一:前缀树(trie)
概念:
1.利用字符串的公共前缀来节省存储空间,并加速查找、插入和删除操作
2.相邻的两个节点之间的路径代表一个字符
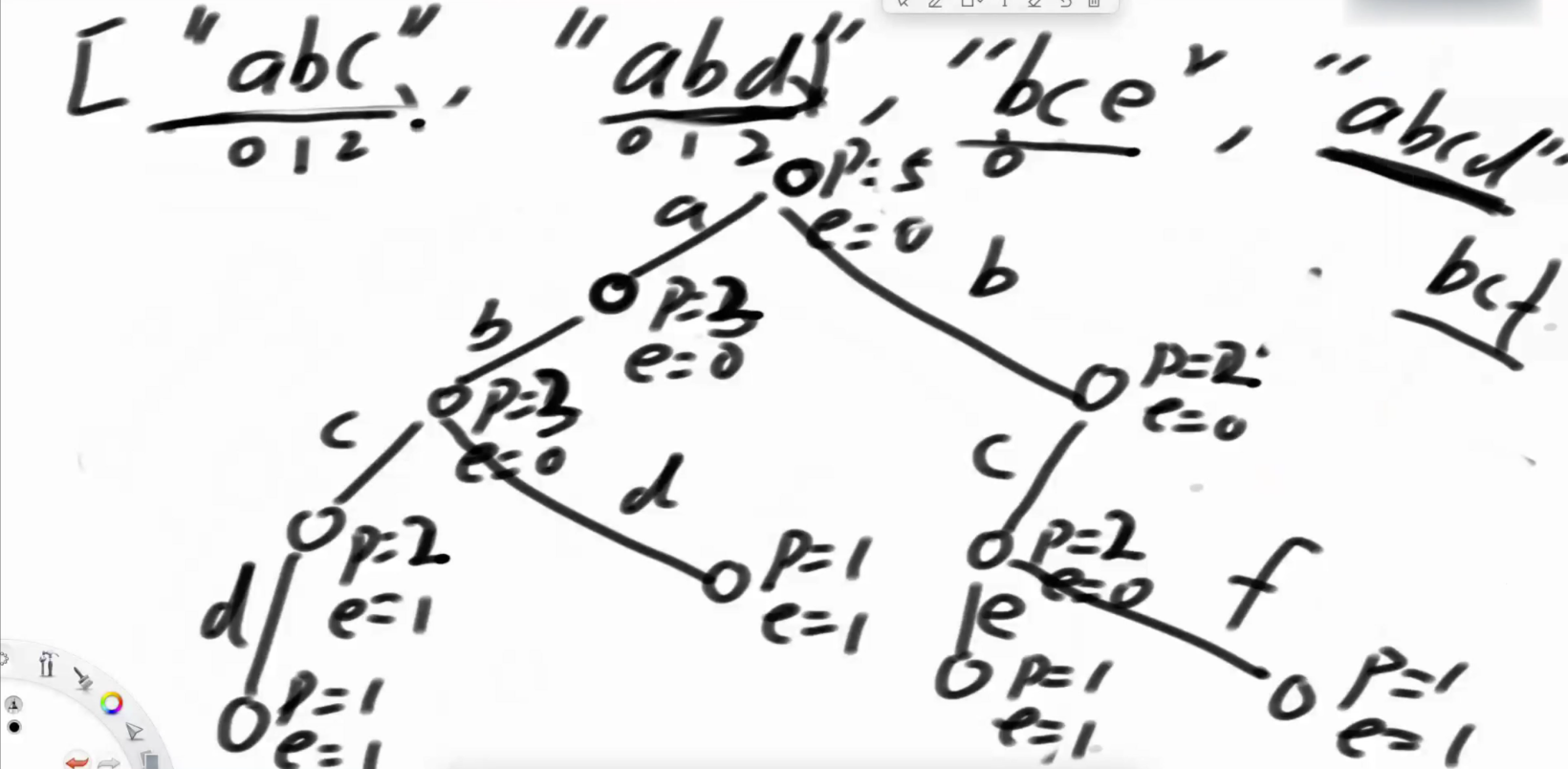
如上图每个节点旁的p(pass) 表示在加字符串时这个节点到达过几次,e(end) 表示当前这个节点有多少个字符串以他结尾
构建前缀树
可以理解为每个节点有26个节点待连接,当path为几时就创建为几的节点
public static class Node1{//构建前缀树
public int pass;
public int end;
public Node1[] nexts;
public Node1(){
pass=0;
end=0;
nexts=new Node1[26];
}
}
实现前缀树(增加,查找字符串个数,查找以pre为前缀的字符串个数,删除)
public static class Trie1{//实现前缀树
private Node1 root;
public Trie1(){
root=new Node1();
}
public void insert(String word){//插入
if(word==null)
return;
char[] str=word.toCharArray();
Node1 node=root;//用于记录节点pass和end加减的
node.pass++;
int path=0;
for(int i=0;i<str.length;i++)
{
path=str[i]-'a';//对应走那条路
if(node.nexts[path]==null)
node.nexts[path]=new Node1();
node=node.nexts[path];//下沉
node.pass++;
}
node.end++;
}
public int Search(String word){//查找这个字符串的个数
if(word==null)
return 0;
Node1 node=root;
char[] str=word.toCharArray();
int path=0;
for(int i=0;i<str.length;i++)
{
path=str[i]-'a';
if(node.nexts[path]==null)
return 0;
node=node.nexts[path];
}
return node.end;
}
public int prefixNumber(String pre){//有几个是以pre字符串作为前缀的
if(pre==null)
return 0;
Node1 node=root;
char[] str=pre.toCharArray();
int path=0;
for(int i=0;i<str.length;i++)
{
path=str[i]-'a';
if(node.nexts[path]==null)
return 0;
node=node.nexts[path];
}
return node.pass;
}
public void delete(String word){//删除字符串
if(Search(word)!=0)//树中存在要删除的字符串
{
Node1 node=root;
char[] str=word.toCharArray();
int path=0;
for(int i=0;i<str.length;i++)
{
path=str[i]='a';
if(--node.nexts[path].pass==0)//如果减了之后就没有了就可以直接断掉后面的
{
node.nexts[path]=null;
return;
}
node=node.nexts[path];
}
node.end--;//树中存在多个此字符串
}
}
}
}
二:二叉树
1.递归遍历二叉树
前序遍历
public static void pre(Node head) {
if (head == null) {
return;
}
System.out.println(head.value); // 第一次到达节点时处理
pre(head.left);
pre(head.right);
}
中序遍历
public static void in(Node head) {
if (head == null) {
return;
}
in(head.left);
System.out.println(head.value); // 从左子树返回时处理
in(head.right);
}
后序遍历
public static void pos(Node head) {
if (head == null) {
return;
}
pos(head.left);
pos(head.right);
System.out.println(head.value); // 从右子树返回时处理
}
2.非递归遍历二叉树
构建二叉树
public static class Node {
public int value;
public Node left;
public Node right;
public Node(int v) {
value = v;
}
}
前序遍历
public static void pre(Node head) {
System.out.print("前序遍历为: ");
if (head != null) {
Stack<Node> stack = new Stack<Node>();
stack.add(head);
while (!stack.isEmpty()) {
head = stack.pop();
System.out.print(head.value + " ");
if (head.right != null) {
//先将右孩子压入栈
stack.push(head.right);
}
if (head.left != null) {
//再将左孩子压入栈
stack.push(head.left);
}
}
}
System.out.println();
}
后序遍历
第一个栈出来为(右->左-> 根),第二个栈出来就是后序遍历
public static void pos1(Node head) {
System.out.print("后序遍历为: ");
if (head != null) {
Stack<Node> s1 = new Stack<Node>();
Stack<Node> s2 = new Stack<Node>();
