主要内容
- MapReduce编程模型简介
- WordCount编程实例
- Hadoop MapReduce架构
- MapReduce实战开发
一、MapReduce编程模型简介
MapReduce是一种可用于数据处理的编程模型。该模型比较简单,但用于编写有用的程序并不简单。Hadoop可以运行由各种语言编写的MapReduce程序。例如:Java、Ruby、Python和C++语言等。最重要的是,MapReduce程序本质上是并行运行的,因此可以将大规模的数据分析任务交给任何一个拥有足够多机器的运行商。MapReduce的优势在于处理大规模数据集。
- MapReduce是一种可用于海量数据(PB级以上)分布式并行处理的模型框架
- 模型简单
把万事万物都可以看做两个阶段来处理
map阶段
reduce阶段
- 编写有用的程序
如何写map
如何写reduce
- MapReduce可以用除Java以外的其他语言来实现
python Ruby C++ …
Java语言为主
- MapReduce的程序本质上是并行运行的
map阶段 可以开启多个map任务(线程)
map()函数
master,
slave,
YarnChild/TaskTracker(进程)
五个map任务(线程)
一个reduce任务(线程)
slave1,
YarnChild/TaskTracker(进程)
四个map任务(线程)
slave2,
YarnChild/TaskTracker(进程)
十个map任务(线程)
...
reduce阶段
reduce()
reduce 任务的个数取决于开发人员的设定 1个任务
slave,
YarnChild/TaskTracker(进程)
五个map任务(线程)
一个reduce任务(线程)
- MapReduce善于处理大规模的数据分析任务
1、从MapReduce自身的命名特点可以看出,MapReduce由两个阶段组成:Map和Reduce。用户只需map()和reduce()两个函数,即可完成简单的分布式程序设计。
2、map()函数以key/value对作为输入,产生另外一系列key/value对作为中间输出写入本地磁盘。MapReduce框架会自动将这些中间数据按照key值进行聚合,且key值相同的数据被统一交给reduce()函数处理。
3、reduce()函数以key及对应的value列表作为输入,经合并key相同的value值后,产生另外一系列key/value对作为最终输出写入HDFS。
MapReduce设计目的:
易于编程
良好的扩展性
高容错性
WordCount编程实例
统计词频
public class WordsCount {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException, InterruptedException {
if(args==null || args.length<2){
System.out.println("please input main method's parameters");
System.exit(0);
}
String inputPath = args[0];
String outputPath = args[1];
Configuration conf = new Configuration();
Job job = Job.getInstance(conf, WordsCount.class.getSimpleName());
job.setJarByClass(WordsCount.class);
FileInputFormat.addInputPath(job, new Path(inputPath));
FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job, new Path(outputPath));
job.setMapperClass(WordsMapper.class);
job.setReducerClass(WordsReducer.class);
job.setOutputKeyClass(Text.class);
job.setOutputValueClass(IntWritable.class);
//提交作业
job.waitForCompletion(true);
}
}
class WordsMapper extends Mapper<LongWritable, Text, Text, IntWritable>{
public void map(LongWritable key, Text value, Context context) throws IOException,InterruptedException {
String wordsLine = value.toString();
String[] words = wordsLine.split(" ");
for(String word : words){
context.write(new Text(word), new IntWritable(1));
}
}
}
class WordsReducer extends Reducer<Text, IntWritable, Text, IntWritable>{
public void reduce(Text key, Iterable<IntWritable> values, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException{
int sum = 0;
for(IntWritable value : values){
sum += value.get();
}
context.write(key, new IntWritable(sum));
}
}
要统计的单词
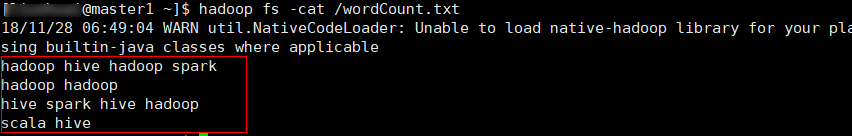
结果如下

用户编写完MapReduce程序后,按照一定的规则指定程序的输入和输出目录,并提交到Hadoop集群中,作业在Hadoop中的执行过程如图所示。Hadoop将输入数据切分成若干个输入分片(input split),并将每个split交给一个Map Task处理;Map Task不断的从对应的split中解析出一个个key/value,并调用map()函数处理,处理完之后根据Reduce Task个数将结果分成若干个分区(partition)写到本地磁盘;同时,每个Reduce Task从每个Map Task上读取属于自己的那个partition,然后基于排序的方法将key相同的数据聚集在一起,调用reduce()函数处理,并将结果输出到文件中。
流程图如下

三、Hadoop MapReduce架构
以下是hadoop1.0的架构,2.0参考(略)

