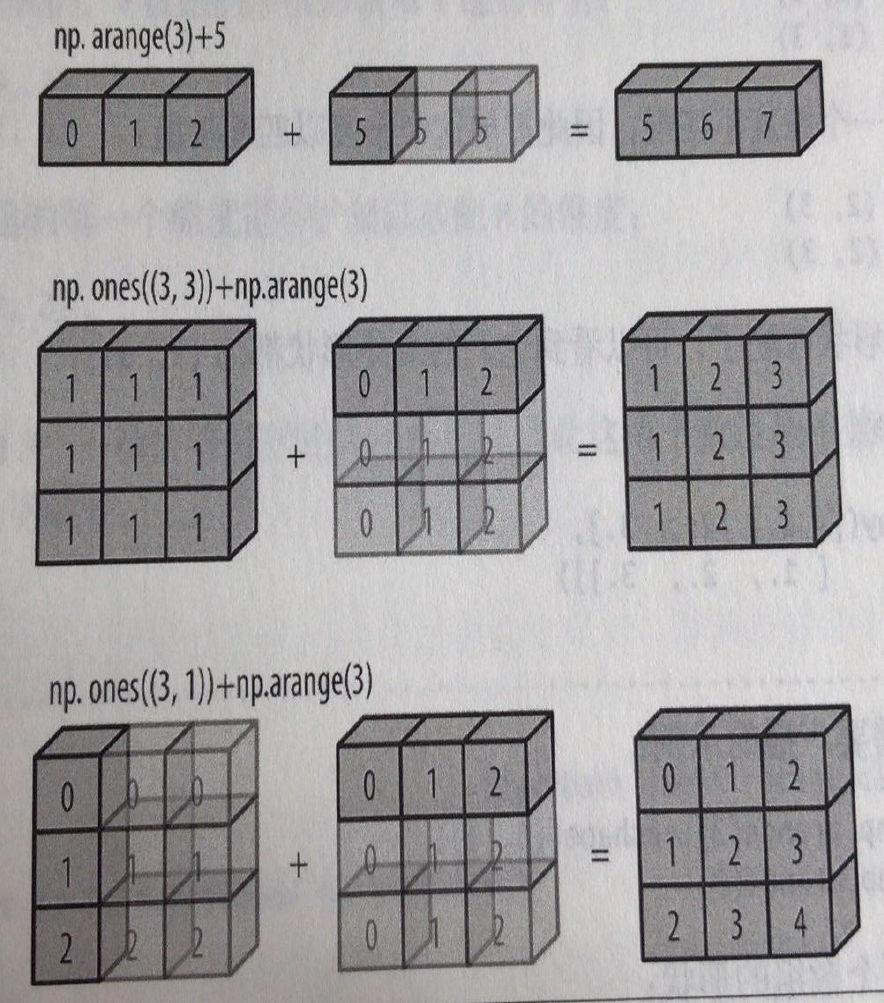
x = np.arange(3).reshape(1, 3)
x
array([[0, 1, 2]])
x+5
array([[5, 6, 7]])
**规则**
如果两个数组的形状在维度上不匹配
那么数组的形式会沿着维度为1的维度进行扩展以匹配另一个数组的形状。
x1 = np.ones((3,3))
x1
array([[1., 1., 1.],
[1., 1., 1.],
[1., 1., 1.]])
x2 = np.arange(3).reshape(1, 3)
x2
array([[0, 1, 2]])
x1+x2
array([[1., 2., 3.],
[1., 2., 3.],
[1., 2., 3.]])
x3 = np.logspace(1, 10, 10, base=2).reshape(2, 5)
x3
array([[ 2., 4., 8., 16., 32.],
[ 64., 128., 256., 512., 1024.]])
x4 = np.array([[1, 2, 4, 8, 16]])
x4
array([[ 1, 2, 4, 8, 16]])
x3/x4
array([[ 2., 2., 2., 2., 2.],
[64., 64., 64., 64., 64.]])
