所有引用基类的地方必须能透明的使用其子类对象
7.单一职责原则
不要存在多余一个导致类变更的原因,即一个类只负责一个职责
9.异常处理
try {
//平级关系无所谓,非平级,如果是大小关系,只写一个大的就好,直接写一个Exception e偶尔也是可以的
} catch (ArithmeticException | NullPointerException e) {
}
try{
}cache(Exception e){//偶尔可以简单这样处理
}
try{
}cache(AException | BException b ){//AB平级时都适用,不是平级,只写一个大的就好了
}
受检异常:extends exception 编译期必须要用try catch包含代码
非受检异常:extends runtimeException
自定义异常:
package com.test.testjva.error;
public class MyException extends Exception{
private String message;
public MyException(String message){
super();
this.message = message;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return message;
}
}
package com.test.testjva.error;
public class UserRequest {
public static boolean login(String admin,String ps) throws MyException{
if(!admin.equals("admin")) {
throw new MyException("用户名错误");
}
if(!ps.equals("111")) {
throw new MyException("密码错误");
}
return true;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
login("1", "111");
} catch (MyException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
System.out.println("用户名或者密码错误");
}
}
}
调试:
f5:进入方法中
f6:进入下一行
f7:退出调试
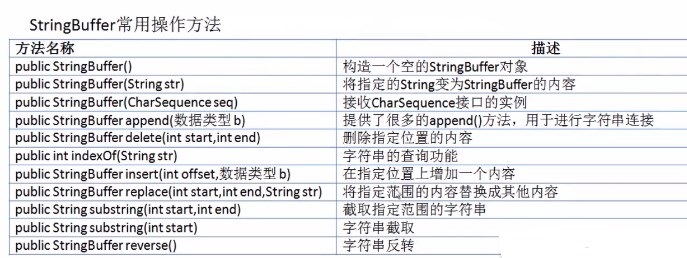
10.StringBuffer
不要用“+”进行字符串连接,很消耗内存,建议使用StringBuffer
package com.test.testjva.StringBuffer;//同步
public class StringBufferDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//这种写法效率非常低
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
System.out.println(“nihao”+i);
}
//StringBuffer,比上面节省内存,2倍+2 = 新的容量扩充
StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer(26);//可以给他一个容量,避免它扩充
for (int i = 0; i < 17; i++) {
sb.append(i);
}
System.out.println(sb);
System.out.println(sb.length());
System.out.println(sb.capacity());
}
}
StringBuffer 同步:我在用,你就得等(比如公司用微波炉);效率慢,安全
StringBuilder 不同步:并行一起用;效率高,不安全
11.程序国际化
package com.test.testjva.StringBuffer.Local;
import java.text.MessageFormat;
import java.util.Locale;
import java.util.ResourceBundle;
import java.util.Scanner;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
public class LocaleDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
Locale locale = Locale.CHINA;
Locale locale2 = new Locale("en", "US");
ResourceBundle rb = ResourceBundle.getBundle("com.test.testjva.StringBuffer.Local.info",locale2);
System.out.println(rb.getString("input.username"));
String username = input.next();
System.out.println(rb.getString("input.password"));
String ps = input.next();
if(username.equals("1") && ps.equals("1")){
String info= MessageFormat.format(rb.getString("info"), username);
System.out.println(info);
}
}
}
创建文件info_en_US.properties
input.username=input username
input.password=input.password
info= {0}login success
创建文件info_zh_CN.properties
input.username=请输入用户名
input.username=请输入密码
info=登录成功
12.Math,Random,Arrays工具类
四舍五入:
Math.round(3.22222*100)/100.00
二分查找法(又称:折半查找),必须保证数组是排序的算法
优点:
又称折半查找,优点是比较次数少,查找速度快,平均性能好;缺点:
要求待查表为有序表,且插入删除困难,因此折半查找适用于不经常变动而查找频繁的有序列表
package com.test.testjva.utils;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Iterator;
public class Utils {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int [] a = {11,22,3,4,4,};
int[] b = Arrays.copyOf(a, 10);
Arrays.sort(a);
int index=Arrays.binarySearch(a, 22);//必须要求数组是有序的,高效查找
System.out.println("inxex=="+index);
for (int i: a) {
System.out.println(i);
}
}
}
//实现:
package com.test.testjva.utils;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class BanrySearchDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int nums[] = {22,444,44,645,77765,78,2};
Arrays.sort(nums);//先排序
int index = binarySearch(nums, 78);
System.out.println("index=="+index);
}
//二分查找算法
// 查找速度快,要求必须要排序
public static int binarySearch(int [] nums,int key){
int star = 0;
int end = nums.length - 1;
int mid = -1;
