这意味着无论是转屏还是系统字体变化等因配置变化产生的 Controller 重建都不会回收 ViewModel 中维护的数据,重建的 Controller 仍然可以从同一个 ViewModel 中通过获取数据恢复状态。
2 ViewModel 实现原理
2.1 ViewModel 类
如果大家去看一下 ViewModel 类的实现,会发现虽然它是一个 abstract 类,但是没有暴露任何外部可访问的方法,其预留的方法都是 package 访问权限的, 其预留了一些数据清理工作的功能,推测可能是系统保留用作以后扩展,因为与我们对 ViewModel 原理的理解没有什么关联,我们暂且略过。
2.2 ViewModel 的构造过程
我们用一个结构图来剖析 ViewModel 的构造过程:
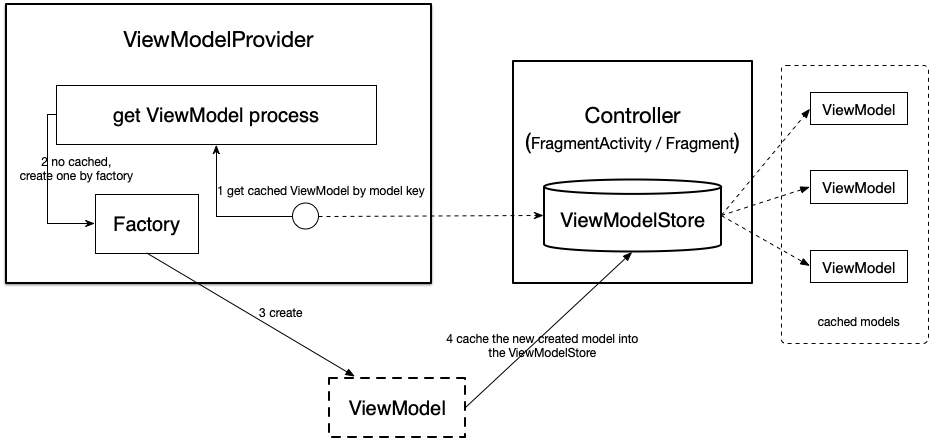
如图所示:
-
所有已经实例化的 ViewModel 都缓存在一个叫做 ViewModelStore 的封装对象中,其实质是一个 HashMap;
-
ViewModelStore 与具体的 Controller 绑定,并与宿主 Controller 俱生俱灭,所以这就解释了为何 ViewModel 与宿主 Controller 的生命周期是一样长了,因为缓存它的 ViewModelStore 与宿主 Controller 寿命相等;
-
获取 ViewModel 实例的过程委托给了一个叫做 ViewModelProvider 的工具类,它包含一个创建 ViewModel 的工厂类 Factory 和一个对 ViewModelStore 的引用;
-
总的构造过程为:先从 ViewModelStore 中获取缓存的 ViewModel,若没有缓存过则用 Facotry 实例化一个新的 ViewModel 并缓存,具体的过程分为 4 步,具体可参考图示。
本小节剩下部分分析源码,对于只关心原理的同学此部分可以略过:
我们在获取 ViewModel 的时候,一般通过如下方式:
// 在 Controller(这里以 Fragment 为例)的 onCreate 方法中调用
final UserModel viewModel = ViewModelProviders.of(this).get(UserModel.class);
我们看一下 ViewModelProviders.of() 的实现:
public static ViewModelProvider of(@NonNull Fragment fragment) {
return of(fragment, null);
}
public static ViewModelProvider of(@NonNull Fragment fragment, @Nullable Factory factory) {
Application application = checkApplication(checkActivity(fragment));
if (factory == null) {
factory = ViewModelProvider.AndroidViewModelFactory.getInstance(application);
}
// 最终用宿主 Controller 的 ViewModelStore 和一个 Factory 实例化一个
// ViewModelProvider
return new ViewModelProvider(fragment.getViewModelStore(), factory);
}
我们再看一下 ViewModelProvider.get() 方法获取 ViewModel 实例的过程:
public T get(@NonNull Class modelClass) {
String canonicalName = modelClass.getCanonicalName();
if (canonicalName == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(“Local and anonymous classes can not be ViewModels”);
}
// 我们看到了 ViewModel 在 ViewModelStore 中的 key 表示
return get(DEFAULT_KEY + “:” + canonicalName, modelClass);
}
public T get(@NonNull String key, @NonNull Class modelClass) {
// 先检查缓存中是否存在
ViewModel viewModel = mViewModelStore.get(key);
if (modelClass.isInstance(viewModel)) {
//noinspection unchecked
return (T) viewModel;
} else {
//noinspection StatementWithEmptyBody
if (viewModel != null) {
// TODO: log a warning.
