在Java中,时不时我们会把两个对象进行,然而得到的结果却不是我们想的结果,这是怎么回事呢?
一、两种形式的比较:比较时,我们要弄清楚是哪一种比较。
1.值类型比较
即内容相同,我们就认为是相等的。比如:int i=5;int j =5;此时我们说i和j相等,其实指的是i和j的内容相同。
2.引用类型比较
但在Java中,除了值类型,另外还有一种引用类型,而不同的对象,其引用值其实并不相等,即在内存中的不同的地 址单元中。比如我们定义了学生类,分别有两个学生对象实例 :
Student stu= new Student(); Student stu1= new Student();
此时我们无论是使用stu==stu1符号,或者stu.equals(stu1)方法,把两个对象进行比较,得到的结果都是不相等的,因为对于引用类型来说,默认是比较两个对象引用的地址,显示,每个对象的引用有自己唯一的地址,所以,是不相等。
二、有时,我们比较两个对象时,如果他们的内容一样,那么我们就认为这两个对象是相等的,如上面的两个学生对象。这时,我们该怎么办呢?其实,非常简单,只要在类里面重写equals()方法,进行对象里面的内容比较久可以了。如上面,我们只需要在Student类中重写equals()方法即可。
下面,让我们来看看实例吧! 没有重写equals()方法时的比较:
学生类:Student类
- package com.bluesky;
- public class Student {
- String name;
- public Student(){
- }
- public Student(String name){
- this.name=name;
- }</strong>
- }</span>
测试类Test:
- package com.bluesky;
- public class Test {
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- int i=5;
- int j=5;
- if(i==j) System.out.println("i和j相等!");
- else System.out.println("不相等!");
- Student s = new Student("BlueSky");
- Student s1=new Student("BlueSky");
- if(s==s1) System.out.println("s和是s1相等!");
- else System.out.println("s和是s1不相等!");
- if(s.equals(s1)) System.out.println("s和是s1相等!");
- else System.out.println("s和是s1不相等!");
- }
- }
运行结果:
重写equals()方法后再次进行比较:
Student类:
- package com.bluesky;
- public class Student {
- String name;
- public Student(){
- }
- public Student(String name){
- this.name=name;
- }
- public boolean equals(Object obj) {
- if (this == obj) //传入的对象就是它自己,如s.equals(s);肯定是相等的;
- return true;
- if (obj == null) //如果传入的对象是空,肯定不相等
- return false;
- if (getClass() != obj.getClass()) //如果不是同一个类型的,如Studnet类和Animal类,
- //也不用比较了,肯定是不相等的
- return false;
- Student other = (Student) obj;
- if (name == null) {
- if (other.name != null)
- return false;
- } else if (!name.equals(other.name)) //如果name属性相等,则相等
- return false;
- return true;
- }
- }
测试类Test:
- package com.bluesky;
- public class Test {
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- int i=5;
- int j=5;
- if(i==j) System.out.println("i和j相等!");
- else System.out.println("不相等!");
- Student s = new Student("BlueSky");
- Student s1=new Student("BlueSky");
- if(s==s1) System.out.println("s和是s1相等!");
- else System.out.println("s和是s1不相等!");
- if(s.equals(s1)) System.out.println("s和是s1相等!");
- else System.out.println("s和是s1不相等!");
- }
- }
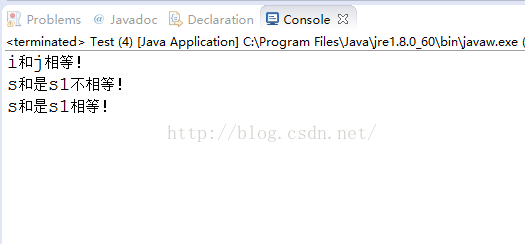
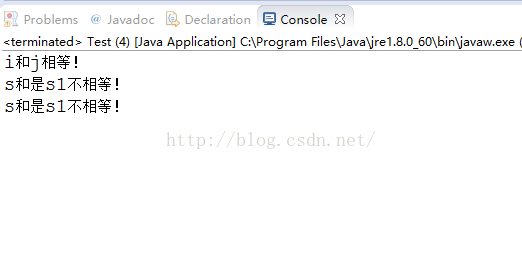
重写equals()方法后,得到s和s1相等。==对引用类型的只能进行地址比较,故还是不相等的。






















 1034
1034











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