while(star<=end) {
mid = (star+end)/2;
if(nums[mid] == key) {
return mid;
} else if(nums[mid] < key) {
star = mid+1;
} else if(nums[mid] > key){
end = mid -1;
}
}
return -1;
}
}
13.日期操作类
package com.test.testjva.utils;
import java.text.DateFormat;
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util.Calendar;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.GregorianCalendar;
public class DateUtils {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Calendar cr = Calendar.getInstance();
Calendar cr2 = new GregorianCalendar();
int year = cr.get(Calendar.YEAR);
int month = cr.get(Calendar.MONTH);
int day = cr.get(Calendar.DAY_OF_MONTH);
int dayw = cr.get(Calendar.DAY_OF_WEEK);
int dayh = cr.get(Calendar.HOUR_OF_DAY);
int dayhm = cr.get(Calendar.MINUTE);
int dayhs = cr.get(Calendar.MILLISECOND);
System.out.println("=="+year + month+day+"星期"+dayw+"shijian"+dayh+":"+dayhm+":"+dayhs);
DateFormat df= new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy年MM月dd HH:mm:ss SSS");
System.out.println(df.format(new Date()));
System.currentTimeMillis();//当前系统时间
}
}
14.对象比较器
package com.test.testjva.compare;
public class Cat implements Comparable<Cat> {
private String name;
private int age;
public Cat() {
}
public Cat(String name, int age) {
super();
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Cat [name=" + name + ", age=" + age + "]";
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
// 通过此方法对对象排序
public int compareTo(Cat o) {
if (age < o.age) {
return -1;
} else if (age > o.age) {
return 1;
}
return 0;
}
}
package com.test.testjva.compare;
public class Dog {
private String name;
private int age;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Dog [name=" + name + ", age=" + age + "]";
}
public Dog(String name, int age) {
super();
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
}
package com.test.testjva.compare;
import java.util.Comparator;
public class DogComparator implements Comparator<Dog>{
@Override
public int compare(Dog o1, Dog o2) {
if(o1.getAge() < o2.getAge()) {
return -1;
} else if(o1.getAge() > o2.getAge()) {
return 1;
}
return 0;
}
}
package com.test.testjva.compare;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class CompareDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Cat[] cats = {new Cat("tom", 1),
new Cat("mory", 2),
new Cat("jer", 5),};
Arrays.sort(cats);
for (Cat cat : cats) {
System.out.println(cat);
}
Dog[] dogs = {new Dog("tom", 1),
new Dog("mory", 2),
new Dog("jer", 5),};
Arrays.sort(dogs,new DogComparator());
for (Dog cat : dogs) {
System.out.println(cat);
}
}
}
15.对象克隆
package com.test.testjva.utils;
public class Dog implements Cloneable {//这个类具有克隆的功能了
private String name;
private int age;
public Dog(String name, int age) {
super();
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Dog [name=" + name + ", age=" + age + "]";
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
//重写object中的clone方法
@Override
protected Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException {
return super.clone();
}
}
package com.test.testjva.utils;
public class CloneDemo {
private static Dog dog1;
public static void main(String[] args) {
Dog dog = new Dog("sack", 2);
System.out.println("dog"+dog);
try {
dog1 = (Dog) dog.clone(); //用的非常少,在你突然要创建100个对象的情况,它比你new 100个dog的效率要高
System.out.println("dog1"+dog1);
} catch (CloneNotSupportedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
//方法1
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
dog = new Dog("sack", 2);
}
//方法2
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
try {
dog1 = (Dog) dog1.clone();
} catch (CloneNotSupportedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
//方法2比方法1效率高,
System.out.println(dog == dog1);