}
}
// 缓存中没有,通过 Factory 构造
if (mFactory instanceof KeyedFactory) {
viewModel = ((KeyedFactory) (mFactory)).create(key, modelClass);
} else {
viewModel = (mFactory).create(modelClass);
}
// 新实例保存缓存
mViewModelStore.put(key, viewModel);
//noinspection unchecked
return (T) viewModel;
}
3 ViewModel 与配置无关的原理(与宿主 Controller 俱生俱灭)
上一节我们说到,ViewModel 之所以能够与宿主 Controller 保持生命周期一致,是因为存储它的 ViewModelStore 与宿主 Controller 生命周期一致。那么为什么 ViewModelStore 能够保持和 Controller 生命周期一致呢?
这里我们需要先理清 FragmentActivity 和其寄生的 Fragment 的 ViewModelStore 之间的关系:
3.1 ViewModelStore 树
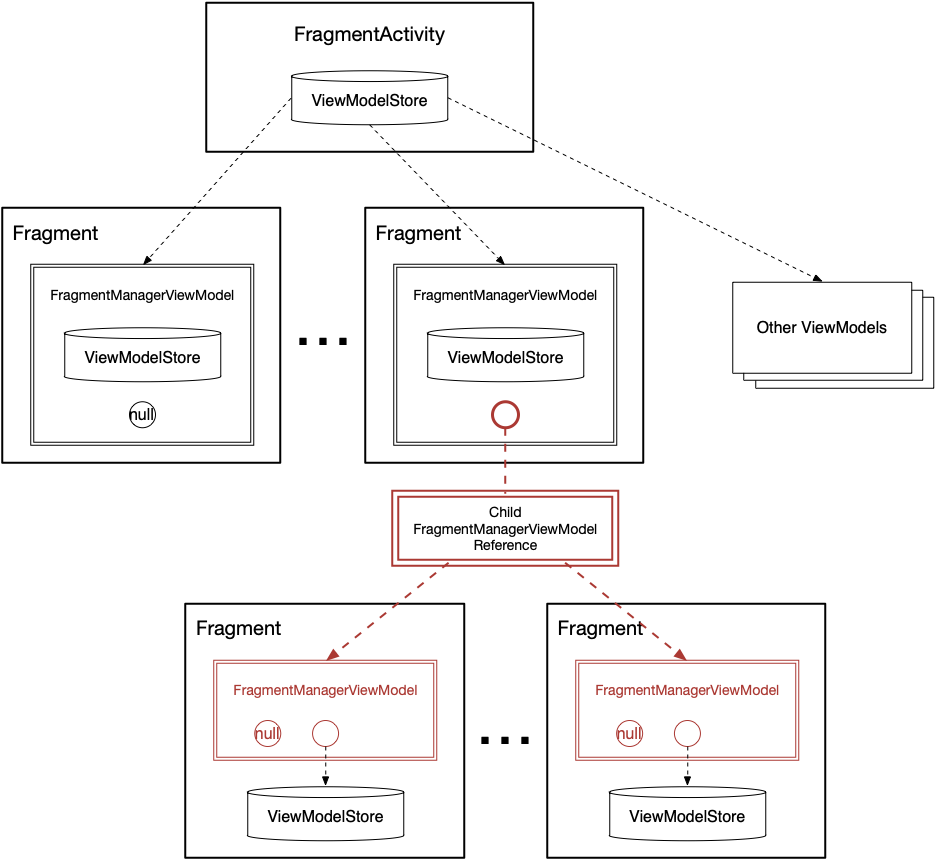
如图所示:
-
每个 ViewModelStore 依附于其宿主 Controller,所以各个 Controller 的 ViewModelStore 组成一个树状的引用关系;
-
处于顶层的 ViewModelStore 依附于 FragmentActivity,它除了保存用户级的 ViewModel 以外,还保存其儿子 Fragment 的 FragmentManagerViewModel;
-
FragmentManagerViewModel 主要维护两个对象:所属 Fragment 的 ViewModelStore 和其儿子 Fragment 的 FragmentManagerViewModel 的引用,注意图中的红色部分,所有二级及以下的子孙 Fragment 都共用同一个父节点的 Child FragmentManagerModel,这样当父 Fragment 销毁的时候方便一次性清除其所有子 Fragment 共用的 FragmentManagerViewModel;
-
但是二级及以下的子孙 Fragment 的 ViewModelStore 都是独立的,一个 Fragment 自身的 ViewModel 变化应该不影响其兄弟节点的 ViewModel,所以可以推导出,它们共同的 FragmentManagerViewModel 应该是维护了一个保存各个子 Fragment 的 ViewModelStore 的容器,大家如果细看 FragmentManagerViewModel 的源代码,实际上就是这么做的。
所以,我们看到,处于顶层的 FragmentActivity 的 ViewModelStore 是一个超级 Store,它引用了所有的 ViewModels,包括自身的数据、所有子孙 Fragment 的 ViewModels,只要各子孙 Fragment 不清除自有 ViewModelStore,则所有的数据都维护在这棵 ViewModelStore 树中。
那么在配置发生变化的时候,ViewModelStore 树如何保持不变呢?
3.2 系统级的配置无关支持
