前言:
本文是PPT内容整理+复制+翻译(有机翻有我翻),笔者挑选了一些自认为有可能考的东西,或者比较重要的东西。当然,做个期末复习突击还是OK的,但是即使是我自己复习,我也更推荐一边看PPT一边看这个总结,PPT还是真道理。
本文跟随课程进度实时更新,如有谬误,欢迎指正。不要喷我,谢谢了。
那我们开始吧
Part 1 Industry Dynamics of Technological Innovation
1 Sources of Innovation
Source of innovation: Firms, Universities, Individuals, Private Nonprofits, Government-funded research(可以结合适当的对象举出例子,可以说明之间的联系)
1.1 Creativity
-
Definition: The ability to produce novel and useful work. It is the beginning of innovation. Creativity can be trained, improved and managed.
-
Nature: look at the problems in unconventional ways.
-
Individual Creativity: a function of Intellectual abilities, Knowledge, Style of thinking, Personality, Motivation, Environment
1.2 Translating Creativity into Innovation
- Participants: Inventors, Innovation by users and R&D, ect.
- R&D by firms
- Development refers to activities that apply knowledge to produce useful devices, materials, or processes.(应用知识来生产有用的设备、材料或过程的活动)
- Applied research: Research targeted at increasing knowledge for a specific application or need. It aims at increasing understanding of a topic or field to meet a specific need.
- Basic research: Research targeted at increasing scientific knowledge for its own sake. It may or may not have any long-term commercial application. It aims at increasing understanding of a topic or field without an immediate commercial application in mind.

- 关于探讨如何度过死亡谷的企业案例可以举Kirin和任正非的华为。关键是要把技术钥匙变成产品优势,再转化为竞争优势。
- Demand Pull approaches argued that innovation originates with unmet customer need: Customer suggestions -> invention -> manufacturing
- Science Push approaches suggest that innovation proceeds linearly: Scientific discovery -> invention -> manufacturing -> marketing
- Development refers to activities that apply knowledge to produce useful devices, materials, or processes.(应用知识来生产有用的设备、材料或过程的活动)
- Firm Linkages with Customers, Suppliers, Competitors and Complementors
- Most frequent collaborations are between firms and their customers, suppliers, and local universities.
- Complementors: Producers of complementary goods or services
- External versus Internal Sourcing of Innovation
- Relationship: External and internal sources are complements.
解释:拥有内部研发的公司也是外部协作网络的最大用户。内部研发可以帮助企业建立吸收能力,使其能够更好地利用外部获得的信息。
- Absorptive capacity: The ability of an organization to recognize, assimilate, and utilize new knowledge.
- Universities and Government-funded Research
-

- 大学鼓励,但收入少
- TTO (Technology transfer offices): Offices designed to facilitate the transfer of technology developed in a research environment to an environment where it can be commercially applied.(旨在促进在研究环境中开发的技术向可以进行商业应用的环境转移的办公室)
- Governments invest in research through: laboratories, Science parks and incubators, Grants
1.3 Innovation in Collaborative Networks
There is a growing recognition of the importance of collaborative research and development networks for successful innovation. 在个别公司很少拥有所有必要资源和能力的高科技部门,合作研究尤其重要。
公司可以弄那种关系网络。
- Technology Clusters are regional clusters of firms that have a connection to a common technology.
- Agglomeration Economies: Proximity facilitates knowledge exchange. Cluster of firms can attract other firms to area. Supplier and distributor markets grow to service the cluster. Cluster of firms may make local labor pool more valuable by giving them experience. Cluster can lead to infrastructure improvements.
集聚经济:邻近促进知识交流。企业集群可以吸引其他企业入驻。供应商和分销商市场为集群服务。企业集群通过给予当地劳动力经验,使其更有价值。集群可以改善基础设施。
- 科技集群的典型例子:硅谷的半导体公司,曼哈顿下城的多媒体集群,和摩德纳,意大利,针织品区
2 Types and Patterns of Innovation
2.1 Types of Innovation
技术轨迹的定义:The path a technology follows through time is termed its technology trajectory.
- Product innovation VS Process innovation
-
一个组织的产品创新可能是另一个组织的流程创新
- Radical innovation VS Incremental innovation
| system | New series of cars, planes, computers, TV | New generation (MP3 and download as substitution of CD) | Steam engine, ICT, biotechnology, nanotechnology |
| component | Improvement of components | New components for existing systems | Advanced materials improving component properties |
| Incremental把做过的事情做的更好 | 对于公司是新的 | Radical 全新 |
-
Radicalness(激进性)是相对的,可能随着时间和观察者不同而改变。比如对于Kodak来说数字摄影更激进,但是对索尼就那样了
- Competence-Enhancing Innovation VS Competence-Destroying Innovation
- Architectural Innovation VS Component Innovation
- Innovation Categories
- sustaining – better products that can be sold with higher margin to demanding customers; incumbents win高利润卖给高要求客户,行业巨头胜
- disruptive – commercialization of simpler, more userfriendly products, which are cheaper and targeted to new or less demanding customers; new entrants win物美价廉给低要求客户,行业萌新胜
2.2 Disruptive Innovation
- The disruptive Innovation Model
-