}
}
16.数据结构二叉树
package com.test.testjva.binaryTree;
public class BinaryTreeDemo {
private Node root;
public void addNode(int data) {
if (root == null) {
root = new Node(data);
} else {
root.add(data);
}
}
public void printNode() {
if(root != null) {
root.print();
}
}
class Node {
private int data;
private Node left;
private Node right;
//中序遍历,左根右
public void print(){
if(this.left != null) {
this.left.print();
}
System.out.print(this.data+"-->");
if(this.right != null) {
this.right.print();
}
}
public Node(int data) {
this.data = data;
}
public void add(int data) {
if (this.data > data) {
if (this.left == null) {
left = new Node(data);
} else {
left.add(data);
}
} else if (this.data <= data) {
if (this.right == null) {
this.right = new Node(data);
} else {
this.right.add(data);
}
}
}
}
}
package com.test.testjva.binaryTree;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
BinaryTreeDemo bd= new BinaryTreeDemo();
bd.addNode(8);
bd.addNode(3);
bd.addNode(10);
bd.addNode(1);
bd.addNode(6);
bd.addNode(14);
bd.addNode(4);
bd.addNode(7);
bd.addNode(13);
bd.printNode();
}
}
17.file(文件)使用
package com.test.testjva.IO;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.text.DateFormat;
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util.Date;
public class FileDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
findFile(new File("d:"+File.separator+"abc"), ".txt");
testFile();
}
//在java中文件夹也是file
public static void testFile(){
File file = new File("d:"+File.separator+"a.txt");//File.separator代表不同操作系统给的/
//如果不存在这个文件
if(!file.exists()) {
try {
boolean success = file.createNewFile();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
} else {
}
System.out.println(file.getAbsolutePath());
long lastTime = file.lastModified();
DateFormat df = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");
String lastTimes = df.format(new Date(lastTime));
long fileLength = file.length();
System.out.println(lastTimes);
System.out.println("文件长度"+fileLength);
System.out.println("文件长度"+file.isDirectory());//是否是目录、
File f2 = new File("d:"+File.separator+"abc");
if(!f2.exists()) {
f2.mkdir();
}
String fs[]= f2.list();
for (String string : fs) {
System.out.println("文件名称"+string);
}
File files[] = f2.listFiles();
for (File file2 : files) {
System.out.println(file2.getAbsolutePath());
}
System.out.println(f2.delete());
}
public static void findFile(File filePath,String file){
if(filePath!=null) {
if(filePath.isDirectory()) {
File fs[] = filePath.listFiles();
for (File file2 : fs) {
findFile(file2, file);
}
} else {
String path = filePath.getAbsolutePath();
if(path.endsWith(".txt")) {
System.out.println("find"+path);
}
}
}
}
}
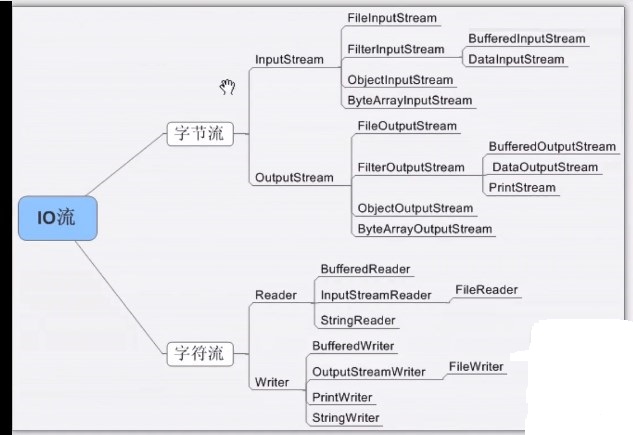
18.byteSteam字节流和CharacterStream字符流
package com.test.testjva.IO;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.io.OutputStream;
//字节流
public class ByteStream {
private static OutputStream mOutputStream;
private static InputStream mInputStream;
public static void main(String[] args) {
File f = new File("d:"+File.separator+"bytes.txt");
write(f);
read(f);
}
//字节输出流,从程序向硬盘文件输出数据
public static void write(File f){
if(f.exists()) {
try {
//针对文件创建一个输出流FileOutputStream(File file, boolean append)这个是追加,不写是默认覆盖上一次的数据
mOutputStream = new FileOutputStream(f,true);//直接写入到文件中
String info = "你好";
//写入数据
mOutputStream.write(info.getBytes());
//关闭
mOutputStream.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
} else {
try {
f.createNewFile();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
public static void read(File f){
try {
mInputStream = new FileInputStream(f);
//读文件时,一个字节一个字节读太慢,一下全部读,太多。
byte[] by = new byte[1024*1024*10];//最大10m
int len = -1;//每次真实读取的长度,每次最大10m
StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer();
while((len = mInputStream.read(by)) != -1){
sb.append(new String(by,0,len));
}
mInputStream.close();
System.out.println(sb);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
package com.test.testjva.IO;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.FileWriter;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.Reader;
import java.io.Writer;
public class CharacterStream {
public static void write(File file){
try {
Writer out = new FileWriter(file,true);
String info = "字符流,你好";
out.write(info);//输出到缓存中
out.write("\r\n");//换行
out.flush();//刷新缓存(把缓存数据清空,并写入到文件中)
out.close();//关闭时会自动调用flush方法
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static void read(File file){
try {
Reader in = new FileReader(file);
char[] cs = new char[2];//一个中文也是一个字符,一个英文也是一个字符
int len = -1;
StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer();
while((len = in.read(cs))!=-1){
sb.append(new String(cs,0,len));
}
System.out.println(sb);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
//如果操作 的是文本类型的文件,建议适用字符流
//如果操作的是非文本类型(如音频文件,视频,都是字节文件)建议适用字节流
public static void main(String[] args) {
File file = new File("d:"+File.separator+"character.txt");
write(file);
read(file);
}
}
字节流和字符流的区别:
1.字符流在out.write(info);//会先输出到缓存中,然后在out.close();//关闭时会自动调用flush方法来刷新缓存(把缓存数据清空,并写入到文件中)
2.字节流mOutputStream.write(info.getBytes());直接写入到文件中去
什么时候使用字节流,什么时候使用字符流?
//如果操作 的是文本类型的文件,建议适用字符流
//如果操作的是非文本类型(如音频文件,视频,都是字节文件)建议适用字节流
19.流转换
package com.test.testjva.IO;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.io.Reader;
//outputStreamWriter输出的字符转为字节
//inputStreamReader 输入的 字节流转为字符流
public class ChangeStream {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);//System.in是字节流
String info = bufferedReader(System.in);
System.out.println(info);
}
//处理字符
public static String read (InputStream in) {
//字节转成字符
Reader reader = new InputStreamReader(in);
char[] cs = new char[1024];
int len = -1;
try {
StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer();
while((len = reader.read(cs))!=-1) {
sb.append(new String(cs, 0,len));
}
reader.close();
return sb.toString();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return null;
}
//可以这样写
public static String bufferedReader (InputStream in) {
//字节转为字符
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(in));
try {
return br.readLine();//读取一行
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return null;
}
}
20.缓冲流
//BufferedInputStream 输入字节缓冲区
//BufferedReader 输入字符缓冲区
//BufferedOutputStream输出字节缓冲区
//BufferedWriter 输出字符缓冲区
//未来写流的时候必须写缓存
package com.test.testjva.IO2;
import java.io.BufferedInputStream;
import java.io.BufferedOutputStream;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.BufferedWriter;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.FileWriter;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.io.OutputStream;
import java.io.Reader;
import java.io.Writer;
//缓冲流
public class BufferDemo {
//BufferedInputStream 输入字节缓冲区
//BufferedReader 输入字符缓冲区
//BufferedOutputStream输出字节缓冲区
//BufferedWriter 输出字符缓冲区
//输出字节缓冲区
public static void byteStreamOut(String path ,byte[] data){
OutputStream out;
try {
out = new FileOutputStream(path);
//让字节输出流具备缓冲功能
// this(out, 8192);默认是(1024个字节=1k)8k的缓存,BufferedOutputStream(OutputStream out, int size)
//你也可以手动设置缓存
BufferedOutputStream bos = new BufferedOutputStream(out);
bos.write(data);
bos.close();
out.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
//输入字节缓冲区
public static void byteStreamIn(String pathin,String pathout){
try {
InputStream in = new FileInputStream(pathin);
BufferedInputStream bis = new BufferedInputStream(in);
byte[] bytes = new byte[1024];//每次读1k
int len = -1;
while((len = bis.read(bytes))!=-1) {
