天天学Java
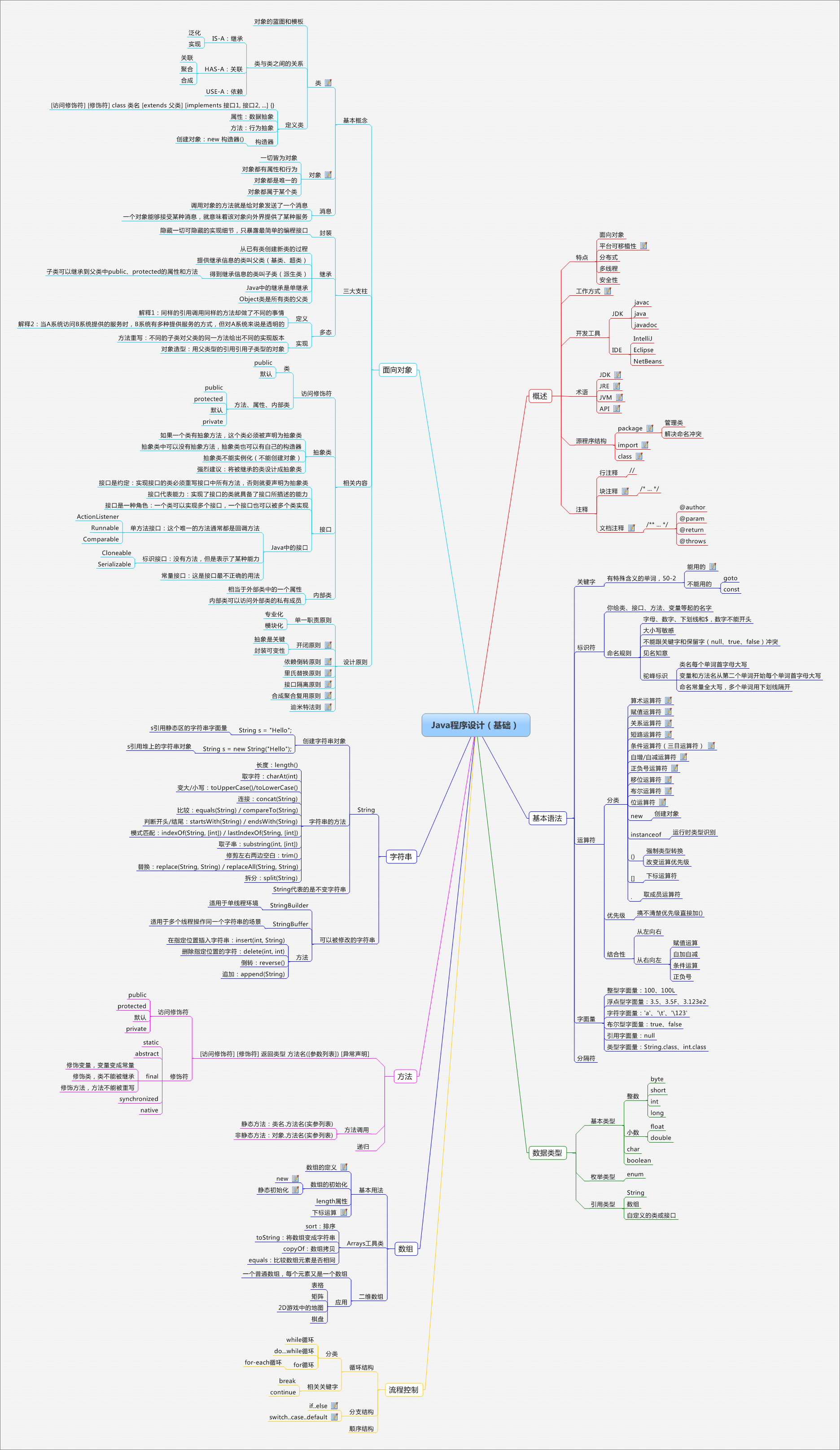
第一天:Java概述和基本语法
Java历史
- 1995年5月23日诞生
- 1998年 Java 2
- 2004年 Java 5
- 2014年 Java 8(目前的最新版本)
Java的特点
- 简单自然
- 面向对象(Object-Oriented)
- 可移植性(Write Once Run Anywhere)
- 分布式
- 多线程
- 安全健壮
Java的工作方式
- 先编译再解释执行
说明:通过JDK提供的Java编译器(javac)将Java源代码(.java文件)编译成类文件(.class文件,也叫做字节码,这是一种人和计算机都无法识别的中间代码),再通过启动Java虚拟机(java)加载类文件解释执行,当然JVM内部使用了JIT技术来提升执行效率。
相关术语
- JDK:Java Developer’s Kit - Java开发者工具
- JRE:Java Runtime Environment - Java运行时环境
- JVM:Java Virtual Machine - Java虚拟机
- API:Application Programming Interface - 应用程序编程接口
集成开发环境
- Eclipse:开放源代码的、基于Java的可扩展开发平台。
- IntelliJ:综合的Java 编程环境,被许多开发人员和行业专家誉为最好的IDE。
Java程序的结构
package com.lovoinfo;
public class Hello {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("Hello, world!");
}
}说明:由于Java是面向对象的编程语言,Java程序通常是由类构成的,定义类的关键字是class,后面跟上类的名字,类名后面的左花括号表示类的开始,最后面的右花括号表示类的结束。main方法是可执行程序的入口,它有三个修饰符,分别是public、static和void,方法的开始和结束仍然是用花括号来界定的。方法中的代码是由语句构成的,分号表示一条语句的结束。上面的程序使用了Java API中的System类的out对象的println方法在控制台进行输出。
练习1:输出下面的图案。
*******************
* *
* 欢迎来朗沃学习 *
* *
*******************package com.lovoinfo;
public class Hello {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("*************************");
System.out.println("*\t\t\t*");
System.out.println("*\t欢迎来到朗沃\t*");
System.out.println("*\t\t\t*");
System.out.println("*************************");
}
}练习2:在弹出式对话框上输出上面的图案。
package com.lovoinfo;
import javax.swing.JOptionPane;
public class HelloGUI {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String name = JOptionPane.showInputDialog("请输入你的名字: ");
String message = "****************************\n"
+ "\n* 欢迎" + name + "来到朗沃 *\n"
+ "\n****************************";
JOptionPane.showMessageDialog(null, message);
}
}练习3:两个数做加减乘除的运算。
package com.lovoinfo;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Calculator {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("请输入第一个整数: ");
int a = sc.nextInt();
System.out.print("请输入第二个整数: ");
int b = sc.nextInt();
System.out.printf("%d+%d=%d\n", a, b, a + b);
System.out.printf("%d-%d=%d\n", a, b, a - b);
System.out.printf("%d*%d=%d\n", a, b, a * b);
System.out.printf("%d/%d=%d\n", a, b, a / b);
sc.close();
}
}练习4:用弹出式对话框完成上面的程序。
package com.lovoinfo;
import javax.swing.JOptionPane;
public class CalculatorGUI {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String a = JOptionPane.showInputDialog("请输入第一个数:");
String b = JOptionPane.showInputDialog("请输入第二个数:");
int num1 = Integer.parseInt(a);
int num2 = Integer.parseInt(b);
String message = String.format(
"%d+%d=%d", num1, num2, num1 + num2);
JOptionPane.showMessageDialog(null, message);
}
}练习5:将英制单位的英寸转换成公制单位的厘米(1英寸=2.54厘米)。