x5 = np.arange(3).reshape(3, 1)
x5
array([[0],
[1],
[2]])
x6 = np.arange(3).reshape(1, 3)
x6
array([[0, 1, 2]])
x5+x6
array([[0, 1, 2],
[1, 2, 3],
[2, 3, 4]])
#### 10.4.4 比较运算和掩码
**1、比较运算**
x1 = np.random.randint(100, size=(10,10))
x1
array([[37, 44, 58, 79, 1, 24, 85, 90, 27, 56],
[74, 68, 88, 27, 46, 34, 92, 1, 35, 45],
[84, 80, 83, 72, 98, 15, 4, 77, 14, 98],
[19, 85, 98, 32, 47, 50, 73, 3, 24, 2],
[ 5, 28, 26, 31, 48, 43, 72, 73, 53, 64],
[81, 87, 56, 59, 24, 42, 84, 34, 97, 65],
[74, 9, 41, 54, 78, 62, 53, 49, 8, 70],
[63, 44, 33, 35, 26, 83, 7, 14, 65, 84],
[57, 10, 62, 8, 74, 47, 90, 25, 78, 48],
[36, 31, 45, 39, 66, 82, 42, 25, 33, 84]])
x1 > 50
array([[False, False, True, True, False, False, True, True, False,
True],
[ True, True, True, False, False, False, True, False, False,
False],
[ True, True, True, True, True, False, False, True, False,
True],
[False, True, True, False, False, False, True, False, False,
False],
[False, False, False, False, False, False, True, True, True,
True],
[ True, True, True, True, False, False, True, False, True,
True],
[ True, False, False, True, True, True, True, False, False,
True],
[ True, False, False, False, False, True, False, False, True,
True],
[ True, False, True, False, True, False, True, False, True,
False],
[False, False, False, False, True, True, False, False, False,
True]])
**2、操作布尔数组**
x2 = np.random.randint(10, size=(3, 4))
x2
array([[1, 4, 2, 9],
[8, 8, 2, 4],
[9, 5, 3, 6]])
print(x2 > 5)
np.sum(x2 > 5)
[[False False False True]
[ True True False False]
[ True False False True]]
5
np.all(x2 > 0)
True
np.any(x2 == 6)
True
np.all(x2 < 9, axis=1) # 按行进行判断 axis = 1。而如果是按列判断,则axis= 0;
array([False, True, False])
x2
array([[1, 4, 2, 9],
[8, 8, 2, 4],
[9, 5, 3, 6]])
(x2 < 9) & (x2 >5)
