1.栈的表示和实现
1.1栈的概念及结构
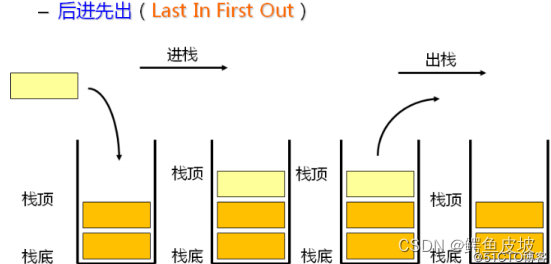
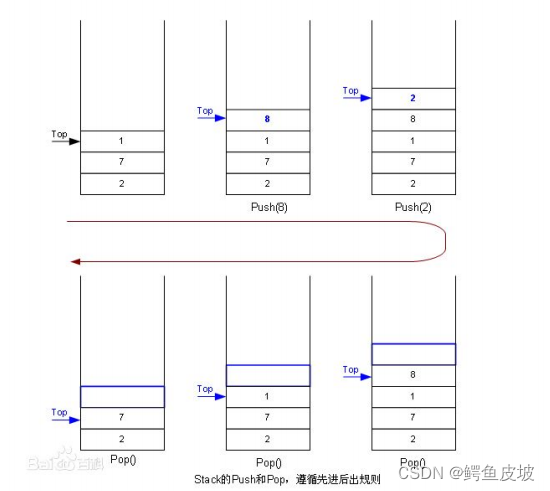
栈:一种特殊的线性表,其只允许在固定的一端进行插入和删除元素操作。进行数据插入和删除
操作的一端称为栈顶,另一端称为栈底。栈中的数据元素遵守后进先出LIFO(Last In First Out)的原则。
压栈:栈的插入操作叫做进栈/压栈/入栈,入数据在栈顶。
出栈:栈的删除操作叫做出栈。出数据也在栈顶。
1.2栈的实现
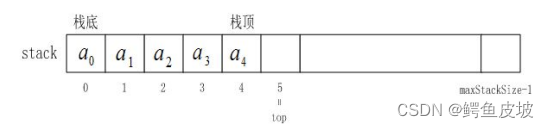
栈的实现一般可以使用数组或者链表实现,相对而言数组的结构实现更优一些。因为数组在尾上插入数据的代价比较小。