- Open Innovation VS Closed Innovation 可能还会融入innovation network
- closed

- open

- 封闭式创新 (Closed Innovation):
- 人才: 所有优秀人才都在为一家公司工作,员工流动性低。
- 研发模式: 研发成果仅在内部进行,外部研发不被重视。
- 知识产权: 严格控制知识产权,不允许竞争对手利用。
- 商业模式: 以产品或服务为核心,注重市场占有率和利润率。
- 市场环境: 创新速度慢,市场竞争激烈,新进入者难以立足。
- 案例: 核工业、大型计算机
- 开放式创新 (Open Innovation):
- 人才: 与公司内外的人才合作,员工流动性高。
- 研发模式: 重视外部研发,积极寻求外部合作和知识共享。
- 知识产权: 利用知识产权获取收益,例如授权、合作开发等。
- 商业模式: 以平台或生态系统为核心,注重创新能力和生态系统建设。
- 市场环境: 创新速度快,市场竞争激烈,新进入者有机会脱颖而出。
- 案例: 电脑、电影
2.3 Technology S-Curves
Technology trajectories are most often used to represent the technology’s rate of performance improvement or its rate of adoption in the marketplace. 技术轨迹最常用于表示技术的性能改进速度或其在市场中的采用率。
技术的改进速度及其向市场扩散的速度通常都遵循s型曲线。

-
著名案例: 集成电路上的晶体管密度发展
注意⚠️:Technologies do not always get to reach their limits. May be displaced by new, discontinuous technology.(一个不连续的技术通过一个全新的知识库来满足类似的市场需求, 不连续技术的初始性能可能很低)

大公司一般不愿意更换自己的技术,除非新的颠覆性技术有着更高的性能极限和更陡峭的S曲线。
- S-Curves in Technology Diffusion
- Unlike s-curves in technology performance, s-curves in technology diffusion are obtained by plotting the cumulative number of adopters of the technology against time.
- Technology diffusion means the spread of a technology through a population.
- 技术扩散往往比信息扩散需要更长的时间
- 新的技术对现有解决方案是重大改进,并不代表着所有公司都会快速转向他。因为:
- Technology may require acquiring complex knowledge or experience. 在掌握这些知识前最好不要采用,这是稳妥之计。
- Technology may require complementary resources to make it valuable.
- S-curves 可以用作规范工具
- Limitations of S-Curves
- 很难判断技术的极限是什么,而且不同公司间往往存在分歧
- 一项技术的S型曲线并不是一成不变的
- 企业可以通过其发展活动影响S型曲线的形状
- 转向一项新技术是否会使公司受益取决于诸多因素
2.4 Technology Cycles
Technological change tends to be cyclical: Each new s-curve ushers in an initial period of turbulence, followed by rapid improvement, then diminishing returns, and ultimately is displaced by a new technological discontinuity.
- The fluid phase (when there is considerable uncertainty about the technology and its market; firms experiment with different product designs in this phase)
每一个不连续性都开启了一个动荡和不确定的时期(发酵时代era of ferment)
- After a dominant design emerges, the specific phase begins (when firms focus on incremental improvements to the design and manufacturing efficiency)
- 除非下一个不连续性过早到来,否则主导设计总能占据大部分市场份额
2.5 Dominant design
- Definition: It refers to a product design that is adopted by the majority of producers, typically creating a stable architecture on which the industry can focus its efforts.
- Characteristics: It was never in the same form as the original discontinuity, but was also not on the leading edge of technology. It bundled the features that would meet the needs of the majority of the market.
- Diffusion of Innovation and Adopter Categories: Innovators, early adopters, early majority, late majority, laggards.
- Technology Trajectories and “Segment Zero”: 技术的改进速度往往快于客户需求,这使得低端技术最终能够满足大众市场的需求。如果企业忽视低端市场,可能会导致强大的竞争对手出现。
3 Standards Battles and Design Dominance
Dominant Design: A product design that is adopted by the majority of producers, typically creating a stable architecture on which the industry can focus its efforts.
3.1 Why dominant designs are selected
- Increasing returns to adoption提高采用回报
- 啥是提高采用回报:the more a technology is adopted, the more valuable it becomes.
- 增收的主要来源:Learning effects, Network externalities===>a self-reinforcing process
- Learning effects: The more a technology is adopted, the more it is developed and the more effective and efficient it becomes.
- 作用:为进一步发展技术的再投资创造收入,经验和知识的积累
- 典型例子:learning curve (impact of cumulative production on cost and productivity)