array([[False, False, False, False],
[ True, True, False, False],
[False, False, False, True]])
np.sum((x2 < 9) & (x2 >5))
3
**3、将布尔数组作为掩码**
x2
array([[1, 4, 2, 9],
[8, 8, 2, 4],
[9, 5, 3, 6]])
x2 > 5
array([[False, False, False, True],
[ True, True, False, False],
[ True, False, False, True]])
x2[x2 > 5]
array([9, 8, 8, 9, 6])
作为掩码后,相应位置为True的就会被取出来,而相应位置为False的就会忽略
#### 10.4.5 花哨的索引
**1、一维数组**
x = np.random.randint(100, size=10)
x
array([43, 69, 67, 9, 11, 27, 55, 93, 23, 82])
**注意:结果的形状与索引数组ind一致**
ind = [2, 6, 9]
x[ind]
array([67, 55, 82])
ind = np.array([[1, 0],
[2, 3]])
x[ind]
array([[69, 43],
[67, 9]])
**2、多维数组**
x = np.arange(12).reshape(3, 4)
x
array([[ 0, 1, 2, 3],
[ 4, 5, 6, 7],
[ 8, 9, 10, 11]])
row = np.array([0, 1, 2])
col = np.array([1, 3, 0])
x[row, col] # x(0, 1) x(1, 3) x(2, 0)
array([1, 7, 8])
row[:, np.newaxis] # 列向量
array([[0],
[1],
[2]])
x[row[:, np.newaxis], col] # 广播机制
array([[ 1, 3, 0],
[ 5, 7, 4],
[ 9, 11, 8]])
### 10.5 其他Numpy通用函数
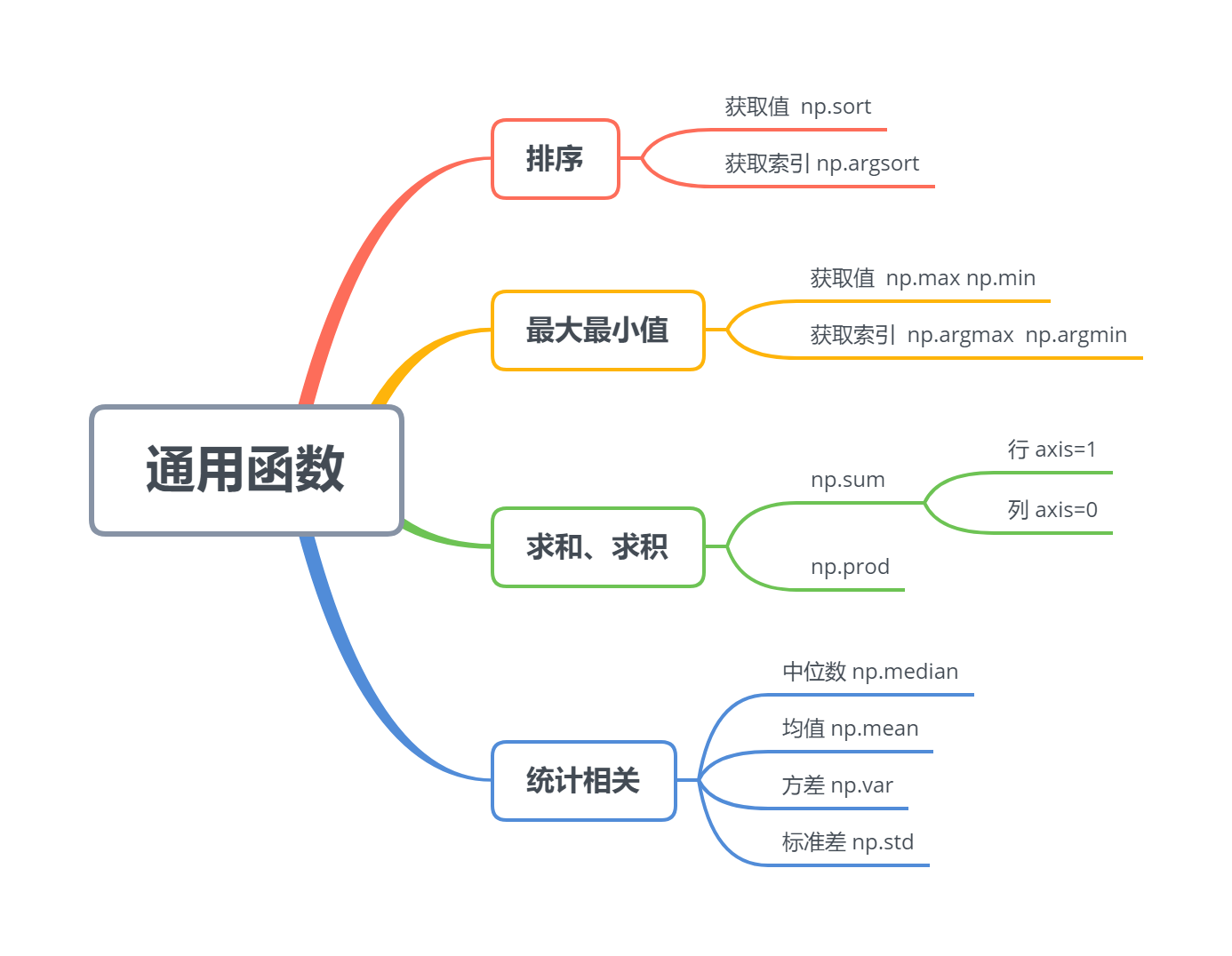
#### 10.5.1 数值排序
x = np.random.randint(20, 50, size=10)
x
array([48, 27, 44, 24, 34, 21, 24, 30, 34, 46])
* 产生新的排序数组
np.sort(x)
array([21, 24, 24, 27, 30, 34, 34, 44, 46, 48])
x
array([48, 27, 44, 24, 34, 21, 24, 30, 34, 46])
* 替换原数组
x.sort()
x
array([21, 24, 24, 27, 30, 34, 34, 44, 46, 48])
* 获得排序索引
x = np.random.randint(20, 50, size=10)
x
array([27, 36, 35, 28, 34, 20, 21, 49, 48, 30])
i = np.argsort(x)
i
array([5, 6, 0, 3, 9, 4, 2, 1, 8, 7], dtype=int64)
#### 10.5.2 最大最小值
x = np.random.randint(20, 50, size=10)
x
array([48, 31, 30, 44, 48, 33, 44, 48, 39, 35])
print(“max:”, np.max(x))
print(“min:”, np.min(x))
max: 48
min: 30
print(“max_index:”, np.argmax(x))
print(“min_index:”, np.argmin(x))
max_index: 0
min_index: 2
#### 10.5.3 数值求和、求积
x = np.arange(1,6)