//bis.read(pathin.getBytes());
byteStreamOut(pathout, bytes);//边读边写
}
bis.close();
in.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
//字符输出缓冲区
public static void charSreamOut(String path,String data){
Writer out;
try {
out = new FileWriter(path);
BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(out);
bw.write(data);
bw.close();
out.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
//字符输入缓冲区
public static void charSreamIn(String pathIn,String pathOut){
try {
Reader in = new FileReader(pathIn);
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(in);
char[] chars = new char[1024];
int len = -1;//读的实际长度
while((len = br.read(chars))!=-1){
charSreamOut(pathOut, new String(chars,0,len));//边读边写
}
br.close();
in.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
String path = "d:/aaa.txt";
String path2 = "d:/aaa2.txt";
byte[] data = "字节输出缓冲区".getBytes();
String datachar = "字符输入缓冲区";
byteStreamOut(path,data);
byteStreamIn(path,path2);
charSreamOut(path, datachar);//先写出
charSreamIn(path, path2);
}
}
21.打印流
package com.test.testjva.IO2;
import java.io.BufferedOutputStream;
import java.io.BufferedWriter;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.FileWriter;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.OutputStream;
import java.io.PrintStream;
import java.io.PrintWriter;
import java.io.Writer;
/*打印流主要功能是用于输出,在整个IO包中打印流分为2中类型
* 字节打印流:printStream
* 字符打印流:printWriter
* 打印流可以方便的进行输出
*/
public class PrintStreams {
public static void printStream(String path ,byte[] data){
OutputStream out;
try {
out = new FileOutputStream(path);
BufferedOutputStream bos = new BufferedOutputStream(out);
//更方便输出到文件
PrintStream ps = new PrintStream(bos);
//bos.write(data);
ps.print(11);
ps.print(true);
ps.println("111");
ps.close();
bos.close();
out.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static void printWrite(String path,String data){
Writer out;
try {
out = new FileWriter(path);
BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(out);
PrintWriter pw = new PrintWriter(bw);
pw.print("2222");
pw.println(111);
//bw.write(data);
pw.close();
bw.close();
out.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
String path = "d:/print.txt";
String data = "打印流";
printStream(path, data.getBytes());
}
}
22.对象流
package com.test.testjva.IO2;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.io.ObjectInputStream;
import java.io.ObjectOutputStream;
import java.io.OutputStream;
/*1.对象序列化
* 对象序列化就是指将一个对象转化成二进制的byte流
* 两种情况:
* 对象序列化(ObjectOutputStream):对象保存到文件
* 对象反序列化(ObjectInputStream):对象从文件中恢复
* 被序列化对象所在类必须实现java.io.Serializable接口(和clone接口类似,都是虚拟机可以检测的)
*
* 对象序列化之后再恢复就不是一个对象了,但是值是一样的
* 保存的是状态(状态就是属性)
* 后面使用可能不会用到对象流,但是序列化会用的比较多
*/
public class ObjectStream {
public static Object objectIn(String path){
try {
InputStream in = new FileInputStream(path);
ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(in);
return ois.readObject();
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
return path;
}
public static void objectOut(String path){
try {
Cat cat = new Cat("mimi",2);
OutputStream out = new FileOutputStream(path);
ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(out);
oos.writeObject(cat);//如果你的类没有implement Serializable被序列化,那么输出的时候回报错
oos.close();
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
String path = "d:/sbb.objjj";//后缀名随便起,这样的话,比较安全,其他软件就解析不了了(因为是对象,如果涉及到用户密码是不允许别人看到的)
objectOut(path);
Cat cat = (Cat) objectIn(path);
System.out.println(cat.getName()+cat.getAge());
}
}
23.字节数组流,数据流,字符串流
package com.test.testjva.IO2;
import java.io.ByteArrayInputStream;
import java.io.ByteArrayOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
/*字节数组流
* ByteArrayInputStream 包含内部缓冲区,从流中读取字节,关闭流后仍可被调用,不会IOException