- Learning rate: tasks' nature, firm strategy, prior experience, absorptive capacity
- Prior learning 优先学习
- Absorptive capacity: The ability of an organization to recognize, assimilate, and utilize new knowledge.
- Network externalities网络外部性
- Network Externalities (network effects, positive consumption externalities): the value of a good to a user increases with the number of other users of the same or similar good.
- Direct network externalities: the utility of a product to each user in a network depends on the number of users.
- Indirect network externalities: a positive link between the utility to a customer and the number of other users of the product by expanding the range of complementary products.
- 例子:涉及物理网络的市场比如铁路或者电信
- Installed base安装基数: The number of users of a particular technology
庞大的安装基数可能会带来更多配套产品的批发商,带来大量的互补性产品,在这时网络外部性也会出现。例子:微软
A self-reinforcing cycle
- Government regulation政府监管
- 政府一般就是法律诱导。比如在公共事业喝电视电信行业。政府一般还要强化单一标准,可提升经济效益并造福大众。
- Path dependence路径依赖
- 采用回报增加(见第一个小分题)意味着技术轨迹有路径依赖特征
- Path dependency: when end results depend greatly on the events that took place leading up to the outcome.结果大概率无法重现.
- Early entrants根深蒂固,Sponsorship by a large powerful firm可帮技术获得市场控制份额(不是决定性因素!)
- Result: Winner-Take-All market, 即走向nature monopolies
- Natural monopolies: the majority of the market is dominated by a single (or few) design(s).
- Standards battles → Big winners and big losers
- 主导设计可能影响未来技术需求!!!赢家通吃市场对消费者是双刃剑,可以参考微软的反垄断诉讼案
3.2 Multiple dimensions of value
- 用于分析收益递增行业中哪一种技术设计占据主导地位(分析角度如下)
- Value of the stand-alone technology
- Combine technology with existing values
- 构成总客户价值的维度
监管机构是如何决定一家公司何时变得过于占主导地位呢?一种方法是比较客户从不同市场份额水平上的网络外部性中获得的价值与相应的垄断成本。
客户的网络外部性效益随着市场份额的累积而上升
随着市场份额的累积,潜在的垄断成本也会上升。
-
Technology’s Stand-Alone Value
-
Buyer Utility Map 买方效用图: six utility levers(Customer Productivity, Simplicity, Convenience, Risk, Fun and Image, Environmental Friendliness) and the six stages of a buyers experience cycle (purchase, delivery, use, supplements, maintenance, and disposal)
-
-
Network Externality Value
-
函数:安装基数大小( size of installed base)&互补商品可用性的函数( ability of complementary goods)
如果一项新技术比现有技术具有更多的独立功能,那么它的整体价值可能会降低,因为它的安装基础较小,或者补充产品的可用性较差。
-
技术比较是在权衡客观信息+主观信息+未来期望
-
-
两者的结合将影响哪一种技术设计成为主导
- Network externality returns(网络外部性回报) refers to the value customers reap as a larger portion of the market adopts the same good.
- Monopoly costs refer to the costs users bear as a larger portion of the market adopts the same good.
- Network externality returns to market share often exhibit the s-shape. Monopoly costs to market share, however, are often considered to be exponentially increasing.
3.3 Strategies in standard battles
- Types of Standards Battles
- 新旧兼容:Evolution strategy: Offering superior performance with minimal consumer switching or adoption costs.最小转换+成本
- 新旧不兼容:Revolution strategy- offering such compelling performance that consumers are willing to incur significant switching or adoption costs.性能过于瞩目
- Key Strategies
- Preemptions: First to market, Penetration pricing, Free samples
- Expectation Management: Vaporware (Pre-advertising), Grand claims about popularity
- Open Policy Plus Technology Protection
- Coalitions/Alliance/Allies
- 赢了也不要掉以轻心!保持警惕,为客户提供迁移路径,将补充产品商品化,与自己的安装基地竞争,保护自己的地位,利用自己的安装基础,保持领先。记住!没什么是永远!
4 Timing of Entry
4.0 Some basic definitions
- First movers are the first entrants to sell in a new product or service category (“pioneers”).
- Early followers are early to market but not the first.
- Late entrants do not enter the market until the product begins to penetrate the mass market or later.
4.1 Advantages and Disadvantages of First-Movers and Followers
4.1.1 Advantages of First-Movers
Being a first mover may confer the advantages of brand loyalty and technological leadership, preemption of scarce assets(稀缺资源), and exploitation of buyer switching costs. Furthermore, in industries characterized by increasing returns, early entrants may accrue learning and network externality advantages that are self-reinforcing over time.
- Brand loyalty and technological leadership
- 更持久的声誉(long-lasting reputation),持续的垄断租金(monopoly rents)
- Preemption of scarce assets
- 如关键地点、政府许可、分销渠道、与供应商的关系等
- Exploiting Buyer Switching Costs
- Reaping Increasing Returns Advantages
- 注意投资于新技术开发的时机!!如Intel
4.1.2 Disadvantages of First-Movers
Incumbent Inertia现任惯性:The tendency for incumbents to be slow to respond to changes in the industry environment due to their large size, established routines, or prior strategic commitments to existing suppliers and customers
- Research and Development Expenses
- 新产品开发失败风险有95%
- Undeveloped Supply and Distribution Channels
- 公司要面临自己研发+自产自销的艰难局面
- Immature Enabling Technologies and Complements
- 可能要依赖其他授权技术的生产商
- Uncertainty of Customer Requirements
- 产品必须随着客户的需求和要求做调整
4.1.3 Advantages of Followers
- A type of "free ride"
- Technology: 模仿可能比创新更便宜.
- Buyer education: 先锋的广告增强了消费者的意识.
- Employee training : 追随者可以雇佣先驱培训过的员工。知识溢出效应.
- Infrastructure development: 先锋在发展支持产业和获得监管批准方面的投资使其他人受益
- Avoid some of the costs and uncertainties
- Grasp the discontinuities in technology and in customers' needs
- 进入的时间与锁定的可能性有u型关系:在很早或很晚的时候进入会增加技术锁定的可能性