x
array([1, 2, 3, 4, 5])
x.sum()
15
np.sum(x)
15
x1 = np.arange(6).reshape(2,3)
x1
array([[0, 1, 2],
[3, 4, 5]])
* 按行求和
np.sum(x1, axis=1)
array([ 3, 12])
* 按列求和
np.sum(x1, axis=0)
array([3, 5, 7])
* 全体求和
np.sum(x1)
15
* 求积
x
array([1, 2, 3, 4, 5])
x.prod()
120
np.prod(x)
120
#### 10.5.4 中位数、均值、方差、标准差
x = np.random.normal(0, 1, size=10000)
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
plt.hist(x, bins=50)
plt.show()

* 中位数
np.median(x)
-0.01024418366119727
* 均值
x.mean()
-0.004164442327293362
np.mean(x)
-0.004164442327293362
* 方差
x.var()
1.0221853234535774
np.var(x)



**既有适合小白学习的零基础资料,也有适合3年以上经验的小伙伴深入学习提升的进阶课程,涵盖了95%以上Go语言开发知识点,真正体系化!**
**由于文件比较多,这里只是将部分目录截图出来,全套包含大厂面经、学习笔记、源码讲义、实战项目、大纲路线、讲解视频,并且后续会持续更新**
**[如果你需要这些资料,可以戳这里获取](https://bbs.csdn.net/topics/618658159)**
max_index: 0
min_index: 2
10.5.3 数值求和、求积
x = np.arange(1,6)
x
array([1, 2, 3, 4, 5])
x.sum()
15
np.sum(x)
15
x1 = np.arange(6).reshape(2,3)
x1
array([[0, 1, 2],
[3, 4, 5]])
- 按行求和
np.sum(x1, axis=1)
array([ 3, 12])
- 按列求和
np.sum(x1, axis=0)
array([3, 5, 7])
- 全体求和
np.sum(x1)
15
- 求积
x
array([1, 2, 3, 4, 5])
x.prod()
120
np.prod(x)
120
10.5.4 中位数、均值、方差、标准差
x = np.random.normal(0, 1, size=10000)
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
plt.hist(x, bins=50)
plt.show()

- 中位数
np.median(x)
-0.01024418366119727
- 均值
x.mean()
-0.004164442327293362
np.mean(x)
-0.004164442327293362
- 方差
x.var()
1.0221853234535774
np.var(x)
[外链图片转存中…(img-4wDWc9jl-1715403812604)]
[外链图片转存中…(img-4Q9ke1j0-1715403812604)]
[外链图片转存中…(img-XfIFzqgx-1715403812604)]
既有适合小白学习的零基础资料,也有适合3年以上经验的小伙伴深入学习提升的进阶课程,涵盖了95%以上Go语言开发知识点,真正体系化!
由于文件比较多,这里只是将部分目录截图出来,全套包含大厂面经、学习笔记、源码讲义、实战项目、大纲路线、讲解视频,并且后续会持续更新






















 244
244

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