-
1、Client
用户编写的MapReduce程序通过Client提交到JobTracker端;同时,用户可通过Client提供的一些接口查看作业的运行状态。在Hadoop内部用“作业”(Job)表示MapReduce程序。一个MapReduce程序可对应若干个作业,而每个作业会被分解成若干个Map/Reduce任务(Task)。 -
2、JobTracker
JobTracke负责资源监控和作业调度。JobTracker 监控所有TaskTracker 与job的健康状况,一旦发现失败,就将相应的任务转移到其他节点;同时,JobTracker 会跟踪任务的执行进度、资源使用量等信息,并将这些信息告诉任务调度器,而调度器会在资源出现空闲时,选择合适的任务使用这些资源。在Hadoop 中,任务调度器是一个可插拔的模块,用户可以根据自己的需要设计相应的调度器。 -
3、TaskTracker
TaskTracker 会周期性地通过Heartbeat 将本节点上资源的使用情况和任务的运行进度汇报给JobTracker,同时接收JobTracker 发送过来的命令并执行相应的操作(如启动新任务、杀死任务等)。TaskTracker 使用槽“slot”等量划分本节点上的资源量。“slot”代表计算资源(CPU、内存等)。一个Task 获取到一个slot 后才有机会运行,而Hadoop 调度器的作用就是将各个TaskTracker 上的空闲slot 分配给Task 使用。slot 分为Map slot 和Reduce slot 两种,分别供MapTask 和Reduce Task 使用。TaskTracker 通过slot 数目(可配置参数)限定Task 的并发度。 -
4、Task
Task 分为Map Task 和Reduce Task 两种,均由TaskTracker 启动。HDFS 以固定大小的block 为基本单位存储数据,而对于MapReduce 而言,其处理单位是split。split 是一个逻辑概念,它只包含一些元数据信息,比如数据起始位置、数据长度、数据所在节点等。它的划分方法完全由用户自己决定。但需要注意的是,split 的多少决定了Map Task 的数目,因为每个split 只会交给一个Map Task 处理。
Map Task 执行过程如下图 所示。由该图可知,Map Task 先将对应的split 迭代解析成一个个key/value 对,依次调用用户自定义的map() 函数进行处理,最终将临时结果存放到本地磁盘上,其中临时数据被分成若干个partition,每个partition 将被一个Reduce Task 处理。

Reduce Task 执行过程如下图所示。该过程分为三个阶段:
①从远程节点上读取MapTask 中间结果(称为“Shuffle 阶段”);
②按照key 对key/value 对进行排序(称为“Sort 阶段”);
③依次读取<key, value list>,调用用户自定义的reduce() 函数处理,并将最终结果存到HDFS 上(称为“Reduce 阶段”)。

四、MapReduce实战开发
数据源
- sogou500w数据或sogou4000w数据
数据字段描述
- Time:用户访问时间
- Uid:用户的id
- Keyword:访问的关键字
- Rank:点击排名
- Order:页数
- Url:网址
条件过滤
- 统计出搜索过包含有“仙剑奇侠传”内容的UID及搜索关键字记录
public class UidAndRecordIncludeKeyword {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException, InterruptedException {
if(args==null || args.length<2){
System.out.println("please input main method' parameters");
System.exit(0);
}
System.out.println(args[0]);
String inputPath = args[0];
String outputPath = args[1];
Configuration conf = new Configuration();
Job job = Job.getInstance(conf, UidAndRecordIncludeKeyword.class.getSimpleName());
job.setJarByClass(UidAndRecordIncludeKeyword.class);
job.setMapperClass(MyMapper.class);
job.setReducerClass(MyReducer.class);
FileInputFormat.addInputPath(job, new Path(inputPath));
FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job, new Path(outputPath));
job.setInputFormatClass(TextInputFormat.class);
job.setOutputFormatClass(TextOutputFormat.class);
job.setOutputKeyClass(Text.class);
job.setOutputValueClass(Text.class);
job.waitForCompletion(true);
}
}
class MyMapper extends Mapper<LongWritable, Text, Text, Text>{
@Override
public void map(LongWritable key, Text value, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
String line = value.toString();
String[] field = line.split("\t");
if(field!=null && field.length==6){
String record = field[2];
if(record.indexOf("仙剑奇侠传")>=0){
context.write(new Text(field[1]), new Text(field[2]));
}
}
}
}
class MyReducer extends Reducer<Text,Text,Text,Text>{
public void reduce(Text key, Iterable<Text> values, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
for(Text value : values){
sb.append(value.toString());
}
context.write(key, new Text(sb.toString()));
}
}
部分结果如下:

- rank<3并且order>2的所有UID及数量
public class Sogou500wDemo2 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException, InterruptedException {
if(args==null && args.length<2){
System.out.println("please input main method' parameters");
System.exit(0);
}
Configuration conf = new Configuration();
Job job = Job.getInstance(conf, Sogou500wDemo2.class.getSimpleName());
job.setJarByClass(Sogou500wDemo2.class);
FileInputFormat.addInputPath(job, new Path(args[0]));
FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job, new Path(args[1]));
job.setMapperClass(MyMapper2.class);
job.setReducerClass(MyReducer2.class);
job.setOutputKeyClass(Text.class);
job.setOutputValueClass(IntWritable.class);
// job.setNumReduceTasks(10);
job.waitForCompletion(true);
}
}
class MyMapper2 extends Mapper<LongWritable, Text, Text, IntWritable> {
public void map(LongWritable key, Text value, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
String line = value.toString();
String[] fields = line.split("\t");
if(fields!=null && fields.length==6){
int rank = Integer.parseInt(fields[3]);
int order = Integer.parseInt(fields[4]);
if(rank<3 && order>2){
context.write(new Text(fields[1]), new IntWritable(1));
}
}
}
}
class MyReducer2 extends Reducer<Text, IntWritable, Text, IntWritable>{
public void reduce(Text key, Iterable<IntWritable> values, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
int sum = 0;
for (IntWritable value : values){
sum += value.get();
}
context.write(key, new IntWritable(sum));
}
}

部分数据

条件查询
- 上午7-9点之间,搜索过“赶集网”的用户
本章小结
- MapReduce主要分为input、splitting、Mapping、Shuffling、Reducing、Final reduce这几个阶段。
- Hadoop MapReduce处理的数据一般位于底层分布式文件系统中。该系统往往将用户的文件切分为若干个固定大小的block存储到不同的节点上。默认情况下,MapReduce的每个Task处理一个block。
- MapReduce主要由四个组件构成,分别是Client,JobTracker,TaskTracker和Task,它们共同保障一个作业的成功运行。






















 2360
2360











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