将 ViewModelStore 作为配置无关数据进行保持,在 FragmentActivity 中是这么做的:

是的,流程就是这么简单,只需要将 ViewModelStore 封装在一个特殊对象中保存并在 FragmentActivity 的 onRetainNonConfigurationInstance() 方法中返回即可:
/**
-
Called by the system, as part of destroying an
-
activity due to a configuration change, when it is known that a new
-
instance will immediately be created for the new configuration. You
-
can return any object you like here, including the activity instance
-
itself, which can later be retrieved by calling
-
{@link #getLastNonConfigurationInstance()} in the new activity
-
instance.
*/
@Override
@Nullable
public final Object onRetainNonConfigurationInstance() {
Object custom = onRetainCustomNonConfigurationInstance();
ViewModelStore viewModelStore = mViewModelStore;
// …省略与原理无关代码
NonConfigurationInstances nci = new NonConfigurationInstances();
nci.custom = custom;
nci.viewModelStore = viewModelStore;
return nci;
}
这样,在顶层源头上就保证了所有 Controller 的 ViewModels 不会在发送配置变化的时候由于 Controller 重建而被销毁。
另外在 Fragment 层中,必须区分 Fragment 实例销毁时到底是因为调用了 onDestroy 还是配置发生了变化,如果是前者则必须清理自身持有的 ViewModelStore,如果是后者则不能清理:
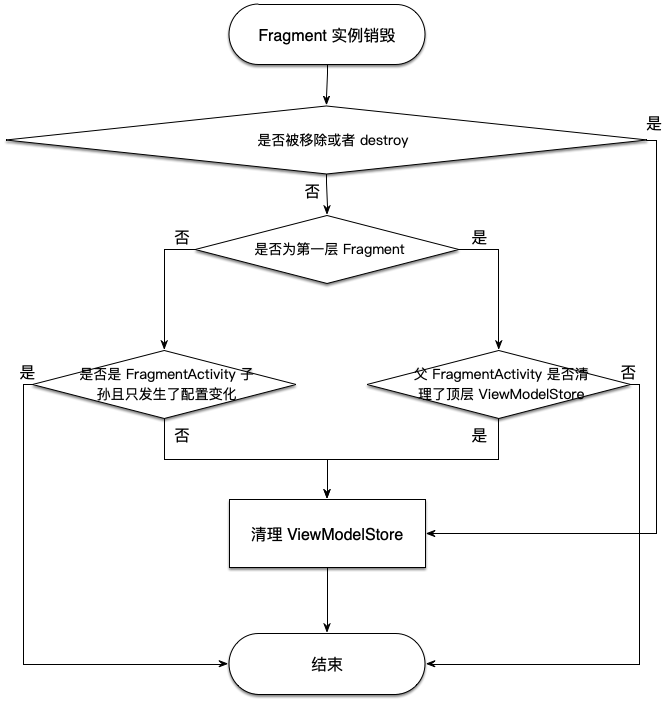
如图所示,也说明了 Fragment 的 ViewModel 生命周期与该 Fragment 生命周期是一致的。
// FragmentManagerImpl.moveToState()
//…省略
boolean beingRemoved = f.mRemoving && !f.isInBackStack(); // 是否 destroy,如果只是配置变化,则为 false
if (beingRemoved || mNonConfig.shouldDestroy(f)) {
boolean shouldClear;
if (mHost instanceof ViewModelStoreOwner) {
// 说明这是第一层 Fragment,只要顶层 ViewModelStore 没有清除该 FragmentManagerViewModel 就说明不用清理
shouldClear = mNonConfig.isCleared();
