A 皇后
题目

代码
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
vector<vector<string>> result;
vector<string> chessboard;
int n;
// 检查在 (row, col) 位置放置皇后是否合法
bool able(int row, int col, const vector<string>& chessboard, int n)
{
// 检查列
for (int i = 0; i < row; i++)
{
if (chessboard[i][col] == 'Q')
{
return false;
}
}
// 检查 45 度角
for (int i = row - 1, j = col - 1; i >= 0 && j >= 0; i--, j--)
{
if (chessboard[i][j] == 'Q')
{
return false;
}
}
// 检查 135 度角
for (int i = row - 1, j = col + 1; i >= 0 && j < n; i--, j++)
{
if (chessboard[i][j] == 'Q')
{
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
// 深度优先搜索函数
void DFS(int row)
{
if (row == n)
{
result.push_back(chessboard);
return;
}
for (int col = 0; col < n; col++)
{
if (able(row, col, chessboard, n))
{
chessboard[row][col] = 'Q';
DFS(row + 1);
chessboard[row][col] = '.';
}
}
}
int main()
{
cin >> n;
// 初始化棋盘
chessboard = vector<string>(n, string(n, '.'));
DFS(0);
// 输出所有解
for (const auto& solution : result)
{
for (const auto& row : solution)
{
cout << row << endl;
}
cout << endl;
}
return 0;
}解析
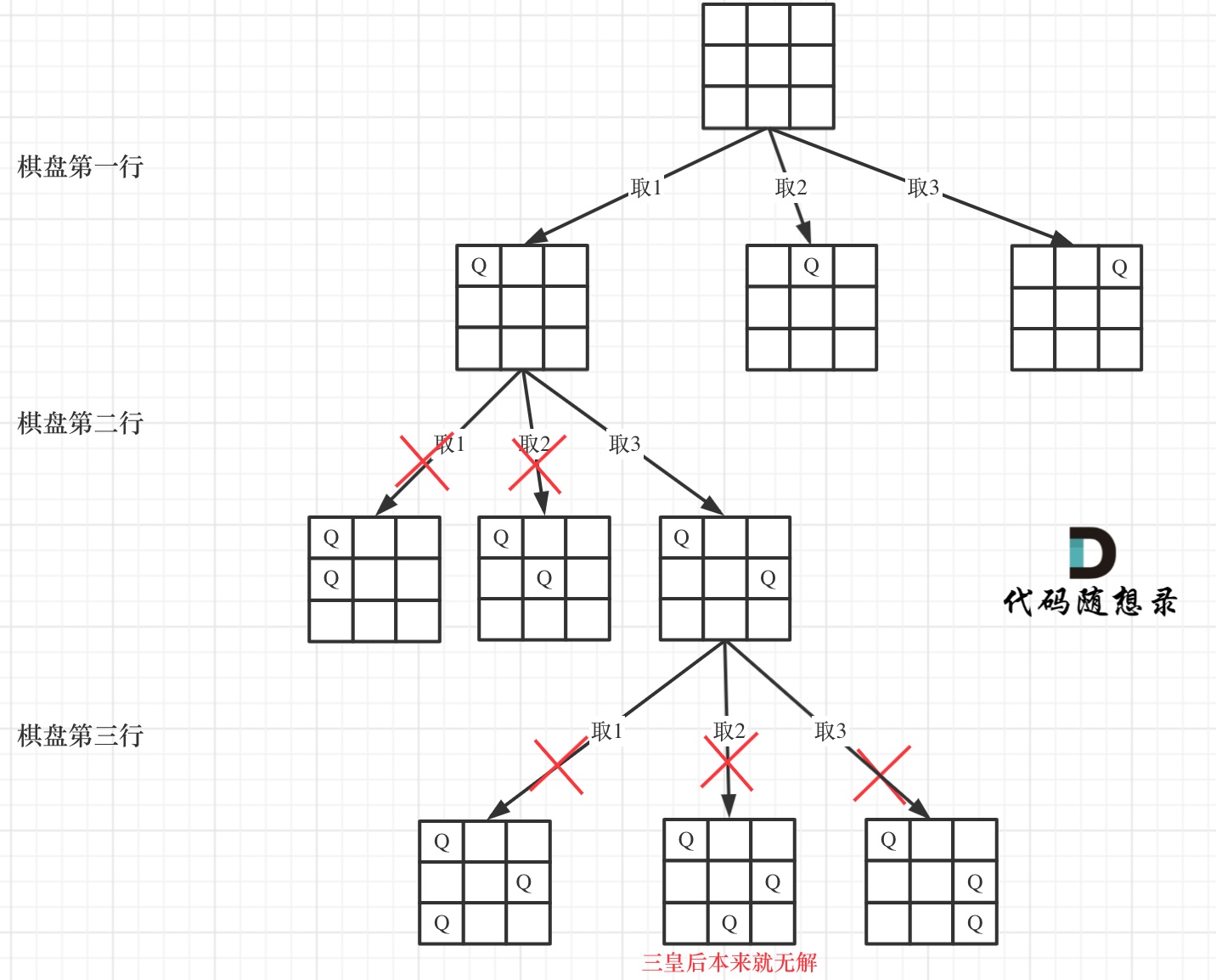
这是一道经典的N皇后模板题,使用DFS深度搜索每一行
图解
代码解析
chessboard = vector<string>(n, string(n, '.'));(棋盘初始化)
棋盘是一个vector<string>类型,在 N 皇后问题的场景中,这个 vector 容器的每一个 string 元素代表棋盘的一行
vector<string>(n,...):这里使用了 vector 的构造函数,n 作为参数传递给构造函数,表示要创建一个包含 n 个元素的 vector。也就是说,chessboard 这个容器将包含 n 个 string 类型的元素,对应着棋盘的 n 行。
string(n, '.'):这是一个 string 类型的构造函数调用。它表示创建一个长度为 n 的字符串,并且字符串中的每个字符都初始化为字符 '.'。在 N 皇后问题中,字符 '.' 通常用来表示棋盘上的空位置。
整体效果:vector<string>(n, string(n, '.')) 这样的表达式会创建一个包含 n 个 string 元素的 vector,每个 string 元素的长度都是 n,并且每个字符都被初始化为 '.'。这样就构建出了一个大小为 n x n 的棋盘,其中每个位置都被初始化为空(用 '.' 表示),为后续在棋盘上放置皇后并进行回溯搜索等操作做好了准备。
D 巧克力
题目

代码
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
const int dx[4] = { -1, 1, 0, 0 };
const int dy[4] = { 0, 0, -1, 1 };
int dfs(int x, int y, vector<vector<int>>& chocolate, vector<vector<bool>>& visited, int n, int m) {
if (x < 0 || x >= n || y < 0 || y >= m || visited[x][y] || chocolate[x][y] == 1) {
return 0;
}
visited[x][y] = true;
int area = 1;
for (int i = 0; i < 4; ++i) {
area += dfs(x + dx[i], y + dy[i], chocolate, visited, n, m);
}
return area;
}
int main() {
int n, m;
cin >> n >> m;
