1.2 Advice
SpringAOP中,通过Advice定义横切逻辑,Advice也就是我们想要的功能,也就是上面说的 安全,事物,日志等。我们先定义好,然后在想用的地方用一下。Advice有五种类型,如下:

接下来就开始我们对AOC的实现了。
1.3 准备
使用AOP需要导入一个依赖包
org.aspectj
aspectjweaver
1.9.4
2 使用Spring实现AOP
===============
业务接口
package com.yixin.service;
public interface BlogService {
public void add();
public void delete();
public void update();
public void search();
}
实现类:
package com.yixin.service;
public class BlogServiceImpl implements BlogService{
public void add() {
System.out.println(“添加Blog”);
}
public void delete() {
System.out.println(“删除Blog”);
}
public void update() {
System.out.println(“更新Blog”);
}
public void search() {
System.out.println(“查找Blog”);
}
}
写我们的增强类 也就是上面提到的Advice, 我们编写两个 , 一个前置增强 一个后置增强
前置增强:
package com.yixin.log;
import org.springframework.aop.MethodBeforeAdvice;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
public class BeforeLog implements MethodBeforeAdvice {
//method : 要执行的目标对象的方法
//objects : 被调用的方法的参数
//Object : 目标对象
public void before(Method method, Object[] objects, Object o) throws Throwable {
System.out.println( o.getClass().getName() + “的” + method.getName() + “方法被执行了”);
}
}
后置增强:
package com.yixin.log;
import org.springframework.aop.AfterReturningAdvice;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
public class AfterLog implements AfterReturningAdvice {
//returnValue 返回值
//method被调用的方法
//args 被调用的方法的对象的参数
//target 被调用的目标对象
public void afterReturning(Object returnValue, Method method, Object[] args, Object target) throws Throwable {
System.out.println(“执行了” + target.getClass().getName()
+“的”+method.getName()+“方法,”
+“返回值:”+returnValue);
}
}
(1)在XML头文件添加aop
xmlns:aop=“http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop”
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd

(2)注册Bean和实现aop切入实现
aop:config
<aop:pointcut id=“pointcut” expression=“execution(* com.yixin.service.BlogServiceImpl.*(…))”/>
<aop:advisor advice-ref=“beforeLog” pointcut-ref=“pointcut”/>
<aop:advisor advice-ref=“afterLog” pointcut-ref=“pointcut”/>
</aop:config>
测试:
@Test
public void test3(){
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(“bean2.xml”);
BlogService blogService=context.getBean(“blogService”, BlogService.class);
blogService.add();
}
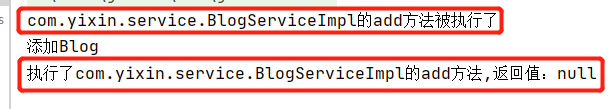
结果:
3.自定义类来实现AOP
======================
(1)写入自定义切入类
package com.yixin.log;
public class MyPointcut {
public void before(){
System.out.println(“---------方法执行前---------”);
}
public void after(){
System.out.println(“---------方法执行后---------”);
}
}
(2)XML配置:
aop:config
<aop:aspect ref=“myPoincut”>
<aop:pointcut id=“diyPonitcut” expression=“execution(* com.yixin.service.BlogServiceImpl.*(…))”/>
<aop:before pointcut-ref=“diyPonitcut” method=“before”/>
<aop:after pointcut-ref=“diyPonitcut” method=“after”/>
</aop:aspect>
</aop:config>
测试:
@Test
public void test3(){
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(“bean1.xml”);
BlogService blogService=context.getBean(“blogService”, BlogService.class);
blogService.add();
}
结果:

4.注解实现
======================
(1)编写注解实现的增强类
@Aspect:生成代理对象
package com.yixin.log;
import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.*;
@Aspect
public class
MyAnnotationPointcut {
@Before(“execution(* com.yixin.service.BlogServiceImpl.*(…))”)
public void before(){
System.out.println(“---------方法执行前---------”);
}
//后置通知(返回通知)
@AfterReturning(value = “execution(* com.yixin.service.BlogServiceImpl.*(…))”)
public void afterReturning() {
System.out.println(“afterReturning…”);
}
//异常通知
@AfterThrowing(value = “execution(* com.yixin.service.BlogServiceImpl.*(…))”)
public void afterThrowing() {
System.out.println(“afterThrowing…”);
}
@After(“execution(* com.yixin.service.BlogServiceImpl.*(…))”)
public void after(){
System.out.println(“---------方法执行后---------”);
}
@Around(“execution(* com.yixin.service.BlogServiceImpl.*(…))”)
public void around(ProceedingJoinPoint jp) throws Throwable {
System.out.println(“环绕前”);
System.out.println(“签名:”+jp.getSignature());
//执行目标方法proceed
Object proceed = jp.proceed();
System.out.println(“环绕后”);
System.out.println(proceed);
}
}
(2)注册bean,并增加支持注解的配置
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?><beans xmlns=“http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans”
xmlns:xsi=“http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance”
xmlns:aop=“http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop”
xmlns:context=“http://www.springframework.org/schema/context”
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd">
aop:aspectj-autoproxy/
<context:component-scan base-package=“com.yixin.log”/>
测试:
@Test
public void test3(){
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(“bean3.xml”);
BlogService blogService=context.getBean(“blogService”, BlogService.class);
blogService.add();
}
输出:






















 2796
2796











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