s1.push(head);
while (!s1.isEmpty()) {
head = s1.pop();
// 头节点先进入s2(使得出栈时右节点先出)
s2.push(head);
if (head.left != null) {
s1.push(head.left);
}
if (head.right != null) {
s1.push(head.right);
}
}
// s2弹出顺序就是后序
while (!s2.isEmpty()) {
System.out.print(s2.pop().value + " ");
}
}
System.out.println();
}
中序遍历
public static void in(Node cur) {
System.out.print("中序遍历为: ");
if (cur != null) {
Stack<Node> stack = new Stack<Node>();
while (!stack.isEmpty() || cur != null) {
if (cur != null) {
stack.push(cur);
cur = cur.left;
} else {
cur = stack.pop();
System.out.print(cur.value + " ");
cur = cur.right;
}
}
}
System.out.println();
}
层序遍历
public static void level(Node head){
if(head==null)
return;
Queue<Node> queue=new LinkedList<>();//双端队列
queue.add(head);
while(!queue.isEmpty())
{
Node cur=queue.poll();
System.out.print(cur.value+" ");
if(cur.left!=null){
queue.add(cur.left);
}
if(cur.right!=null){
queue.add(cur.right);
}
}
}
3.二叉树的序列化和反序列化
序列化:给定一个树,将他转换成字符串
反序列化:给定一个序列化过的字符串将他还原成树的结构
二叉树的先序序列化
public static Queue<String> preSerial(Node head){
Queue<String> ans = new LinkedList<>();
pres(head,ans);
return ans;
}
public static void pres(Node head,Queue<String> ans){
if(head==null)
ans.add(null);
ans.add(String.valueOf(head.value));
pres(head.left,ans);
pres(head.right,ans);
}
二叉树的先序反序列化
public static Node bulidByPreQueue(Queue<String> prelist){
if(prelist==null|| prelist.size()==0)
return null;
return preb(prelist);
}
public static Node preb(Queue<String> prelist){
String value=prelist.poll();
if(value==null)
return null;
Node head=new Node(Integer.valueOf(value));//将value转换成整形后赋值给head.value
head.left=preb(prelist);//递归head的左子树
head.right=preb(prelist);//递归head的右子树
return head;
}
二叉树的层序序列化
public static Queue<String> levelSerial(Node head){
Queue<String> ans=new LinkedList<>();//用于序列化
if(head==null)
ans.add(null);
else
{
ans.add(String.valueOf(head.value));//序列化
Queue<Node> queue=new LinkedList<>();
queue.add(head);
while(!queue.isEmpty())
{
head=queue.poll();
if(head.left!=null)
{
ans.add(String.valueOf(head.left.value));
queue.add(head.left);
}else{
ans.add(null);
}
if(head.right!=null)
{
ans.add(String.valueOf(head.right.value));
queue.add(head.right);
}else{
ans.add(null);
}
}
}
return ans;
}
二叉树的层序反序列化
public static Node bulidByLevelQueue(Queue<String> levellist){
if(levellist==null||levellist.size()==0)
return null;
Node head=generateNode(levellist.poll());//头节点
Queue<Node> queue=new LinkedList<>();
queue.add(head);
Node node=null;
while(!queue.isEmpty())
{
node=queue.poll();//头节点
node.left=generateNode(levellist.poll());//反序列化
node.right=generateNode(levellist.poll());
if(node.left!=null)
queue.add(node.left);
if(node.right!=null)
queue.add(node.right);
}
return head;
}
//类型转换
public static Node generateNode(String val){
if(val==null)
return null;
return new Node(Integer.valueOf(val));
}
二叉树的递归套路!!!