package com.lovoinfo;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class InchToCentimeter {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("请输入英寸: ");
double a = sc.nextDouble();
double b = a * 2.54;
System.out.printf("%.2f 英寸 = %.2f 厘米\n", a, b);
sc.close();
}
}作业:编程实现摄氏温度转换成华氏温度。
第二天:数据类型和常用运算
基本语言元素
- 关键字:程序中有特殊含义和通途的单词
标识符:给变量、方法、类等起的名字
- 字母、数字、下划线和$,数字不能开头
- 大小写敏感(区分大小写)
- 不能跟关键字相同,不能包含特殊字符
- 见名知意,驼峰标识
运算符:指定某种运算的特殊符号
- 算术运算符:+、-、*、/、%
- 赋值运算符:=、+=、-=、*=、/=、%=、……
- 关系运算符:>、<、>=、<=、==、!=
- 短路运算符:&&、||
- 条件运算符:? :
- 自增自减运算符:++、–
- 类型转换运算符:()
- 其他运算符:逻辑运算符、位运算符、移位运算符、下标运算符、成员运算符等
字面量:程序中不变的部分
- 引用型字面量:null
- 布尔型字面量:true和false
- 字符型字面量:‘q’,‘\n’,‘\t’,‘\ddd’[*]
- 整型字面量:29,035,0x1d
- 实型字面量:3.14,.25e2,5.5f
- 字符串字面量:“Hello, world”
- 类字面量:String.class,int.class
分隔符:空格、花括号、方括号、圆括号、分号、逗号、冒号等
数据类型
基本类型(primitive type)
- 整型:byte、short、int、long
- 实型:float、double
- 布尔型:boolean
- 字符型:char
枚举类型(enumeration type):用于定义符号常量。
- 引用类型(reference type):除了基本数据类型和枚举类型,剩下的类型都是引用类型。
变量和常量
- 变量:计算机语言中能储存计算结果或能表示值抽象概念。变量可以通过变量名访问。在指令式语言中,变量存储的值通常是可变的,因此称之为变量。
- 常量:在程序运行时,不会被修改的量。Java中可以使用final关键字定义常量。
练习1:输入两个数找出其中较大的那个数。
package com.lovoinfo;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class FindMax {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("请输入两个数: ");
int a = sc.nextInt();
int b = sc.nextInt();
/*
if(a >= b) {
System.out.println(a);
}
else {
System.out.println(b);
}
*/
System.out.println(a >= b? a : b);
sc.close();
}
}练习2:输入身高(cm)和体重(kg)判断身材是否正常。判断标准"身高-110>=体重"认为是正常的。
package com.lovoinfo;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class AreYouFat {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("请输入你的名字: ");
String name = sc.nextLine();
System.out.print("请输入你的身高: ");
int height = sc.nextInt();
System.out.print("请输入你的体重: ");
int weight = sc.nextInt();
/*
if(height - 110 >= weight) {
System.out.println(name + "的身材正常!");
}
else {
System.out.println(name + "是个胖子!");
}
*/
System.out.println(name +
(height - 100 >= weight? "身材正常!" : "是个胖子!"));
sc.close();
}
}练习3:输入一个年份,判断是不是闰年。
package com.lovoinfo;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class IsLeapYear {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("请输入一个年份: ");
int year = sc.nextInt();
if((year % 4 == 0 && year % 100 != 0) || year % 400 == 0) {
System.out.println(year + "是闰年");
}
else {
System.out.println(year + "不是闰年");
}
sc.close();
}
}练习4:输入圆的半径,计算圆的周长和面积。
package com.lovoinfo;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class CalcCircle {
private static final double PI = 3.14;
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("请输入圆的半径: ");
double radius = sc.nextDouble();
double area = PI * radius * radius;
double circumference = 2 * PI * radius;