4.2 Factors Influencing Optimal Timing of Entry
公司如何决定是尝试开启新的技术类别还是等待其他公司这么做?
The answer will depend on several factors, including customer certainty, the margin of improvement offered by the new technology, the state of enabling technologies and complementary goods, the threat of competitive entry, the degree to which the industry exhibits increasing returns, and the firm’s resources.
4.2.1 Customer Certainty
一开始客户可能不清楚技术的重要性,但是随着时间发展,原本不重要的点可能变得至关重要。例如索尼的PS2和微软的Xbox。
If customer needs(User pain points) are well understood, it is more feasible to enter the market earlier.
4.2.2 The margin of improvement offered by the new technology
When a technology makes a dramatic improvement over previous generations or different technologies that serve similar functions, it will more rapidly gain customer acceptance.
4.2.3 The state of enabling technologies and complementary goods
评估技术成熟性来决定下一步的发展
不是所有创新都需要互补产品。要考虑互补产品的可用性。创新可以利用现有的互补产品。
4.2.4 The threat of competitive entry
现有市场可能非常激烈
进入壁垒和新产品的可模仿性(例如,它是否能得到专利的有效保护)相互作用,产生了不同的时机激励。
-
只有一家公司能够生产一种独一无二的商品===》随时
-
几家公司能够生产出一种随后将是独一无二的产品===》早到
-
商品被认为是高度可模仿的===》更愿意等待
4.2.5 The degree to which the industry exhibits increasing returns
如果有力量鼓励采用单一的主导设计,就可以选择竞争对手的技术。如果专利等保护机制阻止了竞争公司提供兼容的技术,那么该公司可能会被拒之门外
4.2.6 The firm’s resources
Early Loss: 是否能够承担得起
Accelerating market takeoff:加速新的早期采用
Firm's Reputation: 在其他条件平等的情况下,有良好声誉的进入者可以比没有良好声誉的进入者更早吸引收养。
4.3 Strategies to Improve Timing Options
Parallel development process means When multiple stages of the new product development process occur simultaneously(新产品开发过程的多个阶段同时发生)
一些公司被迫成为追随者,然后他们在时机策略上没有选择。要想在进入时间上有更多的选择,公司需要能够尽早或快速地开发创新。一家拥有快速周期开发流程的公司,它既可以是早期的进入者,又可以根据客户的反馈快速改进其创新。本质上,具有快速周期开发流程的公司可以获得先发和第二动优势。
Part 2 Formulating Technological Innovation Strategy
5 Defining the Organization’s Strategic Direction
5.1 Overview
- Formulating a company's technological innovation strategy requires the firm to assess its current position, and define its strategic direction.
- A company’s strategic intent should be ambitious. Strategic intent development begins with an evaluation of the firm’s capabilities and ideally ends in a plan that cohesively leverages all of the firm’s resources to create a sustainable competitive advantage.
5.2 Assessing the Firm’s Current Position
5.1.1 Macroscopic: PEST
5.1.2 Microcosmic
- Porter's Five-Force Model:竞争对手的数量和相对规模将塑造竞争的本质。用于分析公司/行业的吸引力以及一个公司的机会和威胁
- The degree of existing rivalry: 多因素影响行业竞争,也收到竞争对手差异的影响,需求条件也会影响竞争程度
- Threat of potential entrants: 受该行业吸引的程度+ entry barriers行业壁垒。要考虑启动成本和合作情况。
-
Entry barriers: Conditions that make it difficult or expensive for new firms to enter an industry (government regulation, large start-up costs, etc).
-
- Bargaining power of suppliers: 公司对一个或几个供应商的依赖程度将影响其协商良好条款的能力。Switching costs+ Vertical integration 转换成本和垂直整合(供应商backward/买家forward)
- Bargain power of Buyers
- Threat of substitutes: Substitutes are products or services that are not considered competitors, but fulfill a strategically equivalent role for the customer. 潜在的替代品越多,替代品的威胁就越大。注意,区分竞争对手和替代品取决于行业的定义。
Threat of complements (Products or services that enhance the usefulness or desirability of another product.)
- Relationships between Innovation and the Five Forces:
- 创新可以产生替代品,而现有的公司可以改进他们的产品,以与替代品竞争。
- 创新可以降低进入壁垒,而现有的公司可以通过技术保护来提高进入壁垒。
- 供应商可以加强对买家的控制,而买家可以通过创新来削弱对供应商的依赖。
- 公司可以通过创新建立垄断,同时也可以通过创新打破垄断。
- Stakeholder Analysis利益相关者分析
-
Stakeholder: Any entity that has an interest (“stake”) in the organization
-
涉众模型通常用于战略和规范目的
- strategic stakeholder analysis: 强调可能影响公司财务绩效的利益相关者管理问题
- normative stakeholder analysis: 强调利益相关者管理问题,由于其伦理或道德的影响,公司应该参加
-
Identify all the parties that will be affected by the behavior of the firm
-
Stakeholders include stockholders, employees, customers, suppliers, lenders, the local community, government, and rivals
5.1.3 Internal Analysis
-
The analysis of the internal environment of the firm most often begins with identifying the firm’s strengths and weaknesses. 这个任务是通过检查价值链中的每个活动来组织的
-

