创建多个线程
创建多个线程时,一般由主线程统一创建,并等待释放资源或者分离线程
,
不要递归创建
1.
多个线程如果任务相同,则可以使用同一个线程执行函数
2.
多个线程如果任务不同,则可以使用不同的线程执行函数
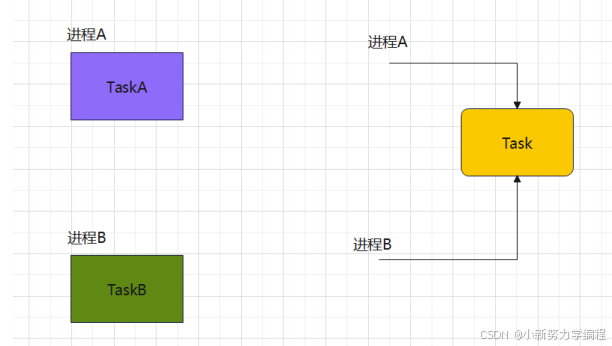
例代码:进程
A
和进程
B
执行相同的任务
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <unistd.h>
// 线程执行函数
void* do_thread_function(void* args)
{
for(int i=0;i<5;i++)
{
printf("i=%d\n",i+1);
sleep(1);
}
pthread_exit(NULL);
}
int main()
{
pthread_t threadids[2]={0};
int result;
for(int i=0;i<2;i++)
{
result =pthread_create(threadids+i,NULL,do_thread_function,NULL);
if(result!=0)
{
fprintf(stderr,"pthreaderror:%s\n",strerror(result));
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
printf("threadA id is %ld\n",*(threadids+i));
}
pthread_join(threadids[0],NULL);
pthread_join(threadids[1],NULL);
return 0;
}
例代码:进程
A
和进程
B
执行不同的任务
#include <unistd.h>
// 线程执行函数
void* do_thread_funA(void* args)
{
printf("do thread A\n");
pthread_exit(NULL);
}
void* do_thread_funB(void* args)
{
printf("do thread b\n");
pthread_exit(NULL);
}
int main()
{
pthread_t thread_id_a,thread_id_b;
int result = pthread_create(&thread_id_a,NULL,do_thread_funA,NULL);
if(result!=0)
{
fprintf(stderr,"pthread error:%s\n",strerror(result));
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
printf("threadA id is %ld\n",thread_id_a);
pthread_detach(thread_id_a);
result = pthread_create(&thread_id_b,NULL,do_thread_funB,NULL);
if(result!=0)
{
fprintf(stderr,"pthread error:%s\n",strerror(result));
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
printf("threadB id is %ld\n",thread_id_b);
pthread_detach(thread_id_b);
while(1);
return 0;
}线程间通信
为什么需要线程通信?
线程是操作系统调度的最小单元,有自己的栈空间,可以按照既定的代码逐步的执行,但是如果每个线
程间都孤立的运行,那就会造资源浪费。所以在现实中,我们需要这些线程间可以按照指定的规则共同
完成一件任务,所以这些线程之间就需要互相协调,这个过程被称为线程的通信。
线程通信就是当多个线程共同操作共享的资源时,互相告知自己的状态以避免资源争夺。
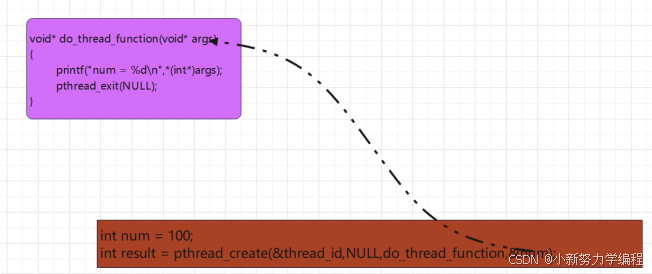
一、主线程向子线程传递参数
通过
pthread_create
函数的第
4
个参数
arg
进行传递

#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <pthread.h>
// 线程执行函数
void* do_thread_function(void* args)
{
printf("num = %d\n",*(int*)args);
pthread_exit(NULL);
}
int main()
{
pthread_t thread_id;
int num = 100;
int result =pthread_create(&thread_id,NULL,do_thread_function,&num);
if(result!=0)
{
fprintf(stderr,"pthread error:%s\n",strerror(result));
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
printf("thread id is %ld\n",thread_id);
pthread_join(thread_id,NULL);
return 0;
}
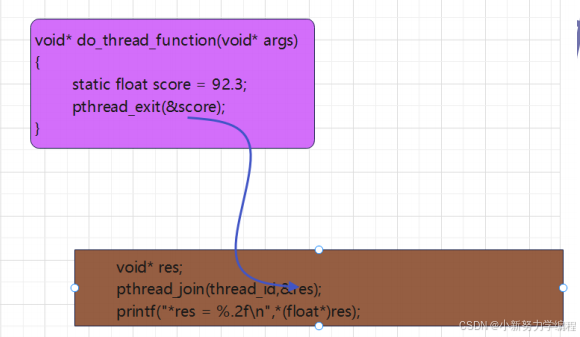
三、子线程给主线程传递参数
子线程给主线程传参的方式如下
:
在子线程将需要返回的值存储在
pthread_exit
函数中的
retval
参数中
在主线程中通过
pthread_join
函数的第
2
个参数
retval
得到返回
,
pthread_join
函数会将线程的
返回值
(
指针
)
保存到
retval
中

#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <pthread.h>
// 线程执行函数
void* do_thread_function(void* args)
{
static float score = 92.3;
pthread_exit(&score);
}
int main()
{
pthread_t thread_id;
int result =pthread_create(&thread_id,NULL,do_thread_function,NULL);
if(result!=0)
{
fprintf(stderr,"pthread error:%s\n",strerror(result));
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
printf("thread id is %ld\n",thread_id);
void* res = NULL;
pthread_join(thread_id,&res);
printf("*res = %.2f\n",*(float*)res);
return 0;
}





















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