System.out.println("周长: " + circumference);
System.out.println("面积: " + area);
sc.close();
}
}练习5:输入三个整数,按从小到大的顺序输出。
package com.lovo;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class SortThreeNumber {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("请输入三个数: ");
int a = sc.nextInt();
int b = sc.nextInt();
int c = sc.nextInt();
if(a > b) {
int temp = a;
a = b;
b = temp;
}
if(a > c) {
int temp = a;
a = c;
c = temp;
}
if(b > c) {
int temp = b;
b = c;
c = temp;
}
System.out.printf("%d\t%d\t%d\n", a, b, c);
sc.close();
}
}作业:输入三个整数,输出其中最大的数。
第三天:程序逻辑-1(分支和循环)
程序的结构
- 顺序结构
- 分支结构
- 循环结构
流程图
- 圆角矩形:开始/结束
- 矩形:执行步骤
- 平行四边形:输入
- 菱形:判断决策
分支结构
- if…else…
- switch…case…default…
循环结构
- while循环
- do…while…循环
- for循环
break和continue
- break:终止循环
- continue:让循环进入下一轮
练习1:分段函数求值。
package com.lovoinfo;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Fx {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("x = ");
double x = sc.nextDouble();
double y;
if(x < -1) {
y = 3 * x + 5;
}
else if(x <= 1) {
y = x - 1;
}
else {
y = 5 * x - 3;
}
System.out.println("f(x) = " + y);
sc.close();
}
}练习2:个人所得税计算。在我国,个人所得税的起征点是3500元,计算公式是:
个人所得税 = (工资收入 - 五险一金 - 个税起征点) * 税率 - 速算扣除数
其中,税率和速算扣除数可以查下表得到:
| 级数 | 含税级距 | 税率 | 速算扣除数 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 不超过1500元的 | 3 | 0 |
| 2 | 超过1500元至4500元的部分 | 10 | 105 |
| 3 | 超过4500元至9000元的部分 | 20 | 555 |
| 4 | 超过9000元至35000元的部分 | 25 | 1005 |
| 5 | 超过35000元至55000元的部分 | 30 | 2755 |
| 6 | 超过55000元至80000元的部分 | 35 | 5505 |
| 7 | 超过80000元的部分 | 45 | 13505 |
package com.lovoinfo;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Tax {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("请输入工资: ¥");
double salary = sc.nextDouble();
double add = salary - salary * 0.08 - 3500;
double tax;
if(add <= 0) {
tax = 0;
}
else if(add <= 1500) {
tax = add * 0.03;
}
else if(add <= 4500) {
tax = add * 0.1 - 105;
}
else if(add <= 9000) {
tax = add * 0.2 - 555;
}
else if(add <= 35000) {
tax = add * 0.25 - 1005;
}
else if(add <= 55000) {
tax = add * 0.3 - 2755;
}
else if(add <= 80000) {
tax = add * 0.35 - 5505;
}
else {
tax = add * 0.45 - 13505;
}
System.out.printf("需要缴纳的个人所得税: ¥%.2f元\n", tax);
sc.close();
}
}
作业:输入一个百分制的成绩,将其转换成对应的等级,规则如下表所示:
| 成绩 | 等级 |
|---|---|
| 90-100 | A |
| 80-89 | B |
| 60-79 | C |
| <60 | D |
public class Test01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("请输入成绩(0-100): ");
int score = sc.nextInt();
if(score >= 0 && score <= 100) {
String level;
if(score >= 90) {
level = "A";
}
else if(score >= 80) {
level = "B";
}
else if(score >= 60) {
level = "C";
}
else {
level = "D";
}
System.out.println(level);
}
else {
System.out.println("输入错误!");
}
sc.close();
}
}练习4:输入成绩等级输出对应的评语,规则如下表所示:
