集美大学课程实验报告-实验5-图
| 项目名称 | 内容 |
|---|---|
| 课程名称 | 数据结构 |
| 班级 | 网安2412 |
| 指导教师 | 郑如滨 |
| 学生姓名 | 缪书华 |
| 学号 | 202421336060 |
| 实验项目名称 | 实验5-图 |
| 上机实践日期 | 2025.5.15 |
| 上机实践时间 | 2学时 |
一、目的(本次实验所涉及并要求掌握的知识点)
- 理解图的概念和基础知识
- 学习有向图的创建和遍历及基础操作
- 学习应用
二、实验内容与设计思想
题目1:图的创建—题目2:图的遍历
时间复杂度和空间复杂度
- initGraph
时间复杂度:O(n^2)
空间复杂度:O(1) - addVertex
时间复杂度:O(1)
空间复杂度:O(1) - addEdge
时间复杂度:O(1)
空间复杂度:O(1) - printGraph
时间复杂度:O(n^2)
空间复杂度:O(1) - DFS
时间复杂度:O(n)
空间复杂度:O(n) - BFS
时间复杂度:O(n)
空间复杂度:O(n)
函数相关伪代码
// 图的初始化
initGraph
将G的顶点数vertexNum设置为n
将G的边数arcNum设置为m
遍历邻接矩阵adjMatrix的每一个元素,将其值设置为0
end
// 添加顶点
addVertex
将顶点字符vertex存储到G的vexs数组的index位置
在G的vertexIndex映射中,将顶点字符vertex映射到索引index
end
// 添加边
addEdge
根据G的vertexIndex映射,获取顶点u的索引uIndex
根据G的vertexIndex映射,获取顶点v的索引vIndex
将G的邻接矩阵adjMatrix中uIndex行vIndex列的元素值设置为cost
将G的邻接矩阵adjMatrix中vIndex行uIndex列的元素值设置为cost
end
// 打印图
printGraph
打印提示信息“顶点列表: ”
遍历G的vexs数组,依次打印每个顶点字符
换行
打印提示信息“邻接矩阵: ”
打印一个空格和制表符
遍历G的vexs数组,依次打印每个顶点字符作为列标题
换行
遍历G的vexs数组,对于每个顶点字符:
打印该顶点字符和一个空格
再遍历G的vexs数组,对于每个顶点字符:
打印G的邻接矩阵adjMatrix中对应位置的元素值和一个空格
换行
end
// 深度优先搜索
DFS
将visited数组中start位置的元素设置为true,表示已访问
将G的vexs数组中start位置的顶点字符添加到result字符串中
遍历G的vexs数组,对于每个顶点字符对应的索引i:
如果G的邻接矩阵adjMatrix中start行i列的元素值不为0,且visited数组中i位置的元素为false(未访问):
递归调用DFS函数,传入G、i、visited和result
end
// 广度优先搜索
BFS
创建一个整数类型的队列q
将start入队到队列q中
将visited数组中start位置的元素设置为true,表示已访问
将G的vexs数组中start位置的顶点字符添加到result字符串中
当队列q不为空时:
取出队列q的队首元素,赋值给变量current
将队首元素出队
遍历G的vexs数组,对于每个顶点字符对应的索引i:
如果G的邻接矩阵adjMatrix中current行i列的元素值不为0,且visited数组中i位置的元素为false(未访问):
将visited数组中i位置的元素设置为true
将G的vexs数组中i位置的顶点字符添加到result字符串中
将i入队到队列q中
end
// 主函数
main函数:
创建Graph类型的对象G
读入顶点数n和边数m
调用initGraph进行图的初始化
输入每个顶点的字符,依次调用addVertex函数,传入G、顶点字符和对应的索引进行顶点添加
输入每条边的两个顶点字符和边的权值,依次调用addEdge函数,传入G、顶点字符和权值进行边的添加
调用printGraph函数,传入G进行图的打印
创建一个布尔数组visited,大小为MAX_VERTEX,并初始化为false
创建一个空字符串dfsResultA
调用DFS函数,传入G、从G的vertexIndex映射中获取的字符'a'对应的索引、visited和dfsResultA
打印提示信息“从A节点进行DFS,遍历结果为: ”和dfsResultA
将visited数组重新初始化为false
创建一个空字符串dfsResultF
调用DFS函数,传入G、从G的vertexIndex映射中获取的字符'f'对应的索引、visited和dfsResultF
打印提示信息“从F节点进行DFS,遍历结果为: ”和dfsResultF
将visited数组重新初始化为false
创建一个空字符串bfsResultF
调用BFS函数,传入G、从G的vertexIndex映射中获取的字符'f'对应的索引、visited和bfsResultF
