现假设有3个任务需要去处理,分别对应AsyncTask类的taskOne、taskTwo、taskThree方法,这里做了线程的sleep来模拟实际运行。
@Slf4j
@Component
public class AsyncTask {
private Random random = new Random();
public void taskOne() throws InterruptedException {
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
Thread.sleep(random.nextInt(10000));
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
log.info(“任务一执行完成耗时{}秒”, (end - start)/1000f);
}
public void taskTwo() throws InterruptedException {
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
Thread.sleep(random.nextInt(10000));
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
log.info(“任务二执行完成耗时{}秒”, (end - start)/1000f);
}
public void taskThree() throws InterruptedException {
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
Thread.sleep(random.nextInt(10000));
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
log.info(“任务三执行完成耗时{}秒”, (end - start)/1000f);
}
}
然后编写测试类,由于@Async注解需要再Spring容器启动后才能生效,所以这里讲测试类放到了SpringBoot的test包下,使用了SpringBootTest。
@Slf4j
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest(classes = SpringbootApplication.class)
public class AsyncTaskTest {
@Autowired
private AsyncTask asyncTask;
@Test
public void doAsyncTasks(){
try {
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
asyncTask.taskOne();
asyncTask.taskTwo();
asyncTask.taskThree();
Thread.sleep(5000);
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
log.info(“主程序执行完成耗时{}秒”, (end - start)/1000f);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
运行测试方法,可以在控制台看到任务一二三按顺序执行,最后主程序完成,这和我们的预期一样,因为我们没有任何额外的处理,他们就是普通的方法,按编码顺序依次执行。

而如果要使任务并发执行,我们只需要在任务方法上使用@Async注解即可,需要注意的是@Async所修饰的方法不要定义为static类型,这样异步调用不会生效。
@Slf4j
@Component
public class AsyncTask {
private Random random = new Random();
//@Async所修饰的函数不要定义为static类型,这样异步调用不会生效
@Async
public void taskOne() throws InterruptedException {
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
Thread.sleep(random.nextInt(10000));
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
log.info(“任务一执行完成耗时{}秒”, (end - start)/1000f);
}
@Async
public void taskTwo() throws InterruptedException {
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
Thread.sleep(random.nextInt(10000));
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
log.info(“任务二执行完成耗时{}秒”, (end - start)/1000f);
}
@Async
public void taskThree() throws InterruptedException {
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
Thread.sleep(random.nextInt(10000));
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
log.info(“任务三执行完成耗时{}秒”, (end - start)/1000f);
}
}
然后我们在运行测试类,这个时候输出可能就五花八门了,任意任务都可能先执行完成,也有可能有的方法因为主程序关闭而没有输出。
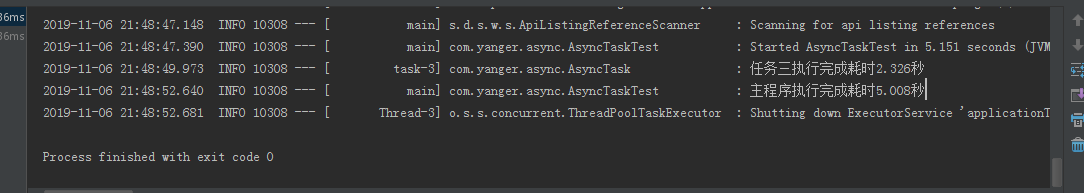
二、Future获取异步执行结果
上面演示了@Async,但是有时候除了需要任务并发调度外,我们还需要获取任务的返回值,且在多任务都执行完成后再结束主任务,这个时候又该怎么处理呢?
在多线程里通过Callable和Future可以获取返回值,这里也是类似的,我们使用Future返回方法的执行结果,AsyncResult是Future的一个实现类。
@Slf4j
@Component
public class FutureTask {
private Random random = new Random();
//@Async所修饰的函数不要定义为static类型,这样异步调用不会生效
@Async
public Future taskOne() throws InterruptedException {
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
Thread.sleep(random.nextInt(10000));
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
log.info(“任务一执行完成耗时{}秒”, (end - start)/1000f);
return new AsyncResult <>(“任务一Ok”);
}
@Async
public Future taskTwo() throws InterruptedException {
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
Thread.sleep(random.nextInt(10000));
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
log.info(“任务二执行完成耗时{}秒”, (end - start)/1000f);
return new AsyncResult <>(“任务二OK”);
}
@Async
public Future taskThree() throws InterruptedException {
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
Thread.sleep(random.nextInt(10000));
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
log.info(“任务三执行完成耗时{}秒”, (end - start)/1000f);
return new AsyncResult <>(“任务三Ok”);
}
}
在AsyncResult中:





















 320
320

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