-
The applicability of this model: This generic model can be adapted to better fit a particular firm’s needs.
-
要成为可持续竞争优势的潜在来源,资源必须是rare, valuable, durable, and inimitable. 例子:Talent 和 First-mover
比如,如果有价值的资源是隐性的、路径依赖的、社会复杂的、因果模棱两可的,它们将非常难以模仿
- Tacit resources: Resources of an intangible nature that cannot be readily codified.
- Socially complex resources: Resources or activities that emerge through the interaction of multiple individuals.
- Causal ambiguity: The relationship between a resource and the outcome it produces is poorly understood.
-
一旦公司建立了一个基本的内部分析,它就可以继续确定其核心竞争力,并制定其战略意图。
-
Growth Mindset(关注你可以改变和影响的事情) VS Fixed Mindset(关注你不能掌握的事情)
-
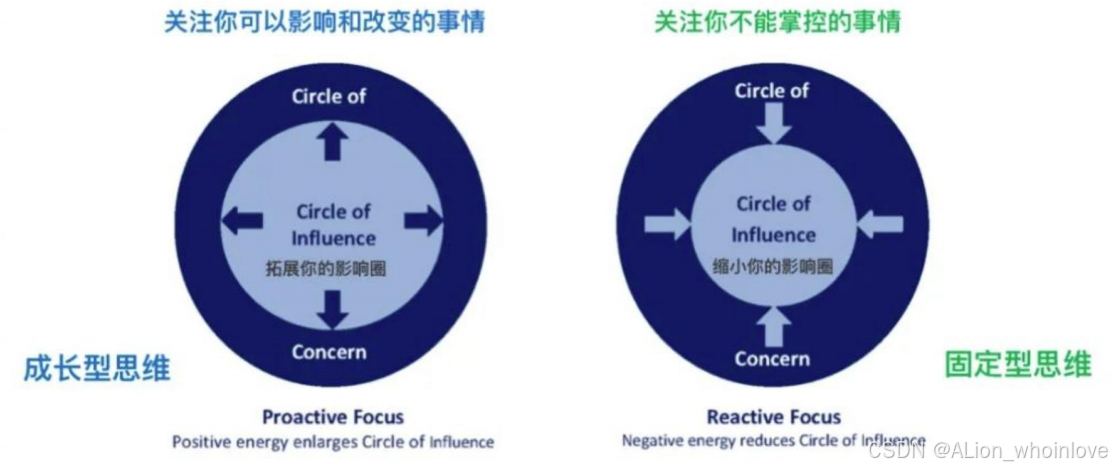
5.3 Identifying Core Competencies and Capabilities
5.3.1 Core Competencies
- Significant source of competitive differentiation差异化竞争的重要来源. e.g.,索尼小型化技术
- Transcend a single business超越单一业务. e.g., 本田的发动机可以用在割草机上
- Hard for competitors to imitate竞争对手很难模仿
5.3.2 六步的方法来识别和培养一个公司的核心能力

- 项目开始于成立一个指导委员会,任命一个项目经理,并向所有团队成员沟通总体目标。
- 通过对类型、强度、重要性和对企业操作的能力进行分类来构建能力清单。
- 评估能力的方法是通过评估每个能力的临界性,然后评估组织当前每个能力的专业水平。
- 确定候选能力可以筛选出公司应该关注和发展的能力列表。
- 下一步是使用Prahalad和Hamel的原始标准来测试候选的核心能力。
- 评估公司的核心能力地位,以确定竞争对手是否具有类似的能力,并确定组织需要改进的领域。
competency & capability在本文中可以互换使用
5.3.3 Summary

- A core competency arises from a firm’s ability to combine and harmonize multiple primary abilities. A firm’s core competencies also depend on building high quality relationships across different functions and business units.
- Risk of Core Rigidities: is faced by firms when they focus on current capabilities and do not develop new ones.
- Dynamic Capabilities enable a firm to quickly reconfigure its organizational structure and routines in response to new opportunities and are not related to specific products or technologies. It is a set of abilities that make a firm more agile and responsive to change.
5.4 Strategic Intent
Strategic Intent: A long-term goal that is ambitious, builds upon and stretches firm’s core competencies, and draws from all levels of the organization.
Functions: Strategic intent provides clarity, brings about focus, and inspires people.
5.5 Resources Gap-Actions
5.5.1 Identifying the Resource and Capability Gap

5.5.2 The Balanced Scorecard
- Financial perspective: Measures include return on capital, net cash flow, and earning’s growth. 资本回报率、净现金流、收入增长
- Customer perspective: Measures include market share, percent of repeat purchases, customer satisfaction surveys, etc.市场份额,重购百分比,客户满意度
- Internal perspective: Measures include the number of safety incidents per month, franchise quality ratings, stock-out rates, inventory costs, etc. 安全事故数量、特许经营质量评级、缺货率、库存成本
- Innovation and learning: Mission + Vision. Measures include the percentage of sales from products developed within last five years, average length of the new product development cycle, employee training targets, etc. 销售百分比,开发周期,员工培训目标。
6 Choosing Innovation Projects
6.1 Overview
- New product development is inherently risky and expensive.
- Firms use a mix of formal, informal, quantitative and qualitative methods when selecting and managing innovation projects.
- Often the choices are driven by strategic implications rather than strictly financial analysis.
6.2 The Development Budget
Capital Rationing资源配给: The allocation of a finite quantity of resources over different possible uses.
Percentage is typically determined through industry benchmarking(行业基准), or historical benchmarking(历史基准) of firm’s performance, and/or on a desired level of R&D intensity(研发强度水平).
- Some Definitions
- Internal Financing: 大公司
- External Financing: 小公司
- 创业第一阶段,企业家可能需要依赖家人、朋友和信用卡.政府可能会给拨款
- Angel investors: 通常是种子阶段和<100万美元
- Venture capitalists: 多个早期阶段,>100万美元
6.3 Quantitative Methods for Choosing Projects
6.3.1 Discounted Cash Flow (DCF) Methods 贴现现金流方法
- Net Present Value (NPV): Expected cash inflows are discounted and compared to outlays. 净现值:预期现金流入被折现并与支出进行比较.
- NPV = Present value of cash inflow – Present value of cash outflows.大于0就是挣上钱了。
- 要找到上面这俩值每个现金流都要使用折现率折现回当期