打印提示信息“从F节点进行BFS,遍历结果为: ”和bfsResultF
返回0
end
函数代码
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <map>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
#define MAX_VERTEX 100
struct Graph {
int vertexNum;
int arcNum;
char vexs[MAX_VERTEX]; // 存储顶点名称
int adjMatrix[MAX_VERTEX][MAX_VERTEX];
map<char, int> vertexIndex; // 顶点名称到索引的映射
};
void initGraph(Graph& G, int n, int m) {
G.vertexNum = n;
G.arcNum = m;
memset(G.adjMatrix, 0, sizeof(G.adjMatrix));
}
void addVertex(Graph& G, char vertex, int index) {
G.vexs[index] = vertex;
G.vertexIndex[vertex] = index;
}
void addEdge(Graph& G, char u, char v, int cost) {
int uIndex = G.vertexIndex[u];
int vIndex = G.vertexIndex[v];
G.adjMatrix[uIndex][vIndex] = cost;
G.adjMatrix[vIndex][uIndex] = cost;
}
void printGraph(Graph& G) {
cout << "顶点列表: ";
for (int i = 0; i < G.vertexNum; ++i) {
cout << G.vexs[i] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
cout << "邻接矩阵: " << endl;
cout << " ";
for (int i = 0; i < G.vertexNum; ++i) {
cout << G.vexs[i] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
for (int i = 0; i < G.vertexNum; ++i) {
cout << G.vexs[i] << " ";
for (int j = 0; j < G.vertexNum; ++j) {
cout << G.adjMatrix[i][j] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
}
void DFS(Graph& G, int start, bool visited[], string& result) {
visited[start] = true;
result += G.vexs[start];
for (int i = 0; i < G.vertexNum; ++i) {
if (G.adjMatrix[start][i] != 0 && !visited[i]) {
DFS(G, i, visited, result);
}
}
}
void BFS(Graph& G, int start, bool visited[], string& result) {
queue<int> q;
q.push(start);
visited[start] = true;
result += G.vexs[start];
while (!q.empty()) {
int current = q.front();
q.pop();
for (int i = 0; i < G.vertexNum; ++i) {
if (G.adjMatrix[current][i] != 0 && !visited[i]) {
visited[i] = true;
result += G.vexs[i];
q.push(i);
}
}
}
}
int main() {
Graph G;
int n, m;
cout << "输入顶点数和边数: ";
cin >> n >> m;
initGraph(G, n, m);
cout << "输入顶点: ";
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
char vertex;
cin >> vertex;
addVertex(G, vertex, i);
}
cout << "输入边: " << endl;
for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i) {
