Thread coreThread = new Thread(
() -> {
final int currentValue = atomicInteger.get();
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " ----
– currentValue=" + currentValue);
// 这段目的:模拟处理其他业务花费的时间
try {
Thread.sleep(300);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
boolean casResult = atomicInteger.compareAndSet(1, 2);
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()
+ " ------ currentValue=" + currentValue
+ ", finalValue=" + atomicInteger.get()
+ ", compareAndSet Result=" + casResult);
}
);
coreThread.start();
// 这段目的:为了让 coreThread 线程先跑起来
try {
Thread.sleep(100);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
Thread amateurThread = new Thread(
() -> {
int currentValue = atomicInteger.get();
boolean casResult = atomicInteger.compareAndSet(1, 2);
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()
+ " ------ currentValue=" + currentValue
+ ", finalValue=" + atomicInteger.get()
+ ", compareAndSet Result=" + casResult);
currentValue = atomicInteger.get();
casResult = atomicInteger.compareAndSet(2, 1);
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()
+ " ------ currentValue=" + currentValue
+ ", finalValue=" + atomicInteger.get()
+ ", compareAndSet Result=" + casResult);
}
);
amateurThread.start();
}
}
输出内容如下:
```java
Thread-0 ------ currentValue=1
Thread-1 ------ currentValue=1, finalValue=2, compareAndSet Result=true
Thread-1 ------ currentValue=2, finalValue=1, compareAndSet Result=true
Thread-0 ------ currentValue=1, finalValue=2, compareAndSet Result=true
下面我们来详细介绍一下这些原子类。
二、基本类型原子类
1.基本类型原子类介绍
使用原子的方式更新基本类型
AtomicInteger:整型原子类AtomicLong:长整型原子类AtomicBoolean:布尔型原子类
上面三个类提供的方法几乎相同,所以我们这里以AtomicInteger为例子来介绍。
AtomicInteger 类常用方法
public final int get() //获取当前的值
public final int getAndSet(int newValue)//获取当前的值,并设置新的值
public final int getAndIncrement()//获取当前的值,并自增
public final int getAndDecrement() //获取当前的值,并自减
public final int getAndAdd(int delta) //获取当前的值,并加上预期的值
boolean compareAndSet(int expect, int update) //如果输入的数值等于预期值,则以原子方式 将该值设置为输入值(update)
public final void lazySet(int newValue)//最终设置为newValue,使用 lazySet 设置之后可能导致其他线程在之后的一小段时间内还是可以读到旧的值。
2. AtomicInteger常见方法使用
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicInteger;
public class AtomicIntegerTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
int temvalue = 0;
AtomicInteger i = new AtomicInteger(0);
temvalue = i.getAndSet(3);
System.out.println("temvalue:" + temvalue + "; i:" + i);//temvalue:0; i:3
temvalue = i.getAndIncrement();
System.out.println("temvalue:" + temvalue + "; i:" + i);//temvalue:3; i:4
temvalue = i.getAndAdd(5);
System.out.println("temvalue:" + temvalue + "; i:" + i);//temvalue:4; i:9
}
}
3.基本数据类型原子类的优势
通过一个简单例子带大家看一下基本数据类型原子类的优势
①多线程环境不使用原子类保证线程安全(基本数据类型)
class Test {
private volatile int count = 0;
//若要线程安全执行执行count++,需要加锁
public synchronized void increment() {
count++;
}
public int getCount() {
return count;
}
}
②多线程环境使用原子类保证线程安全(基本数据类型)
class Test2 {
private AtomicInteger count = new AtomicInteger();
public void increment() {
count.incrementAndGet(); }
//使用AtomicInteger之后,不需要加锁,也可以实现线程安全。
public int getCount() {
return count.get();
}
}
4. AtomicInteger线程安全原理简单分析
AtomicInteger类的部分源码:
// setup to use Unsafe.compareAndSwapInt for updates(更新操作时提供“比较并替 换”的作用)
private static final Unsafe unsafe = Unsafe.getUnsafe();
private static final long valueOffset;
static {
try {
valueOffset = unsafe.objectFieldOffset
(AtomicInteger.class.getDeclaredField("value"));
} catch (Exception ex) { throw new Error(ex); }
}
private volatile int value;
AtomicInteger类主要利用CAS (compare and swap) + volatile和 native方法来保证原子操作,从而避免synchronized的高开销,执行效率大为提升。
CAS的原理是拿期望的值和原本的一个值作比较,如果相同则更新成新的值。 UnSafe类的objectFieldOffset()方法是一个本地方法,这个方法是用来拿到“原来的值”的内存地址。另外value是一个volatile变量,在内存中可见,因此JVM可以保证任何时刻任何线程总能拿到该变量的最新值。
三、数组类型原子类
1.数组类型原子类介绍
使用原子的方式更新数组里的某个元素
AtomicIntegerArray:整形数组原子类AtomicLongArray:长整形数组原子类AtomicReferenceArray:引用类型数组原子类
上面三个类提供的方法几乎相同,所以我们这里以AtomicIntegerArray为例子来介绍。
AtomicIntegerArray类常用方法
