System.out.println(“update”);
}
public void query() {
System.out.println(“query”);
}
}
(3)执行动态代理
package com.guor.aop.dynamicproxy;
import com.guor.aop.UserService;
import com.guor.aop.UserServiceImpl;
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//真实角色
UserService userService = new UserServiceImpl();
//代理角色
ProxyInvocationHandler pih = new ProxyInvocationHandler();
//通过调用程序处理角色来处理我们要调用的接口对象
pih.setTarget(userService);
UserService proxy = (UserService) pih.getProxy();
proxy.update();
}
}
(4)控制台输出
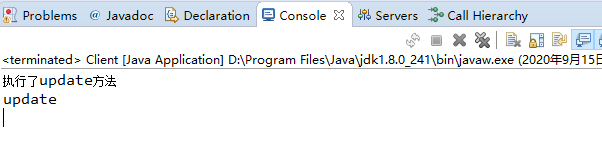
七、动态代理底层实现
1、动态代理具体步骤
-
通过实现 InvocationHandler 接口创建自己的调用处理器;
-
通过为 Proxy 类指定 ClassLoader 对象和一组 interface 来创建动态代理类;
-
通过反射机制获得动态代理类的构造函数,其唯一参数类型是调用处理器接口类型;
-
通过构造函数创建动态代理类实例,构造时调用处理器对象作为参数被传入。
2、源码分析
(1)newProxyInstance
既然生成代理对象是用的Proxy类的静态方newProxyInstance,那么我们就去它的源码里看一下它到底都做了些什么?
@CallerSensitive
public static Object newProxyInstance(ClassLoader loader,
Class<?>[] interfaces,
InvocationHandler h)
throws IllegalArgumentException
{
Objects.requireNonNull(h);
final Class<?>[] intfs = interfaces.clone();
final SecurityManager sm = System.getSecurityManager();
if (sm != null) {
checkProxyAccess(Reflection.getCallerClass(), loader, intfs);
}
/*
- Look up or generate the designated proxy class.
*/
Class<?> cl = getProxyClass0(loader, intfs);
/*
- Invoke its constructor with the designated invocation handler.
*/
try {
if (sm != null) {
checkNewProxyPermission(Reflection.getCallerClass(), cl);
}
final Constructor<?> cons = cl.getConstructor(constructorParams);
final InvocationHandler ih = h;
if (!Modifier.isPublic(cl.getModifiers())) {
AccessController.doPrivileged(new PrivilegedAction() {
public Void run() {
cons.setAccessible(true);
return null;
}
});
}
return cons.newInstance(new Object[]{h});
} catch (IllegalAccessException|InstantiationException e) {
throw new InternalError(e.toString(), e);
} catch (InvocationTargetException e) {
Throwable t = e.getCause();
if (t instanceof RuntimeException) {
throw (RuntimeException) t;
} else {
throw new InternalError(t.toString(), t);
}
} catch (NoSuchMethodException e) {
throw new InternalError(e.toString(), e);
}
}
(2)getProxyClass0
利用getProxyClass0(loader, intfs)生成代理类Proxy的Class对象。
private static Class<?> getProxyClass0(ClassLoader loader,Class<?>… interfaces) {
if (interfaces.length > 65535) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(“interface limit exceeded”);
}
// If the proxy class defined by the given loader implementing
// the given interfaces exists, this will simply return the cached copy;
// otherwise, it will create the proxy class via the ProxyClassFactory
return proxyClassCache.get(loader, interfaces);
}

