530.二叉搜索树的最小绝对差
题目:530. 二叉搜索树的最小绝对差 - 力扣(LeetCode)
思路:需要两两做差,层序遍历之后套两个for循环?应该可以利用一下二叉搜索树的特点,遍历每一个节点,求左右孩子跟自己的差,然后对比当前的最小绝对差,
递归三步曲
1、参数:当前节点,目前最小绝对差
2、终止条件:扫描到叶子节点
3、单层逻辑:分别求左右孩子跟自己的差值,更新条件是发现了更小的绝对差
尝试(部分AC)
class Solution {
private int result = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
public int getMinimumDifference(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null) return result;
int left = 0;
int right = 0;
if(root.left != null){
left = Math.abs(root.left.val - root.val);
if(left < result) result = left;
}
if(root.right != null){
right = Math.abs(root.right.val - root.val);
if(right < result) result = right;
}
getMinimumDifference(root.right);
getMinimumDifference(root.left);
return result;
}
}只能部分通过,我想的是【最小差值出现在相邻的两层】。事实上不是,题目说了是任意的节点,难道说先遍历一遍,排个顺序,再两两做差?想不通了。
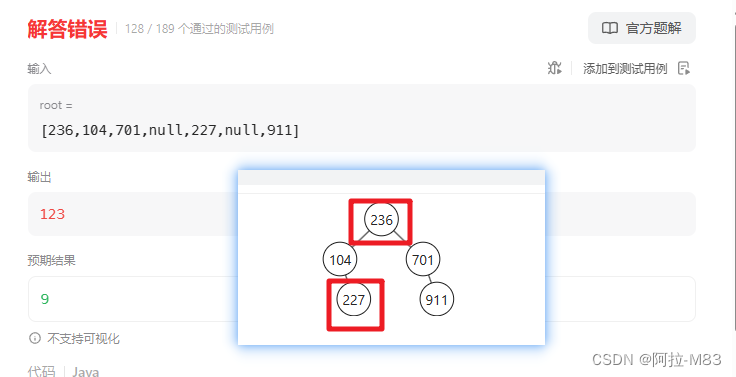
答案
// 递归法
class Solution {
TreeNode pre;// 记录上一个遍历的结点
int result = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
public int getMinimumDifference(TreeNode root) {
if(root==null)return 0;
traversal(root);
return result;
}
public void traversal(TreeNode root){
if(root==null)return;
//左
traversal(root.left);
//中
if(pre!=null){
result = Math.min(result,root.val-pre.val);
}
pre = root;
//右
traversal(root.right);
}
}小结
🍉画图看递归过程是个很不错的方法!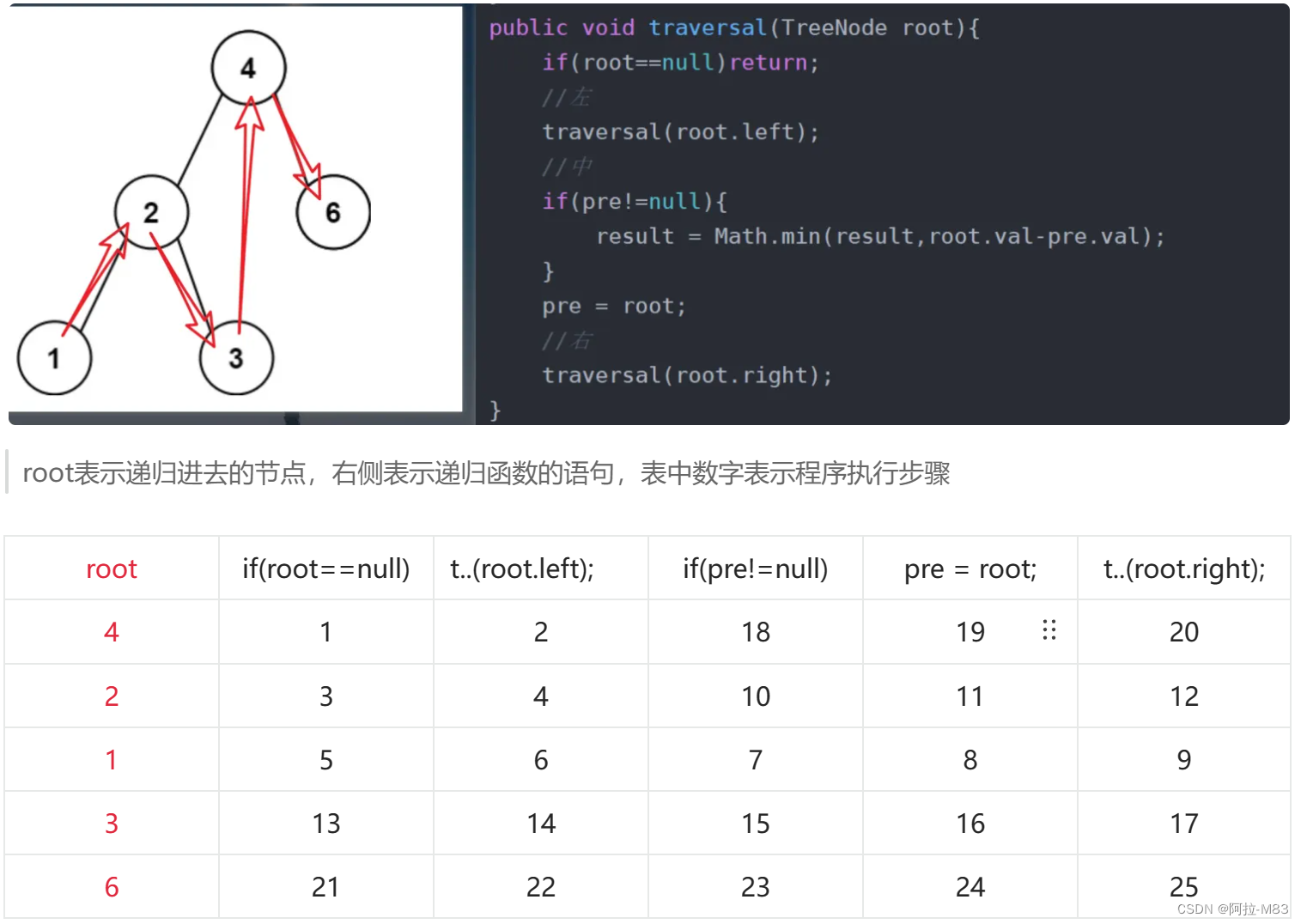
501.二叉搜索树中的众数
题目:501. 二叉搜索树中的众数 - 力扣(LeetCode)
思路:前序遍历,用map来存,记录最大值,取出最大值对应的所有key,不知道map有没有这个操作
尝试(暴力AC)
class Solution {
public Map<Integer, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
public int maxCount = 0;
public int[] findMode(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) return new int[0];
midOrder(root);
// 使用ArrayList来收集众数
List<Integer> modes = new ArrayList<>();
for (Integer key : map.keySet()) {
if (map.get(key) == maxCount) {
modes.add(key);
}
}
// 将ArrayList转换为数组
int[] result = new int[modes.size()];
for (int i = 0; i < modes.size(); i++) {
result[i] = modes.get(i);
}
return result;
}