vector<vector<int>> chocolate(n, vector<int>(m));
vector<vector<bool>> visited(n, vector<bool>(m, false));
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
for (int j = 0; j < m; ++j) {
char c;
cin >> c;
chocolate[i][j] = c - '0';
}
}
int parts = 0;
int maxArea = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
for (int j = 0; j < m; ++j) {
if (!visited[i][j] && chocolate[i][j] == 0) {
++parts;
int area = dfs(i, j, chocolate, visited, n, m);
maxArea = max(maxArea, area);
}
}
}
cout << parts << " " << maxArea << endl;
return 0;
}1. vector<vector<int>> chocolate(n, vector<int>(m));
整体含义
这行代码创建了一个名为 chocolate 的二维整数向量(可以理解为一个二维数组),用来表示巧克力的状态。
详细拆解
vector<vector<int>>:这定义了一个嵌套的 std::vector 类型。外层的 std::vector 存储的元素是内层的 std::vector<int>,内层的 std::vector<int> 存储的是整数类型的数据。这样就构成了一个二维的数据结构,类似于一个二维数组。
chocolate:这是我们给这个二维向量起的名称,后续可以通过这个名称来操作这个二维向量。
(n, vector<int>(m)):这是调用 std::vector 的构造函数进行初始化。
n:表示外层 std::vector 的大小,也就是二维向量的行数。这里意味着 chocolate 这个二维向量有 n 行。
vector<int>(m):这是内层 std::vector 的初始化。m 表示内层 std::vector 的大小,也就是每行有 m 个元素。所以整体上,chocolate 这个二维向量是一个 n 行 m 列的矩阵,初始时每个元素的值是 int 类型的默认值(对于 int 类型,默认值是 0)。
2. vector<vector<bool>> visited(n, vector<bool>(m, false));
整体含义
这行代码创建了一个名为 visited 的二维布尔向量,用于标记巧克力棋盘上每个位置是否已经被访问过。
详细拆解
vector<vector<bool>>:同样是定义了一个嵌套的 std::vector 类型,外层 std::vector 存储的元素是内层的 std::vector<bool>,内层的 std::vector<bool> 存储的是布尔类型的数据。
visited:这是我们给这个二维向量起的名称,用于后续标记访问状态。
(n, vector<bool>(m, false)):这也是调用 std::vector 的构造函数进行初始化。
n:表示外层 std::vector 的大小,即二维向量的行数,说明 visited 有 n 行。
vector<bool>(m, false):这是内层 std::vector 的初始化。m 表示内层 std::vector 的大小,即每行有 m 个元素。false 是指定内层 std::vector 每个元素的初始值,所以整体上,visited 这个二维向量是一个 n 行 m 列的矩阵,并且每个元素的初始值都为 false,表示所有位置初始时都未被访问过。
E 寻找豆汁 ( Easy )
题目

代码
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <queue>
#include<map>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1010;
typedef pair<int, int> pii;
int dx[10] = { -1, -1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, -1 };
int dy[10] = { 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, -1, -1, -1 };
map<pii, pii> mp;
string g[N];
bool st[N][N];
int n, m;
int a, b, c, d;
void bfs()
{
queue<pii> q;
q.push({ a, b });
st[a][b] = true;
while (!q.empty())
{
auto r = q.front();