#pragma once
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<stdbool.h>
#include<assert.h>
typedef int STDataType;
typedef struct stack
{
STDataType* a;
int top;
int capacity;
}ST;
//初始化
void STInit(ST *pst);
//销毁
void STDestroy(ST *pst);
//入栈 出栈
void STPush(ST* pst, STDataType x);
void STPop(ST* pst);
//取栈顶数据
STDataType STTop(ST* pst);
//判空
bool STEmpty(ST* pst);
//获取数据个数
int STSize(ST* pst);#include"Stack.h"
//初始化
void STInit(ST* pst)
{
assert(pst);
pst->a = NULL;
pst->top = 0;
pst->capacity = 0;
}
//销毁
void STDestroy(ST* pst)
{
assert(pst);
free(pst->a);
pst->a = NULL;
pst->top = pst->capacity = 0;
}
//入栈 出栈
void STPush(ST* pst, STDataType x)
{
assert(pst);
//扩容
if (pst->top == pst->capacity)
{
int newcapacity = pst->capacity == 0 ? 4 : pst->capacity * 2;
STDataType* tmp = (STDataType*)realloc(pst->a, newcapacity * sizeof(STDataType));
if (tmp == NULL)
{
perror("realloc fail");
return;
}
pst->a = tmp;
pst->capacity = newcapacity;
}
pst->a[pst->top] = x;
pst->top++;
}
void STPop(ST* pst)
{
assert(pst);
assert(pst->top > 0);
pst->top--;
}
//取栈顶数据
STDataType STTop(ST* pst)
{
assert(pst);
assert(pst->top > 0);
return pst->a[pst->top - 1];
}
//判空
bool STEmpty(ST* pst)
{
assert(pst);
return pst->top == 0;
}
//获取数据个数
int STSize(ST* pst)
{
assert(pst);
return pst->top;
}2.队列的表示和实现
2.1栈的概念及结构
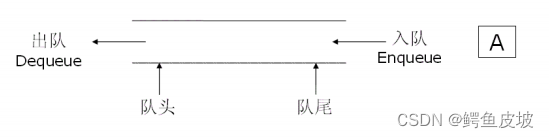
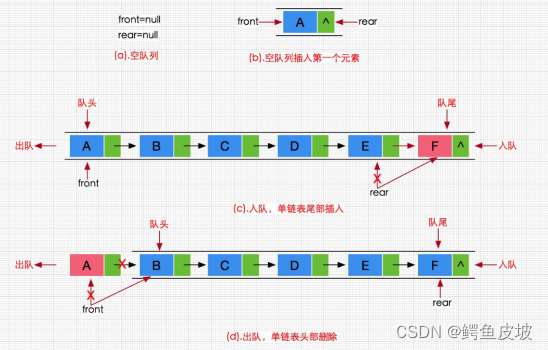
队列:只允许在一端进行插入数据操作,在另一端进行删除数据操作的特殊线性表,队列具有先进先出FIFO(First In First Out)
入队列:进行插入操作的一端称为队尾
出队列:进行删除操作的一端称为队头
2.2栈的实现
队列也可以数组和链表的结构实现,使用链表的结构实现更优一些,因为如果使用数组的结构,出队列在数组头上出数据,效率会比较低。
#pragma once
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<stdbool.h>
#include<assert.h>
typedef int QDataType;
typedef struct QueueNode
{
struct QueueNode* next;
QDataType val;
}QNode;
typedef struct Queue
{
QNode* phead;
QNode* ptail;
int* size;
}Queue;
//初始化
void QueneInit(Queue* pq);
//队尾插入
void QueuePush(Queue*pq, QDataType x);
//
int QueueSize(Queue pq);
//队头删除
void QueuePop(Queue* pq);
//取队头和队尾的数据
QDataType QueueFront(Queue* pq);
QDataType QueueBack(Queue* pq);
//销毁
void QueneDestroy(Queue* pq);#include"Quene.h"
//初始化
void QueneInit(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
pq->phead = NULL;
pq->ptail = NULL;
pq->size = 0;
}
//队尾插入
void QueuePush(Queue* pq, QDataType x)
{
QNode* newnode = (QNode*)malloc(sizeof(QNode));
if (newnode == NULL)
{
perror("malloc fail");
return;
}
newnode->next = NULL;
newnode->val = x;
if (pq->ptail == NULL)
{
pq->phead = pq->ptail = newnode;
}
else
{
pq->ptail->next = newnode;
pq->ptail = newnode;
}
pq->size++;
}
int QueueSize(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
return pq->size;
}
//队头删除
void QueuePop(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
assert(pq->size!=0);
if (pq->phead->next == NULL)
{
free(pq->phead);
pq->phead = pq->ptail = NULL;
}
else//多个节点
{
QNode* next = pq->phead->next;
free(pq->phead);
pq->phead = next;
}
pq->size--;
}
//取队头和队尾的数据
QDataType QueueFront(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
assert(pq->phead);
return pq->phead->val;
}
QDataType QueueBack(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
assert(pq->ptail);
return pq->ptail->val;
}
void QueneDestroy(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
QNode* cur = pq->phead;
while (cur)
{
QNode* next = cur->next;
free(cur);
cur = next;
}
pq->phead = pq->ptail = NULL;
pq->size = 0;
}本篇文章介绍了栈和队列。如果本篇有补充的地方,欢迎私信我或在评论区指出,期待与你们共同进步。





















 6317
6317











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