public void midOrder(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) return;
midOrder(root.left);
// 更新计数并根据需要更新maxCount
map.put(root.val,map.getOrDefault(root.val,0)+1);
maxCount = Math.max(map.getOrDefault(root.val,0), maxCount);
midOrder(root.right);
}
}答案
// 中序遍历
class Solution {
ArrayList<Integer> resList;
int maxCount;
int count;
TreeNode pre;
public int[] findMode(TreeNode root) {
resList = new ArrayList<>();
maxCount = 0;
count = 0;
pre = null;
findMode1(root);
int[] res = new int[resList.size()];
for (int i = 0; i < resList.size(); i++) {
res[i] = resList.get(i);
}
return res;
}
public void findMode1(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return;
}
findMode1(root.left);
int rootValue = root.val;
// 计数,第一个节点,和第一次出现的节点,给count赋值 1
if (pre == null || rootValue != pre.val) {
count = 1;
} else {
count++;
}
// 更新结果以及maxCount
if (count > maxCount) {
resList.clear();
resList.add(rootValue);
maxCount = count;
} else if (count == maxCount) {
resList.add(rootValue);
}
pre = root;
findMode1(root.right);
}
}小结
🍉动态数组转换为普通数组
ArrayList<Integer> resList = new ArrayList<>();
int[] res = new int[resList.size()];
for (int i = 0; i < resList.size(); i++) {
res[i] = resList.get(i);
}🍉之所以可以实现一次遍历就搞定,是有一个清空数组【reList.clear()】的操作,每次检测到【count > maxCount】就重置返回结果
530.二叉树的最近公共祖先
题目:236. 二叉树的最近公共祖先 - 力扣(LeetCode)
思路:一整个人直接懵掉
尝试(标题4)
//尝试答案
class Solution {
public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
if(root == null || root == p || root == q){
return root;
}
TreeNode left = lowestCommonAncestor(root.left,p,q);
TreeNode right = lowestCommonAncestor(root.right,p,q);
if(left == null && right == null){
return null;
}else if(left == null && right !=null){
return right;
}else if(left != null && right == null){
return left;
}else{
return root;
}
}
}小结
🍉递归三部曲
1、返回值:节点,找到 q 或者 p 就返回
2、终止条件:遇到空 或者是 找到了 p q
3、单层递归逻辑:需要接住左、右孩子的返回值,根据返回值进行判断





















 1098
1098











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