q.pop();
if (mp[{r.first, r.second}].first != 0)
{
int x = mp[{r.first, r.second}].first;
int y = mp[{r.first, r.second}].second;
if (x > 0 && x <= n && y > 0 && y <= m && !st[x][y] && g[x - 1][y - 1] == '.')
{
if (x == c && y == d)
{
cout << "YES" << endl;
return;
}
st[x][y] = true;
q.push({ x, y });
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < 8; ++i)
{
int newX = r.first + dx[i];
int newY = r.second + dy[i];
if (newX > 0 && newX <= n && newY > 0 && newY <= m && !st[newX][newY] && g[newX - 1][newY - 1] == '.') {
if (newX == c && newY == d)
{
cout << "YES" << endl;
return;
}
st[newX][newY] = true;
q.push({ newX, newY });
}
}
}
cout << "NO" << endl;
}
int main()
{
cin >> n >> m;
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i)
{
cin >> g[i];
}
cin >> a >> b >> c >> d;
bfs();
return 0;
}解析
初始化:
queue<pii> q;:创建一个存储 pii 类型(坐标)的队列 q。
q.push({ a, b });:将起点 (a, b) 加入队列。
st[a][b] = true;:标记起点已被访问。
BFS 主循环:
while (!q.empty()):只要队列不为空,就持续进行搜索。
auto r = q.front(); q.pop();:取出队列头部元素(当前要处理的坐标),并从队列中移除。
传送门处理:
if (mp[{r.first, r.second}].first != 0):检查当前位置是否存在传送门(即该位置是否是传送门入口)。
若存在传送门,获取传送门的出口坐标 (x, y)。
检查出口坐标是否合法:
在地图范围内(x > 0 && x <= n && y > 0 && y <= m)。
该位置未被访问过(!st[x][y])。
该位置是可通行的(g[x - 1][y - 1] == '.')。
若出口坐标是终点,则输出 YES 并返回。
若出口坐标合法但不是终点,标记该位置已访问,并将其加入队列继续搜索。
八方向移动:
for (int i = 0; i < 8; ++i):遍历八个方向。
计算向每个方向移动后的新坐标 (newX, newY)。
检查新坐标是否合法(同传送门出口坐标的检查条件)。
若新坐标是终点,则输出 YES 并返回。
若新坐标合法但不是终点,标记该位置已访问,并将其加入队列继续搜索。
无法到达终点:
若队列遍历完仍未找到终点,输出 NO。
F 寻找豆汁 ( Hard )
题目

代码
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <queue>
#include <map>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1010;
typedef pair<int, int> pii;
int dx[10] = { -1, -1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, -1 };
int dy[10] = { 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, -1, -1, -1 };
map<pii, pii> mp;
string g[N];
bool st[N][N];
int n, m, k;
int a, b, c, d;
void bfs()
{
queue<pii> q;
q.push({ a, b });
st[a][b] = true;
while (!q.empty())
{
auto r = q.front();
q.pop();
if (mp[{r.first, r.second}].first != 0)
{
int x = mp[{r.first, r.second}].first;
int y = mp[{r.first, r.second}].second;
if (x > 0 && x <= n && y > 0 && y <= m && !st[x][y] && g[x - 1][y - 1] == '.')