1.假设以X节点为头,假设可以向X的左子树和右子树要任何信息
2.在上一步的假设下讨论以X为头节点的树,得到答案的可能性(最重要)
3.列出所有可能性后确定要向左树和右数要什么样的信息(重要)
4.把左树信息和右树信息求全集,就是任何一颗子树都要返回的信息Info
5.递归函数都返回Info每一颗子树都这么要求
6.写代码时,在代码中考虑如何把左树的信息和右树的信息整合出整棵树的信息
1.平衡二叉树
定义:每一颗子树的左数高度和右数高度差<=1,只要有一个子树不符合那么整个二叉树就不是平衡二叉树
==题目:==判断一颗二叉树是否是平衡二叉树
解题方法二叉树的递归,信息体(boolean判断是否是平衡树(isBalance),子树的长度)
当子树两边的长度的差值>1时isBalance=false.
信息体
public static class Info{//信息体
public boolean isBalance;
public int height;
public Info(boolean is,int len){
isBalance=is;
this.height=len;
}
}
2.搜索二叉树(BST)
定义:每一颗子树的左树都比头节点小,右树都比头节点大
题目: 判断一颗二叉树是否是搜索二叉树
解题方法二叉树的递归,信息体(boolean判断是否是搜索二叉树(isBST),最大值,最小值)
当左子树的max大于等于头节点或者右子树的min<=头节点时isBST=false
信息体
public static class Info{//信息体
public boolean isBST;
public int max;
public int min;
public Info(boolean is,int ma,int mi){
isBST=is;
max=ma;
min=mi;
}
}
3.完全二叉树
定义:二叉树中最下层的所有节点都集中在左边,其它各层的节点数都达到最大值
题目: 判断一颗二叉树是否是完全二叉树
解题方法: 答案的可能性:1.左满右满,左高=右高 2.左完右满,左高=右高+1
3.左满右满,左高=右高+1 (4)左满右完,左高=右高
信息体(是否时满二叉树,是否是完全二叉树,高度)
public static boolean isCBT2(Node head){//主函数
return process(head).isCBT;
}
public static class Node{
public int value;
public Node left;
public Node right;
public Node(int data){
this.value=data;
}
}
public static class Info{//信息体
public boolean isCBT;//是否为完全二叉树
public boolean isFull;//是否为满二叉树
public int height;//高度
public Info(boolean isc,boolean isf,int h){
isCBT=isc;
isFull=isf;
height=h;
}
}
public static Info process(Node head){
if(head==null)
return new Info(true,true,0);
Info leftInfo=process(head.left);
Info rightInfo=process(head.right);
int height=Math.max(leftInfo.height, rightInfo.height)+1;
//满二叉树的判断条件:左右子树都是满二叉树并且题目的高度相等
boolean isFull=(leftInfo.isFull&& rightInfo.isFull&&leftInfo.height== rightInfo.height);
boolean isCBT=false;
//事先分析出的4种可能性
if(leftInfo.isFull&& rightInfo.isFull&&leftInfo.height== rightInfo.height)
isCBT=true;
else if(leftInfo.isCBT&&rightInfo.isFull&&leftInfo.height== rightInfo.height+1)
isCBT=true;
else if(leftInfo.isFull&& rightInfo.isFull&&leftInfo.height== rightInfo.height+1)
isCBT=true;
else if(leftInfo.isFull&& rightInfo.isCBT&&leftInfo.height== rightInfo.height)
isCBT=true;
return new Info(isCBT,isFull,height);
}
























 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