- t期每期C美元的现值,折现率r的公式如下:
-
-
如果现金流被预期为永久,那么可以使用
-

- 成本的现值和未来现金流的现值也可以用来计算贴现的回收期[discounted payback period]
-
- Internal Rate of Return (IRR): The discount rate that makes the net present value of investment zero. 内部收益率:使投资净现值为零的贴现率

-
NPV=0时,IRR是贴现率
-
NPV VS IRR
-


- Discounted payback period: The time required to break even on a project using discounted cash flows. 贴现回收期:使用贴现现金流实现项目收支平衡所需的时间
- A&D of DCF methods
- Strengths
- 提供具体的财务估计
- 明确考虑投资的时机和金钱的时间价值
- Weaknesses
- 可能具有欺骗性;只有与现金流量的原始估计一样准确。可能无法捕捉项目的战略重要性。
- Strengths
6.3.2 Real Options(实物期权): Applies stock option model to nonfinancial resource investments.==>准确率存疑
- 研发计划的成本可以被认为是看涨期权的价格。A
- 利用研发计划所需的未来投资成本(如已开发的新技术商业化的成本)可以被视为行使价格。B
- 研发投资的回报类似于通过看涨期权购买的股票的价值。C
- 只要A<B, C=0. A>B, C呈45度角上升(等比增长)
- A&D
- Advantages:技术轨迹具有不确定性,选择方法可能有用。一些地方,期权方法比现金流分析方法能产生更好的技术投资决策。
- Disadvantages:许多创新项目并不符合期权模型背后的资本市场假设。可能无法以低价格获得期权。研发投资的价值受到公司的能力、补充资产和战略的影响。Require high flexibility of management.
6.4 Qualitative Methods for Choosing Projects
Reason: 项目难以量化,或者量化可能导致误导性结果
6.4.1 Types of Methods
- Screening Questions: Assess different dimensions of the project decision.
- They are organized into categories and are used by managers.
- Role of customer (市场、使用、兼容性和易用性、分销和定价)
- Role of capabilities (现有能力、竞争对手的能力、未来能力)
- Project timing and cost (时间,成本因素)
- The Aggregate Project Planning Framework: Emphasizes balance of different types of projects and their match to resource availability, cash flow needs, etc.
- Mapping the company's R&D Portfolio
- Advanced R&D Projects:开发前沿技术;通常没有立即的商业应用;需要很长时间才能获得回报(或者可能根本没有回报),但可以使公司成为技术领导者
- Breakthrough Projects: 将革命性的新技术纳入商业应用
- Platform Projects: 不是革命性的,但对前几代产品提供了根本性的改进
- Derivative Projects: 渐进式改进和设计特征的多样性。这些项目回报最快,并有助于满足公司的短期现金流需求
- Q-Sort: ranks projects on a variety of dimensions.
-
想法被写在卡片上。提出了一系列的项目选择标准。对于正在考虑的每个维度,卡片按照其在该维度上的性能顺序进行堆叠。几轮的排序和辩论被用来对项目达成共识。
6.4.2 Illustrative Factors for Project Selection项目选择的说明性因素
-
Production Factors
-
Financial Factors
-
Marketing Factors
-
Personnel Factors
-
Administrative and Miscellaneous Factors
6.5 Combining Quantitative and Qualitative Information
- Conjoint Analysis : a family of techniques enabling the relative importance of product attributes to be derived statistically.
- Conjoint analysis enables a subjective assessment of a complex decision to be decomposed into quantitative scores of the relative importance of different criteria.联合分析使一个复杂决策的主观评估能够被分解成不同标准相对重要性的定量分数。
- The most common use of conjoint analysis is to assess the relative importance to customers of different product attributes.评估不同产品属性对顾客的相对重要性
- Steps
- Determine the features and levels of features.确定特征和特征级别
- Design virtual products with different features and prices and describe them on cards.设计具有不同功能和价格的虚拟产品,并在卡片上进行描述。
- Individuals rate each in terms of desirability or rank them.每个人都根据自己的喜好给他们打分或排序
- Multiple regression then used to assess the degree to which an attribute influences rating.然后使用多元回归来评估属性影响评级的程度
- These weights in providing different features.这些权重在于提供不同的功能
- Data Envelopment Analysis (DEA): facilitates the comparison of projects using multiple criteria and different kinds of measurement units based on a linear programming.
- 虽然第一个度量是以美元为单位,是一个几乎连续的测量,但第二个度量是等级顺序,因此是分类度量,很少有关于一个等级级别之间的差异的信息。最后两个测量可能是基于排名系统或缩放系统的分数
- Projects can be ranked by assessing their distance from the efficiency frontier.(可以通过评估它们与效率边界的距离来排名)
- Efficiency frontier: the range of hypothetical configurations that optimize a combination of features. (优化功能组合的假设配置范围)