*ByteArrayOutputStream 输出数据到byte[],缓冲区数据自动增长,使用toByteArray()和toString获取数据,关闭仍可被调用,不会IOException
*为什么不会IOException呢?因为它操作的是内存,跟文件什么的没有任何关系,
*ByteArrayOutputStream extends OutputStream和ByteArrayInputStream extends InputStream
*和FileInputStream和FileOutputStream是同级别的
*/
public class ByteArrayStream {
public static String byteArrayStream(byte[] data){
ByteArrayInputStream bis = new ByteArrayInputStream(data);
ByteArrayOutputStream bos = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
byte[] bytes = new byte[1024];
int len = -1;
try {
while((len = bis.read(bytes))!=-1){
bos.write(bytes);
}
byte[] bys = bos.toByteArray();
String s = new String(bys);
return s;
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return null;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
String result = byteArrayStream("你好".getBytes());
System.out.println(result);
}
}
package com.test.testjva.IO2;
import java.io.DataInputStream;
import java.io.DataOutputStream;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.io.OutputStream;
import javax.imageio.stream.FileImageInputStream;
/*数据流
* DataInputStream 读取基本java数据类型
* DataOutputStream 将java基本数据类型写入输入流中
*/
public class DataStream {
//写入的是二进制,缺点:数据会变大优点:按照java基本数据类型写入的
public static void dataStreamOut(String path){
try {
OutputStream out = new FileOutputStream(path);
DataOutputStream dos = new DataOutputStream(out);
dos.writeInt(1);//
dos.writeDouble(2.22);
dos.writeUTF("你好");
dos.close();
out.close();
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static void dataStreamIn(String path){
try {
InputStream in = new FileInputStream(path);
DataInputStream dis = new DataInputStream(in);
//读的时候必须和上面存的顺序一致
int a = dis.readInt();
double b = dis.readDouble();
String str = dis.readUTF();
System.out.println(a+"b"+b+"st"+str);
dis.close();
in.close();
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
String path = "e:/datastream.txt";
dataStreamOut(path);
dataStreamIn(path);
}
}
字符串流
package com.test.testjva.IO2;
import java.io.StringReader;
import java.io.StringWriter;
public class StringStream {
public static void StringSreamOut(String data){
StringReader str = new StringReader(data);
}
public static void StringSreamIn(){
StringWriter sw = new StringWriter();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
String data = "你好,string字符流";
StringSreamOut(data);
}
}
24.RandomAccessFile
package com.test.testjva.IO2;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.RandomAccessFile;
public class RandomAccessFileDemo {
public static void RandomAccessFileTest(String path,String model){
File file = new File(path);
RandomAccessFile raf;
try {
raf = new RandomAccessFile(file, model);
raf.writeInt(18);
raf.writeUTF("大雄");
raf.writeLong(System.currentTimeMillis());
raf.writeBoolean(false);
raf.writeChar('女');
raf.seek(0);//定位到文件开始的位置
int age = raf.readInt();
String name = raf.readUTF();
raf.skipBytes(1);//跳过2个字节
char sex = raf.readChar();
System.out.println(age+name+sex);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
String path = "d:/RandomAccessFile.txt";
RandomAccessFileTest(path, "rw");
}
}
25.装饰者设计模式(完美解决类爆炸)
package com.test.testjva.decorator;
public interface Drink {
String description();
int price();
}
package com.test.testjva.decorator;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
//抽象的装饰者类要实现(继承)被装饰者
public abstract class Decorator implements Drink{
private Drink drink;//要装饰的对象
public Decorator(Drink drink) {
this.drink = drink;
}
@Override
public String description() {
return drink.description();
}
@Override
public int price() {
return drink.price();
}
}
package com.test.testjva.decorator;
//因为它是主要材料豆浆,鸡蛋,糖,黑豆都是它的配料,所以他们继承的是decorator,而不是drink