(3)ProxyClassFactory
ProxyClassFactory内部类创建、定义代理类,返回给定ClassLoader 和interfaces的代理类。
private static final class ProxyClassFactory implements BiFunction<ClassLoader, Class<?>[], Class<?>>
{
// prefix for all proxy class names
private static final String proxyClassNamePrefix = “$Proxy”;
// next number to use for generation of unique proxy class names
private static final AtomicLong nextUniqueNumber = new AtomicLong();
@Override
public Class<?> apply(ClassLoader loader, Class<?>[] interfaces) {
Map<Class<?>, Boolean> interfaceSet = new IdentityHashMap<>(interfaces.length);
for (Class<?> intf : interfaces) {
/*
-
Verify that the class loader resolves the name of this
-
interface to the same Class object.
*/
Class<?> interfaceClass = null;
try {
interfaceClass = Class.forName(intf.getName(), false, loader);
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
}
if (interfaceClass != intf) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(
intf + " is not visible from class loader");
}
/*
-
Verify that the Class object actually represents an
-
interface.
*/
if (!interfaceClass.isInterface()) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(
interfaceClass.getName() + " is not an interface");
}
/*
- Verify that this interface is not a duplicate.
*/
if (interfaceSet.put(interfaceClass, Boolean.TRUE) != null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(
"repeated interface: " + interfaceClass.getName());
}
}
String proxyPkg = null; // package to define proxy class in
int accessFlags = Modifier.PUBLIC | Modifier.FINAL;
/*
-
Record the package of a non-public proxy interface so that the
-
proxy class will be defined in the same package. Verify that
-
all non-public proxy interfaces are in the same package.
*/
for (Class<?> intf : interfaces) {
int flags = intf.getModifiers();
if (!Modifier.isPublic(flags)) {
accessFlags = Modifier.FINAL;
String name = intf.getName();
int n = name.lastIndexOf(‘.’);
String pkg = ((n == -1) ? “” : name.substring(0, n + 1));
if (proxyPkg == null) {
proxyPkg = pkg;
} else if (!pkg.equals(proxyPkg)) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(
“non-public interfaces from different packages”);
}
}
}
if (proxyPkg == null) {
// if no non-public proxy interfaces, use com.sun.proxy package
proxyPkg = ReflectUtil.PROXY_PACKAGE + “.”;
}
/*
- Choose a name for the proxy class to generate.
*/
long num = nextUniqueNumber.getAndIncrement();
String proxyName = proxyPkg + proxyClassNamePrefix + num;
/*
- Generate the specified proxy class.
*/
byte[] proxyClassFile = ProxyGenerator.generateProxyClass(
proxyName, interfaces, accessFlags);
try {
return defineClass0(loader, proxyName,
proxyClassFile, 0, proxyClassFile.length);
} catch (ClassFormatError e) {
/*
-
A ClassFormatError here means that (barring bugs in the
-
proxy class generation code) there was some other
-
invalid aspect of the arguments supplied to the proxy
-
class creation (such as virtual machine limitations
-
exceeded).
*/
throw new IllegalArgumentException(e.toString());
}
}
}
(4)generateProxyClass
一系列检查后,调用ProxyGenerator.generateProxyClass来生成字节码文件。
public static byte[] generateProxyClass(final String name,Class<?>[] interfaces,int accessFlags)
{
ProxyGenerator gen = new ProxyGenerator(name, interfaces, accessFlags);
final byte[] classFile = gen.generateClassFile();
if (saveGeneratedFiles) {
java.security.AccessController.doPrivileged(
new java.security.PrivilegedAction() {
public Void run() {
try {
int i = name.lastIndexOf(‘.’);
Path path;
if (i > 0) {
Path dir = Paths.get(name.substring(0, i).replace(‘.’, File.separatorChar));
Files.createDirectories(dir);
path = dir.resolve(name.substring(i+1, name.length()) + “.class”);
} else {
path = Paths.get(name + “.class”);
}
Files.write(path, classFile);
return null;
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new InternalError(
"I/O exception saving generated file: " + e);
}
}
});
}
return classFile;
}

(5)generateClassFile
生成代理类字节码文件的generateClassFile方法:
private byte[] generateClassFile() {
/* ============================================================
-
Step 1: Assemble ProxyMethod objects for all methods to
-
generate proxy dispatching code for.
*/
/*
-
Record that proxy methods are needed for the hashCode, equals,
-
and toString methods of java.lang.Object. This is done before
-
the methods from the proxy interfaces so that the methods from
-
java.lang.Object take precedence over duplicate methods in the
-
proxy interfaces.
*/
addProxyMethod(hashCodeMethod, Object.class);
addProxyMethod(equalsMethod, Object.class);
addProxyMethod(toStringMethod, Object.class);
/*
-
Now record all of the methods from the proxy interfaces, giving
-
earlier interfaces precedence over later ones with duplicate
-
methods.
*/
for (Class<?> intf : interfaces) {
for (Method m : intf.getMethods()) {
addProxyMethod(m, intf);
}
}
/*
-
For each set of proxy methods with the same signature,
-
verify that the methods’ return types are compatible.
*/
for (List sigmethods : proxyMethods.values()) {
checkReturnTypes(sigmethods);
}
/* ============================================================
-
Step 2: Assemble FieldInfo and MethodInfo structs for all of
-
fields and methods in the class we are generating.
*/
try {
methods.add(generateConstructor());
for (List sigmethods : proxyMethods.values()) {
for (ProxyMethod pm : sigmethods) {
// add static field for method’s Method object
fields.add(new FieldInfo(pm.methodFieldName,
“Ljava/lang/reflect/Method;”,
ACC_PRIVATE | ACC_STATIC));
// generate code for proxy method and add it
methods.add(pm.generateMethod());
}
}
methods.add(generateStaticInitializer());
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new InternalError(“unexpected I/O Exception”, e);
}
最后
2020年在匆匆忙忙慌慌乱乱中就这么度过了,我们迎来了新一年,互联网的发展如此之快,技术日新月异,更新迭代成为了这个时代的代名词,坚持下来的技术体系会越来越健壮,JVM作为如今是跳槽大厂必备的技能,如果你还没掌握,更别提之后更新的新技术了。

更多JVM面试整理:

for (ProxyMethod pm : sigmethods) {
// add static field for method’s Method object
fields.add(new FieldInfo(pm.methodFieldName,
“Ljava/lang/reflect/Method;”,
ACC_PRIVATE | ACC_STATIC));
// generate code for proxy method and add it
methods.add(pm.generateMethod());
}
}
methods.add(generateStaticInitializer());
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new InternalError(“unexpected I/O Exception”, e);
}
最后
2020年在匆匆忙忙慌慌乱乱中就这么度过了,我们迎来了新一年,互联网的发展如此之快,技术日新月异,更新迭代成为了这个时代的代名词,坚持下来的技术体系会越来越健壮,JVM作为如今是跳槽大厂必备的技能,如果你还没掌握,更别提之后更新的新技术了。
[外链图片转存中…(img-dK2zxSOJ-1720081630347)]
更多JVM面试整理:
[外链图片转存中…(img-3gPL6M7Z-1720081630348)]























 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