public final int get(int i) //获取 index=i 位置元素的值
public final int getAndSet(int i, int newValue)//返回index=i位置的当前的值,并将其设置为新值:newValue
public final int getAndIncrement(int i)//获取index=i位置元素的值,并让该位置的元素自增
public final int getAndDecrement(int i) //获取index=i位置元素的值,并让该位置的元素自减
public final int getAndAdd(int i, int delta) //获取 index=i 位置元素的值,并加上预期的值
boolean compareAndSet(int i, int expect, int update) //如果输入的数值等于预期值,则以原子方式将index=i位置的元素值设置为输入值(update)
public final void lazySet(int i, int newValue)//最终将index=i位置的元素设置为 newValue,使用lazySet设置之后可能导致其他线程在之后的一小段时间内还是可以读到旧的值。
2. AtomicIntegerArray常见方法使用
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicIntegerArray;
public class AtomicIntegerArrayTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
int temvalue = 0;
int[] nums = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 };
AtomicIntegerArray i = new AtomicIntegerArray(nums);
for (int j = 0; j < nums.length; j++) {
System.out.println(i.get(j));
}
temvalue = i.getAndSet(0, 2);
System.out.println("temvalue:" + temvalue + "; i:" + i);
temvalue = i.getAndIncrement(0);
System.out.println("temvalue:" + temvalue + "; i:" + i);
temvalue = i.getAndAdd(0, 5);
System.out.println("temvalue:" + temvalue + "; i:" + i);
}
}
四、引用类型原子类
1.引用类型原子类介绍
基本类型原子类只能更新一个变量,如果需要原子更新多个变量,需要使用 引用类型原子类。
AtomicReference:引用类型原子类AtomicStampedReference:原子更新带有版本号的引用类型。该类将整数值与引用关联起来,可用于解决原子的更新数据和数据的版本号,可以解决使用CAS进行原子更新时可能出现的ABA问题。AtomicMarkableReference:原子更新带有标记的引用类型。该类将boolean标记与引用关联起来,也可以解决使用CAS进行原子更新时可能出现的 ABA 问题。
上面三个类提供的方法几乎相同,所以我们这里以AtomicReference为例子来介绍。
2. AtomicReference 类使用示例
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicReference;
public class AtomicReferenceTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
AtomicReference<Person> ar = new AtomicReference<Person>();
Person person = new Person("SnailClimb", 22);
ar.set(person);
Person updatePerson = new Person("Daisy", 20);
ar.compareAndSet(person, updatePerson);
System.out.println(ar.get().getName());
System.out.println(ar.get().getAge());
}
}
class Person {
private String name;
private int age;
public Person(String name, int age) {
super();
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
}
上述代码首先创建了一个Person对象,然后把Person对象设置进AtomicReference对象中,然后调用compareAndSet方法,该方法就是通过CAS操作设置 ar。如果ar的值为person的话,则将其设置为updatePerson。实现原理与AtomicInteger类中的compareAndSet方法相同。运行上面的代码后的输出结果如下:
Daisy
20
3. AtomicStampedReference 类使用示例
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicStampedReference;
public class AtomicStampedReferenceDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 实例化、取当前值和 stamp 值
final Integer initialRef = 0, initialStamp = 0;
final AtomicStampedReference<Integer> asr = new AtomicStampedReference<>
(initialRef, initialStamp);
System.out.println("currentValue=" + asr.getReference() + ",
currentStamp=" + asr.getStamp());
// compare and set
final Integer newReference = 666, newStamp = 999;
final boolean casResult = asr.compareAndSet(initialRef, newReference,
initialStamp, newStamp);
System.out.println("currentValue=" + asr.getReference()
+ ", currentStamp=" + asr.getStamp()
+ ", casResult=" + casResult);
// 获取当前的值和当前的stamp值
int[] arr = new int[1];
final Integer currentValue = asr.get(arr);
final int currentStamp = arr[0];
System.out.println("currentValue=" + currentValue + ", currentStamp=" + currentStamp);
// 单独设置 stamp 值
final boolean attemptStampResult = asr.attemptStamp(newReference, 88);
System.out.println("currentValue=" + asr.getReference()
+ ", currentStamp=" + asr.getStamp()
+ ", attemptStampResult=" + attemptStampResult);
// 重新设置当前值和 stamp 值
asr.set(initialRef, initialStamp);
System.out.println("currentValue=" + asr.getReference() + ",
currentStamp=" + asr.getStamp());
// [不推荐使用,除非搞清楚注释的意思了] weak compare and set
// 困惑!weakCompareAndSet 这个方法最终还是调用 compareAndSet 方法。[版本: jdk-8u191]
// 但是注释上写着 "May fail spuriously and does not provide ordering guarantees,
// so is only rarely an appropriate alternative to compareAndSet."