public class SoyaBeanMilk implements Drink{
@Override
public String description() {
return "纯豆浆";
}
@Override
public int price() {
return 5;
}
}
package com.test.testjva.decorator;
public class BlackBeanDecorator extends Decorator{
public BlackBeanDecorator(Drink drink) {
super(drink);
}
@Override
public String description() {
return super.description()+"黑米";
}
@Override
public int price() {
return super.price()+2;
}
}
package com.test.testjva.decorator;
public class EggDecorator extends Decorator{
public EggDecorator(Drink drink) {
super(drink);
}
@Override
public String description() {
return super.description()+"鸡蛋";
}
@Override
public int price() {
return super.price()+3;
}
}
package com.test.testjva.decorator;
public class SugarDecorator extends Decorator{
public SugarDecorator(Drink drink) {
super(drink);
}
@Override
public String description() {
return super.description()+"糖";
}
@Override
public int price() {
return super.price()+1;
}
}
package com.test.testjva.decorator;
public class Test {
//装饰就代表扩展
public static void main(String[] args) {
//因为它(SoyaBeanMilk)是主要材料豆浆,鸡蛋,糖,黑豆都是它的配料,所以他们继承的是decorator,而不是drink
Drink drink = new SoyaBeanMilk();
BlackBeanDecorator black = new BlackBeanDecorator(drink);
EggDecorator egg = new EggDecorator(black);
SugarDecorator sugar = new SugarDecorator(egg);
System.out.println("早餐"+sugar.description());//就等于是调用了super.description()+"鸡蛋";drink.description();
System.out.println("共花了"+sugar.price());
}
}
25.常见字符编码
常见编码:ISO859-1丶GBK/GB2312丶unicode丶UTF
ISO859-1:单字节编码,英文上应用,一个字符一个字节0-255字符范围
GBK/GB2312:一个中文2个字节,中文国际编码
unicode:java中的编码方式aa
UTF:由于unicode不支持iso8859-1,不定长编码,可以节省空间
造成乱码原因:
1.程序使用的编码和本机的编码不统一
2.在网络中,客户端与服务端编码不一致
26.NIO
package com.test.testjva.NIO;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.RandomAccessFile;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.MappedByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.FileChannel;
import java.nio.channels.FileChannel.MapMode;
/*文件的读写操作
* 1.内存映射方法读写(最快)//虽然最快,但是都是基于传统IO的升级
* 2.NIO文件通道读写(第二快)
* 3.传统的IO读写(最慢)
网络中还是用传统方式进行读写(比如上传下载)
*/
public class CopyFileNIO {
public static void copy(File file,File destFile){
try {
FileInputStream in = new FileInputStream(file);
FileOutputStream out = new FileOutputStream(destFile);
FileChannel inChannel = in.getChannel();//获取文件输入通道
FileChannel outChannel = out.getChannel();
ByteBuffer buf = ByteBuffer.allocate((int)file.length());
inChannel.read(buf);
buf.flip();
outChannel.write(buf);
inChannel.close();
outChannel.close();
out.close();
in.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
//内存映射的速度是最快的,两块内存交换
public static void randomAccessFile(File f1,File f2){
try {
RandomAccessFile in = new RandomAccessFile(f1, "rw");
RandomAccessFile out = new RandomAccessFile(f2, "rw");
FileChannel inf = in.getChannel();
FileChannel outf = out.getChannel();
//映射内存
long size = inf.size();
MappedByteBuffer inbuffer = inf.map(MapMode.READ_ONLY, 0, size);
MappedByteBuffer outbuffer = inf.map(MapMode.READ_WRITE, 0, size);
//inbuffer.flip();
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
byte b = inbuffer.get(i);
outbuffer.put(b);
}
outf.write(inbuffer);
inf.close();
outf.close();
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
File f1 = new File("d:/a.txt");
File f2= new File("d:/a/a.txt");
//copy(f1 , f2);
randomAccessFile(f1, f2);
}
}
27.Set
package com.test.testjva.List.set;
public class Student {
private String name;
private int age;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
//如果hashcode一样的情况下才会调用equals方法
@Override
public int hashCode() {
final int prime = 31;
int result = 1;
result = prime * result + age;
result = prime * result + ((name == null) ? 0 : name.hashCode());
return result;