} else if (mHost.getContext() instanceof Activity) {
// 说明是 FragmentActivity 的子孙 Fragment,根据是否是配置变化来判断是否需要清理
Activity activity = (Activity) mHost.getContext();
shouldClear = !activity.isChangingConfigurations();
} else {
shouldClear = true;
}
if (beingRemoved || shouldClear) {
// 只有确实 destroy 了才需要清理
mNonConfig.clearNonConfigState(f);
}
f.performDestroy();
dispatchOnFragmentDestroyed(f, false);
}
//…省略
4 FragmentActivity 中的 ViewModel 生命周期
最后,我们还需要说明一下,FragmentActivity 中的 ViewModel 的生命周期是如何保持与 FragmentActivity 一致的,除了上一节中 FragmentActivity.onRetainNonConfigurationInstance() 中的配置无关保证以外,还需要保证在 Activity 真正销毁的时候其所持有的 ViewModel 也应该被清理。
其代码实现非常简单,只需要观察该 Activity 的 Lifecycle 状态,并在销毁状态时进行清理即可,关于 Lifecycle 我们将用专门的章节进行说明,以下为清理代码:
getLifecycle().addObserver(new LifecycleEventObserver() {
@Override
public void onStateChanged(@NonNull LifecycleOwner source,
@NonNull Lifecycle.Event event) {
if (event == Lifecycle.Event.ON_DESTROY) {
// 观察到 Activity 被销毁
if (!isChangingConfigurations()) {
// 若不是配置变化,则清理
getViewModelStore().clear();
}
}
}
});
5 多 Controller 共享 ViewModel
我们参考第3.1节的 ViewModelStore 树可知,如果多个 Controller 需要共享同一个 ViewModel 的话,我们只需要将该 ViewModel 保存在这些 Controller 共同的父 Controller 的 ViewModelStore 中即可,而这些子 Controller 可以通过如下方式获取这个共享的 ViewModel:
[Fragment/FragmentActivity] parentContrl = … // 共同的父 Controller
final CommonViewModel viewModel = ViewModelProviders.of(parentContrl).get(CommonViewModel.class);





















 604
604

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