- Advantage: enable comparisons of projects using multiple kinds of measures. Disadvantage: the results of DEA are only as good as the data utilized.
- Scoring Models: scores and ranks projects using criteria systems and quantifying mechanisms.
- 确定标准,定义范围,划分区间,排序并分配权重,评估项目,计算乘积和总和,重复上面的两个步骤,排名
- 优缺点见PPT
7 Collaboration Strategies
7.1 Reasons for Going Solo
-
Availability of Capabilities 技术可用性
-
Protecting Proprietary Technologies 保护专有技术
-
Controlling Technology Development and Use 控制技术开发和使用
-
Building and Renewing Capabilities 建立和更新能力
7.2 Advantages of Collaborating for firms
-
合作加速获取技能资源。
-
减少资产承诺,提高灵活性。
-
合作促进学习交流。
-
分担成本和风险。
-
创建行业标准。
Joint venture: A partnership between two or more firms involving a significant equity stake by the partners and often resulting in the creation of a new business entity.
Reasons of Faliure of Collaboration: Conflicting objectives. Partner malfeasance. Relationships between partners. Cultural Diversity. Lack of trust. Personal conflicts. Unrealistic expects.
相互矛盾的目标。合作伙伴渎职。伙伴之间的关系。文化的多样性。缺乏信任。个人冲突。不切实际的期望
Conditions for Success of Collaboration: Serious attitude. A strong advocate. Trust each other. Well-defined objectives and plan. Good communications. Strictly follow the arrangement. Share the rewards.
严肃的态度。一个强有力的倡导者。相互信任。明确的目标和计划。良好的沟通。严格遵守安排。分享奖励。
7.3 Types of Collaborative Arrangements
Collaboration arrangements range from very informal alliances to highly structured joint ventures or technology exchange agreements (licensing).合作安排的范围从非常非正式的联盟到高度结构化的合资企业或技术交流协议(许可)
7.3.1 Strategic Alliances 战略联盟
公司可能会利用战略联盟来获得内部不具备的关键能力,或者通过在另一家公司的开发工作中利用它们来更充分地利用自己的能力。
两个维度对公司的联盟战略进行分类:
-
The degree to which alliances practice capability complementation versus capability transfer. 联盟实践能力互补与能力转移的程度
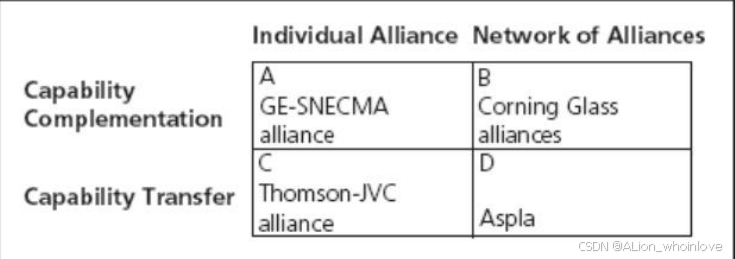
- Capability Complementation: 合并(“汇集”)合作伙伴公司的能力和其他资源,但不一定是在合作伙伴之间转移这些资源。
- Capability Transfer: 跨公司之间的能力交换,使合作伙伴能够将这些能力内化,并独立于特定的开发项目使用这些能力。
-
在象限A中,是指建立个人联盟,结合项目所需的互补技术或技能的公司。在象限B中是指使用联盟网络来结合互补技能和资源的公司。在象限C中是指使用个别联盟在它们之间转移能力的公司。在象限D中是指使用联盟网络来交换能力并共同开发新能力的公司。
-
Whether the firm manages each alliance individually or manages a collective network of alliances 公司是单独管理每个联盟还是管理一个联盟的集体网络
7.3.2 Joint Ventures合资企业
Joint ventures are a particular type of strategic alliance that entails significant structure and commitment.合资企业是一种特殊类型的战略联盟,需要重要的结构和承诺。
7.3.3 Licensing许可
Licensing is a contractual arrangement whereby one organization or individual (the licensee) obtains the rights to use the proprietary technology (or trademark, copyright, etc.) of another organization or individual (the licensor).
许可是一种合同安排,一个组织或个人(被许可方)获得使用另一个组织或个人(许可方)的专有技术(或商标、版权等)的权利。
-
Licensors can penetrate a wider range of markets.
-
许可使公司能够迅速获得它所不具备的技术.
7.3.4 Outsourcing外购
- Outsourcing: An organization (or individual) procures services or products from another rather than producing them in-house.
- 风险:可能失去未来发展创新所需的重要学习机会。潜在的高交易成本,以及合同制造商盗用专有技术的风险。
- Contract manufacturing is one of the most common forms of outsourcing.
7.3.5 Collective Research Organizations集体研究机构
在一些行业中,多个组织已经建立了合作的研发组织,如半导体研究公司或美国钢铁协会。集体研究组织可能采取多种形式,包括行业协会、大学中心或私人研究公司。这些组织中有许多是通过政府或行业协会的倡议而形成的。
7.4 Choosing a Mode of Collaboration
-
Solo Internal Development
-
弊端:相对缓慢且昂贵。很难利用其他公司的专长。
-
优点:允许公司保留对技术发展的控制权。有助于发挥现有专长并发展新专长。
-
适用条件:当公司在新技术上具有强大的专长、有资本支持且不面临巨大时间压力时,独立内部开发是合适的。
-
-
Strategic Alliances
-
利:快速获取技术。更广阔的市场。利用现有竞争力。发展新的竞争力。
-
弊:由于战略联盟的形式多样,它们提供的速度、成本和控制程度差异很大。
-
-
Joint Ventures
-