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object obj) {
if (this == obj)
return true;
if (obj == null)
return false;
if (getClass() != obj.getClass())
return false;
Student other = (Student) obj;
if (age != other.age)
return false;
if (name == null) {
if (other.name != null)
return false;
} else if (!name.equals(other.name))
return false;
return true;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student [name=" + name + ", age=" + age + "]";
}
public Student(String name, int age) {
super();
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public Student() {
super();
// TODO Auto-generated constructor stub
}
}
package com.test.testjva.List.set;
小结:
/*Arraylist(用数组实现的)可以重复和vector的区别就是vector是同步(Synchornized线程安全)的
* LinkedList(用链表实现的)也是而已重复的
* set不允许重复:hashset不保证顺序,treeSet可以实现Comparable接口自定义顺序LinkedHahset可以确保顺序(因为链表里面有顺序(有link关键字的就有顺序))
*/
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.LinkedHashSet;
import java.util.Set;
import java.util.TreeSet;
public class SetDemo {
/*从hashSet继承而来
* 确保对象的插入顺序(其实就是与HashSet的区别)
* 由双向链表+HashMap表实现
*/
public static void LinkHashSet(){
Cat stu = new Cat("张飞",1);
Cat stu1 = new Cat("张飞1",3);
Cat stu2 = new Cat("张飞",1);
Set<Cat> set = new LinkedHashSet<>();
set.add(stu);
set.add(stu1);
set.add(stu2);
System.out.println(set.size());
}
public static void treeSet(){
/*基于treemap实现
* 在treeSet集合中添加的自定义对象,必须实现Comparable接口,(自定义排序)
* 因为添加方法回使用compareTo方法来验证对象的排序位置
* 并验证对象是否重复(如果compareTo返回0,就代表对象重复了)
* 如果不同,使用大小来决定排序的顺序
* 有序的方式排序
### 最后
金三银四到了,送上一个小福利!



txt");
//copy(f1 , f2);
randomAccessFile(f1, f2);
}
}
27.Set
package com.test.testjva.List.set;
public class Student {
private String name;
private int age;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
//如果hashcode一样的情况下才会调用equals方法
@Override
public int hashCode() {
final int prime = 31;
int result = 1;
result = prime * result + age;
result = prime * result + ((name == null) ? 0 : name.hashCode());
return result;
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object obj) {
if (this == obj)
return true;
if (obj == null)
return false;
if (getClass() != obj.getClass())
return false;
Student other = (Student) obj;
if (age != other.age)
return false;
if (name == null) {
if (other.name != null)
return false;
} else if (!name.equals(other.name))
return false;
return true;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student [name=" + name + ", age=" + age + "]";
}
public Student(String name, int age) {
super();
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public Student() {
super();
// TODO Auto-generated constructor stub
}
}
package com.test.testjva.List.set;
小结:
/*Arraylist(用数组实现的)可以重复和vector的区别就是vector是同步(Synchornized线程安全)的
* LinkedList(用链表实现的)也是而已重复的
* set不允许重复:hashset不保证顺序,treeSet可以实现Comparable接口自定义顺序LinkedHahset可以确保顺序(因为链表里面有顺序(有link关键字的就有顺序))
*/
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.LinkedHashSet;
import java.util.Set;
import java.util.TreeSet;
public class SetDemo {
/*从hashSet继承而来
* 确保对象的插入顺序(其实就是与HashSet的区别)
* 由双向链表+HashMap表实现
*/
public static void LinkHashSet(){
Cat stu = new Cat("张飞",1);
Cat stu1 = new Cat("张飞1",3);
Cat stu2 = new Cat("张飞",1);
Set<Cat> set = new LinkedHashSet<>();
set.add(stu);
set.add(stu1);
set.add(stu2);
System.out.println(set.size());
}
public static void treeSet(){
/*基于treemap实现
* 在treeSet集合中添加的自定义对象,必须实现Comparable接口,(自定义排序)
* 因为添加方法回使用compareTo方法来验证对象的排序位置
* 并验证对象是否重复(如果compareTo返回0,就代表对象重复了)
* 如果不同,使用大小来决定排序的顺序
* 有序的方式排序
### 最后
金三银四到了,送上一个小福利!
[外链图片转存中...(img-NeNxjJjx-1716570532247)]
[外链图片转存中...(img-74ng12bX-1716570532247)]
[外链图片转存中...(img-fiHWuSDm-1716570532247)]






















 6083
6083

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








