邻接边顶点类
public class ArcNode {//邻接边顶点类
public int adjvex;//邻接顶点的索引
public ArcNode next;
}顶点类
public class VertexNode {//顶点类
public char vertex;//数据
public ArcNode firstedge;//邻接边顶点类的与顶点相连的边
}图结构
public class graph {//图结构
/**
* 1.广度优先和深度优先为什么不一样?(递归和非递归)
* 广度每次操作都是一样的都是去找下一个
* 深度每次所面临情况不一样,相邻节点的边数是不同的
* 2.广度为什么不用栈而是用队列
* 因为先进先出,用栈的话则会变成广度
*/
public VertexNode[] graph = new VertexNode[6];//创建一个顶点类的数组
public int[] visted = new int[]{0,0,0,0,0,0};//创建一个可以记录是否被访问过的数组,访问过为1,未访问过为0
public void createGraph(char[] vertexs,int[][] edges,int vertexNum,int edgeNum){//传入顶点的数据,边,顶点个数,边的个数
int i;
for(i=0;i<vertexNum;i++){
graph[i]=new VertexNode();
graph[i].vertex = vertexs[i];//将传进去的数据赋值到顶点
graph[i].firstedge = null;//将所有邻接边初始化为null
}
int j;
for(j=0;j<edgeNum;j++){//无向图需要双向奔赴,把顶点逐个赋值,把邻接边和顶点连接起来
//将边的数据分别放入m和n
int m = edges[j][0];
int n = edges[j][1];
ArcNode node1 = new ArcNode();
node1.adjvex=n;//把n赋给node1的第一个位置做索引
node1.next=graph[m].firstedge;
graph[m].firstedge=node1;
//如果是有向图,则下面不用写
ArcNode node2 = new ArcNode();
node2.adjvex=m;//把m赋给node2的第一个位置
node2.next=graph[n].firstedge;
graph[n].firstedge=node2;
}
}
public void DFSVisit(int start){//深度优先
System.out.println(graph[start].vertex);//遍历结点
visted[start]=1;//将此设为一,表示已经访问过
ArcNode p = graph[start].firstedge;//将邻接边顶点赋给p
while(p!=null){
int vex = p.adjvex;
if(visted[vex]==0){
DFSVisit(vex);//若此结点没被访问过,则递归再次使用此方法
}
p=p.next;
}
}
public void WFSVisit(int start){//广度优先
int front,rear;//定义头指针和尾指针
front=rear=-1;
int queue[] = new int[6];
int i=0;
for(;i<6;i++){
visted[i]=0;
}
System.out.println(graph[start].vertex);
visted[start]=1;
queue[++rear]=start;
while (front!=rear){//队列非空
int vex = queue[++front];//队列第一个元素出队
ArcNode p = graph[vex].firstedge;//把第一个邻接点赋给p
while (p!=null){//邻接点非空
int j=p.adjvex;
if(visted[j]==0){//没有被访问过
System.out.println(graph[j].vertex);
visted[j]=1;
queue[++rear]=j;
}
p=p.next;
}
}
}
}
测试类
public class GraphTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
char[] vertexs = new char[]{'a','b','c','d','e','f'};
int [][] edge = new int[8][2];
edge= new int[][]{{0, 1}, {0, 3}, {0, 4}, {1, 4}, {1, 2}, {2, 4}, {2, 5}, {4, 5}};
graph g = new graph();
g.createGraph(vertexs,edge,6,8);
g.DFSVisit(0);
System.out.println();
g.WFSVisit(0);
}
}
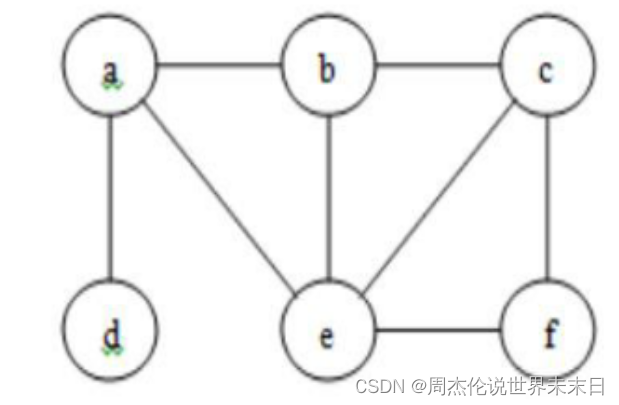

不懂的建议留言,尽量先去哔站看看基础的视频,先了解邻接表





















 3219
3219

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