利:时间优势。成本分摊。合作伙伴的能力访问。
-
适用情况:合资企业在一家公司重视获取其他公司能力的情况下尤其受欢迎。
-
-
Licensing
-
技术引进的利弊:
-
利:是一种快速且价格适中的方式来获取新技术。有潜力利用公司现有的能力,开发新能力。
-
弊: 提供有限的技术使用权和对技术的低控制度。
-
-
技术转让的利弊:
-
利:一种快速且低成本的方式来扩展应用。使公司能够访问其他公司的能力。
-
弊:为新能力的发展提供的机会很少。
-
-
-
Outsourcing
-
利:快速获取专业知识。降低成本。专注核心活动。机会较少的新能力建设。
-
适用情况:外包适合非核心活动。当有许多潜在的外包商提供类似的产品或服务时,外包可以是简单的买卖关系。如果外包商提供差异化产品或服务,外包可能具有更大的战略意义。
-
-
Collective Research Organizations
-
长期承诺形式:是一种长期的投入方式。
-
杠杆作用:帮助公司利用和加强现有的核心竞争力。
-
行业适用性:特别适用于复杂技术和需要大量基础科学投资的行业。
-
7.5 Choosing and Monitoring Partners
Partner Selection
- Resource Fit refers to the degree to which potential partners have resources that can be effectively integrated into a strategy that creates value. 这些资源可以是互补的(Complementary),也可以是补充的(Supplementary)。大多数合作的动机是需要获取公司所不拥有的资源;这种合作是基于互补资源的组合
- Strategic Fit refers to the degree to which partners have compatible objectives and styles.只要这些目标能够在不伤害联盟或伙伴的情况下实现,那么伙伴的目标就不必相同。不知道伙伴的真实目标或与目标不兼容的伙伴结成联盟,可能会导致冲突、浪费资源和丧失机会。
Impact on Opportunities and Threats in the External Environment
Impact on Internal Strengths and Weaknesses
Impact on Strategic Direction
合作中面临风险的资源越多,合作伙伴公司可能对这种关系施加的治理结构就越多。组织用于管理其协作关系的治理机制有三种主要类型:联盟契约(alliance contracts)、股权所有权(equity ownership)和关系治理(relational governance)
8 Protecting Innovation
8.1 Appropriability适用性
Definition: The degree to which a firm is able to capture rents from its innovation.
决定性因素:how easily or quickly competitors can imitate the innovation模仿的容易程度和速度
这也意味着,竞争对手模仿创新的难易程度取决于技术本身的性质和用于保护创新的机制的强度
- Tacit knowledge(隐性知识): Knowledge that cannot be readily codified or transferred in written form.
- Socially complex Knowledge(社会复杂知识): Knowledge that arises from the interaction of multiple individuals.
8.2 Patents, Trademarks and Copyrights
- A patent protects an invention.
- Types: Utility patents, Design patents, Plant patents.
- Patents must be useful, novel and not be obvious.
- A trademark protects words or symbols intended to distinguish the source of a good.
- Trademarks and Service Marks: a word, phrase, symbol, design, or other indicator that is used to distinguish the source of goods form one party from goods of another.
- A copyright protects an original artistic or literary work.
- Copyright: a form of protection granted to works of authorship.
8.3 Trade Secrets
- Trade Secret: information that belongs to a business that is generally unknown to others.
- 商业秘密的特点:以经济租金的形式为公司提供了独特的优势,只要信息保持私人,才有价值
- UniformTrade Secret Act( UTSA )商业秘密法案
8.4 The Effectiveness and Use of Protection Mechanisms
- 专利法在制药业等行业有用,但在电子行业专利和版权保护较少。制造技术等工业过程要整出专利也是很难的,不如依靠商业秘密。对于一些行业,保护技术不如自由扩散他们。
- 为了解决这些权衡,公司经常对其创新采取部分保护的策略,处于完全专有系统和完全开放系统之间的连续体上。
- Wholly Proprietary Systems VS Wholly Open Systems
- 完全专有系统:基于技术的商品,该技术通过专利、版权、保密或其他机制得到有力保护。完全专有的技术只能由其开发者合法生产和扩展。
- 完全开放的系统:基于不受保护的技术的商品,可以自由地用于生产或增强
- 许多技术既不是完全专有的,也不是完全开放的——它们是部分考虑一个从完全专有延伸到完全开放的控制连续体是很有用的。
- 保护(Protection)策略的优点:
- 更高的租金可获性:专有系统提供更高的租金收益。
- 再投资机会:租金可用于进一步的开发、推广和分发。
- 市场主导地位:赞助商可通过定价、广告或补贴确保自身作为唯一标准的制定者。
- 技术演进的控制:公司能够掌控技术的发展方向及其互补品。
- 扩散(Diffusion)策略的优点:
- 更快的采用率:由多家公司生产和推广的技术可能会被更快接受。
- 外部改进的可能性:技术可能因其他公司的参与而得到提升,尽管存在外部开发的风险。
- Factors Influencing Benefits of Protection vs. Diffusion
产销能力和资金。业界反对单一来源技术。内部发展资源。控制碎片化。对架构控制的激励。
- Production and marketing capabilities, and capital.
- Industry opposition against sole source technology.
- Resources for internal development.
- Control over fragmentation.
- Incentives for architectural control.

























 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