char u, v;
int cost;
cin >> u >> v >> cost;
addEdge(G, u, v, cost);
}
printGraph(G);
// 从A节点进行DFS
bool visited[MAX_VERTEX] = { false };
string dfsResultA;
DFS(G, G.vertexIndex['a'], visited, dfsResultA);
cout << "从A节点进行DFS,遍历结果为: " << dfsResultA << endl;
// 从F节点进行DFS
memset(visited, false, sizeof(visited));
string dfsResultF;
DFS(G, G.vertexIndex['f'], visited, dfsResultF);
cout << "从F节点进行DFS,遍历结果为: " << dfsResultF << endl;
// 从F节点进行BFS
memset(visited, false, sizeof(visited));
string bfsResultF;
BFS(G, G.vertexIndex['f'], visited, bfsResultF);
cout << "从F节点进行BFS,遍历结果为: " << bfsResultF << endl;
return 0;
}
题目3:图着色问题
时间复杂度和空间复杂度
- main
时间复杂度:O(E+N(V+E))
空间复杂度:O(E+NV)
函数相关伪代码
main() {
读取顶点数 V,边数 E,颜色数 K
创建一个大小为 V + 1 的二维向量 adj 用于存储邻接表(索引从 1 到 V)
// 构建邻接表
for i 从 0 到 E - 1 {
读取边的两个端点 u 和 v
将 v 添加到 adj[u] 中
将 u 添加到 adj[v] 中
}
读取方案数 N
// 处理每个颜色分配方案
for i 从 0 到 N - 1 {
创建一个大小为 V 的向量 colors 用于存储顶点颜色
创建一个无序集合 color_set 用于存储颜色集合
// 读取顶点颜色并插入到颜色集合中
for j 从 0 到 V - 1 {
读取 colors[j]
将 colors[j] 插入到 color_set 中
}
// 检查颜色集合大小是否等于 K
如果 color_set 的大小不等于 K {
输出 "No"
继续下一个方案
}
设 valid 为 true
// 检查相邻顶点颜色是否相同
for u 从 1 到 V 循环 {
for v 在 adj[u] 中循环 {
如果 colors[u - 1] 等于 colors[v - 1] {
valid 设为 false
跳出内层循环
}
}
如果 valid 为 false {
跳出外层循环
}
}
// 输出结果
如果 valid 为 true {
输出 Yes
} else {
输出 No
}
}
return 0
}
函数代码
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <unordered_set>
using namespace std;
int main() {
int V, E, K;
cin >> V >> E >> K;
vector<vector<int>> adj(V + 1); // 从1到V
for (int i = 0; i < E; ++i) {
int u, v;
cin >> u >> v;
adj[u].push_back(v);
adj[v].push_back(u);
}
int N;
cin >> N;
for (int i = 0; i < N; ++i) {
vector<int> colors(V);
unordered_set<int> color_set;
for (int j = 0; j < V; ++j) {
cin >> colors[j];
color_set.insert(colors[j]);
}
if (color_set.size() != K) {
cout << "No" << endl;
continue;
}
bool valid = true;
for (int u = 1; u <= V; ++u) {
for (int v : adj[u]) {
if (colors[u - 1] == colors[v - 1]) {
valid = false;
break;
}
}
if (!valid) break;
}
cout << (valid ? "Yes" : "No") << endl;
}
return 0;
}
题目4:公路村村通(最小生成树)
时间复杂度和空间复杂度
- find
时间复杂度:O(n)
空间复杂度:O(1) - unite