// todo 感觉有可能是 jvm 通过方法名在 native 方法里面做了转发
final boolean wCasResult = asr.weakCompareAndSet(initialRef,
newReference, initialStamp, newStamp);
System.out.println("currentValue=" + asr.getReference()
+ ", currentStamp=" + asr.getStamp()
+ ", wCasResult=" + wCasResult);
}
}
输出结果如下:
currentValue=0, currentStamp=0
currentValue=666, currentStamp=999, casResult=true
currentValue=666, currentStamp=999
currentValue=666, currentStamp=88, attemptStampResult=true
currentValue=0, currentStamp=0
currentValue=666, currentStamp=999, wCasResult=true
4. AtomicMarkableReference类使用示例
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicMarkableReference;
# 知其然不知其所以然,大厂常问面试技术如何复习?
**1、热门面试题及答案大全**
面试前做足功夫,让你面试成功率提升一截,这里一份热门350道一线互联网常问面试题及答案助你拿offer
> [**面试宝典+书籍+核心知识获取:戳这里免费下载**](https://gitee.com/vip204888/java-p7)!诚意满满!!!
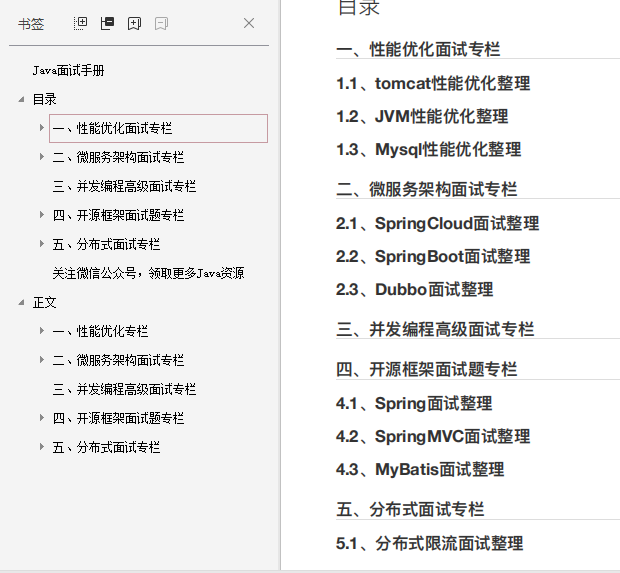
**2、多线程、高并发、缓存入门到实战项目pdf书籍**



**3、文中提到面试题答案整理**
**4、Java核心知识面试宝典**
覆盖了**JVM 、JAVA集合、JAVA多线程并发、JAVA基础、Spring原理、微服务、Netty与RPC、网络、日志、Zookeeper、Kafka、RabbitMQ、Hbase、MongoDB 、Cassandra、设计模式、负载均衡、数据库、一致性算法 、JAVA算法、数据结构、算法、分布式缓存、Hadoop、Spark、Storm的大量技术点且讲解的非常深入**



**4、Java核心知识面试宝典**
覆盖了**JVM 、JAVA集合、JAVA多线程并发、JAVA基础、Spring原理、微服务、Netty与RPC、网络、日志、Zookeeper、Kafka、RabbitMQ、Hbase、MongoDB 、Cassandra、设计模式、负载均衡、数据库、一致性算法 、JAVA算法、数据结构、算法、分布式缓存、Hadoop、Spark、Storm的大量技术点且讲解的非常深入**
[外链图片转存中...(img-aBh3L9WM-1628081321785)]
[外链图片转存中...(img-e3E4lwIE-1628081321786)]
[外链图片转存中...(img-WKePOcRt-1628081321786)]
























 206
206

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