{
if (x == c && y == d)
{
cout << "YES" << endl;
return;
}
st[x][y] = true;
q.push({ x, y });
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < 8; ++i)
{
int newX = r.first + dx[i];
int newY = r.second + dy[i];
if (newX > 0 && newX <= n && newY > 0 && newY <= m && !st[newX][newY] && g[newX - 1][newY - 1] == '.') {
if (newX == c && newY == d)
{
cout << "YES" << endl;
return;
}
st[newX][newY] = true;
q.push({ newX, newY });
}
}
}
cout << "NO" << endl;
}
int main()
{
cin >> n >> m >> k;
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i)
{
cin >> g[i];
}
for (int i = 0; i < k; ++i)
{
int startX, startY, endX, endY;
cin >> startX >> startY >> endX >> endY;
mp[{startX, startY}] = { endX, endY };
}
cin >> a >> b >> c >> d;
bfs();
return 0;
}
解析
与Easy的区别:新增了变量 k,它的作用是记录传送门的数量,这表明当前代码支持处理多个传送门的情况
除了读取地图的行数、列数、地图信息以及起点和终点坐标外,还增加了对传送门信息的读取。通过循环 k 次,每次读取一个传送门的入口坐标 (startX, startY) 和出口坐标 (endX, endY),并将其存储到 mp 这个 map 中,以此来建立传送门的映射关系
G 路障
题目

代码
#include <iostream>
#include <queue>
#include <cstring>
#include <climits>
using namespace std;
const int MAXN = 1005;
int rst[MAXN][MAXN];
bool ch[MAXN][MAXN];
int n;
int dx[] = { -1, 1, 0, 0 };
int dy[] = { 0, 0, -1, 1 };
struct op {
int f, s, t;
};
void bfs()
{
queue<op> q;
q.push({ 1, 1, 0 });
ch[1][1] = true;
while (!q.empty())
{
auto r = q.front();
q.pop();
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++)
{
int x = r.f + dx[i];
int y = r.s + dy[i];
if (x > 0 && x <= n && y > 0 && y <= n && !ch[x][y] && r.t + 1 < rst[x][y])
{
if (x == n && y == n)
{
cout << "Yes\n";
return;
}
ch[x][y] = true;
q.push({ x, y, r.t + 1 });
}
}
}
cout << "No\n";
}
void solve() {
memset(rst, 0x3f, sizeof(rst));
memset(ch, false, sizeof(ch));
cin >> n;
for (int i = 1; i <= 2 * n - 2; i++)
{
int a, b;
cin >> a >> b;
rst[a][b] = min(rst[a][b], i);
}
rst[n][n] = INT_MAX;
bfs();
}
int main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0);
int t = 1;
cin >> t;
while (t--)
{
solve();
}
return 0;
}解析
struct op:定义了一个结构体 op,包含三个成员 f(表示 x 坐标)、s(表示 y 坐标)、t(表示时间),用于在 BFS 中记录位置和时间信息。
初始化:将起点 (1, 1) 以时间 0 加入队列 q,并标记起点已访问。
BFS 循环:当队列不为空时,取出队首元素 r。
遍历四个方向:对于每个方向,计算新位置 (x, y)。
检查新位置:如果新位置在网格内、未被访问过且在当前时间 r.t + 1 时没有障碍物(r.t + 1 < rst[x][y]),则进行以下操作:
如果新位置是终点 (n, n),输出 Yes 并返回。
标记新位置已访问,并将新位置及其时间 r.t + 1 加入队列。
如果循环结束仍未找到终点,输出 No。
初始化:将 rst 数组初始化为很大的值(表示无障碍物),将 ch 数组初始化为 false(表示未访问)。
输入网格大小 n。
读取障碍物信息:循环 2 * n - 2 次,每次读取一个障碍物的位置 (a, b),并记录其出现时间 i(取最小值,确保每个位置只记录最早出现障碍物的时间)。
将终点 (n, n) 的障碍物时间设为 INT_MAX,表示终点初始时无障碍物。
调用 bfs 函数进行搜索。
























 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