时间复杂度:O(n)
空间复杂度:O(1)
函数相关伪代码
// 查找函数
find(int u) {
if parent[u] != u {
parent[u] = find(parent[u]);
}
return parent[u];
}
// 合并函数
unite(int u, int v) {
u = find(u);
v = find(v);
if u 等于 v {
返回 false;
}
parent[v] = u;
返回 true;
}
// 主函数
main() {
读取顶点数 n 和边数 m
创建一个大小为 m 的向量 edges 用于存储边的信息
// 读取每条边的信息
for i 从 0 到 m - 1 循环 {
读取 edges[i].u, edges[i].v, edges[i].cost
}
// 对边集进行排序
对 edges 进行排序
// 初始化并查集的父节点数组
parent 调整大小为 n + 1
for i 从 1 到 n {
parent[i] = i;
}
设 total_cost 为 0
设 connected 为 0
// 遍历排序后的边集
for 每条边 e 在 edges 中{
if unite(e.u, e.v) {
total_cost += e.cost
connected++
if connected 等于 n - 1 {
break;
}
}
}
// 输出结果
if connected 等于 n - 1 {
输出 total_cost
} else {
输出 -1
}
返回 0
}
函数代码
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
struct Edge {
int u, v, cost;
bool operator<(const Edge &other) const {
return cost < other.cost;
}
};
vector<int> parent;
int find(int u) {
if (parent[u] != u) {
parent[u] = find(parent[u]);
}
return parent[u];
}
bool unite(int u, int v) {
u = find(u);
v = find(v);
if (u == v) return false;
parent[v] = u;
return true;
}
int main() {
int n, m;
cin >> n >> m;
vector<Edge> edges(m);
for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i) {
cin >> edges[i].u >> edges[i].v >> edges[i].cost;
}
sort(edges.begin(), edges.end());
parent.resize(n + 1);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {
parent[i] = i;
}
int total_cost = 0;
int connected = 0;
for (const Edge &e : edges) {
if (unite(e.u, e.v)) {
total_cost += e.cost;
connected++;
if (connected == n - 1) break;
}
}
if (connected == n - 1) {
cout << total_cost << endl;
} else {
cout << -1 << endl;
}
return 0;
}
三、实验使用环境(本次实验所使用的平台和相关软件)
以下请根据实际情况编写
- 操作系统:Windows 11专业版
- 编程语言:C++
- 开发工具:Visual Studio 2022
四、实验步骤和调试过程(实验步骤、测试数据设计、测试结果分析)
题目1:图的创建—题目2:图的遍历
本机运行截图
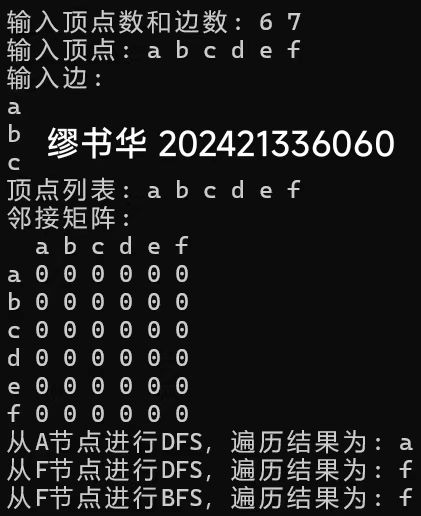
题目3:图着色问题
PTA提交截图

题目4:公路村村通(最小生成树)
PTA提交截图
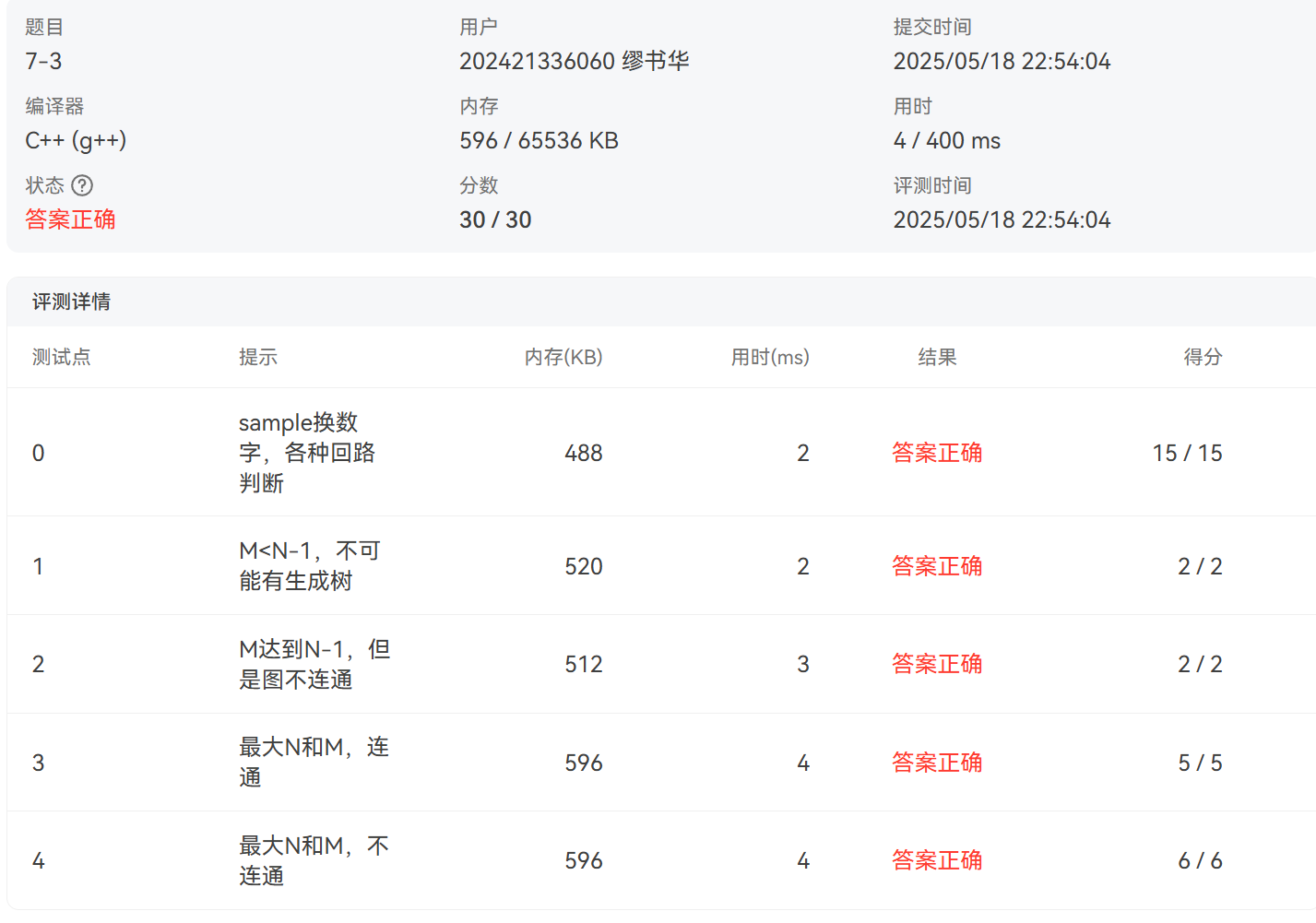
五、实验小结(实验中遇到的问题及解决过程、实验体会和收获)
遇到的问题及解决方法:
- 问题:对图的创建不熟悉,没有完全理解邻接表和邻接矩阵
- 解决方法:查询csdn文章进一步学习
实验体会和收获:
- 学会了图的创建和遍历,理解了邻接表和邻接矩阵
- 掌握了图的基础操作并应用图解决基础问题
























 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