| 成绩等级 | 评语 |
|---|---|
| A | 该生成绩优异,学习踏实认真 |
| B | 该生积极上进,学习态度较好 |
| C | 该生学习努力,成绩有待提高 |
| D | 该生成绩稳定,动手能力很强 |
package com.lovoinfo;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class CommentSystem {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("请输入成绩等级: ");
char level = sc.next().charAt(0);
switch(level) {
case 'a':
case 'A':
System.out.println("该生成绩优异,学习踏实认真");
break;
case 'b':
case 'B':
System.out.println("该生积极上进,学习态度较好");
break;
case 'c':
case 'C':
System.out.println("该生学习努力,成绩有待提高");
break;
case 'd':
case 'D':
System.out.println("该生成绩稳定,动手能力很强");
break;
default:
System.out.println("瓜西西,输错了!");
}
sc.close();
}
}练习5:将一颗色子掷60000次,统计每一面出现的次数。
package com.lovoinfo;
public class ThrowDie {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int f1 = 0, f2 = 0, f3 = 0, f4 = 0, f5 = 0, f6 = 0;
for(int i = 1; i <= 60000; i++) {
int face = (int)(Math.random() * 6 + 1);
switch(face) {
case 1: f1++; break;
case 2: f2++; break;
case 3: f3++; break;
case 4: f4++; break;
case 5: f5++; break;
case 6: f6++; break;
}
}
System.out.println("1点出现了" + f1 + "次");
System.out.println("2点出现了" + f2 + "次");
System.out.println("3点出现了" + f3 + "次");
System.out.println("4点出现了" + f4 + "次");
System.out.println("5点出现了" + f5 + "次");
System.out.println("6点出现了" + f6 + "次");
}
}
练习6:编程计算
package com.lovoinfo;
/**
* 用while循环实现1-100求和
* @author jackfrued
*
*/
public class Test03 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int sum = 0; // 累加变量
int i = 1; // 循环变量
while(i <= 100) {
sum += i++;
}
System.out.println("Sum = " + sum);
}
}package com.lovoinfo;
/**
* 用do...while循环实现1-100求和
* @author jackfrued
*
*/
public class Test04 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int sum = 0;
int i = 1;
do {
sum = sum + i;
i = i + 1;
} while(i <= 100);
System.out.println("Sum = " + sum);
}
}package com.lovoinfo;
/**
* 使用for循环实现1-100求和
* @author jackfrued
*
*/
public class Test05 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int sum = 0;
for(int i = 1; i <= 100; ++i) {
sum += i;
}
System.out.println("Sum = " + sum);
}
}作业:计算1-100之间的偶数的和。
练习7:编程计算
package com.lovoinfo;
public class Test06 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
double sum = 0;
for(int i = 1; i <= 10; i++) {
sum = sum + 1.0 / i;
}
System.out.println(sum);
}
}练习8:编程输入
package com.lovoinfo;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Test07 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("n = ");
int n = sc.nextInt();
double result = 1;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {
result = result * i;
}
System.out.println(n + "! = " + result);
sc.close();
}
}作业:输入两个正整数m和n,计算m^n^。
练习9:找出1-100之间的素数。
package com.lovoinfo;
/**
* 找出1-100之间的素数(质数, 只能被1和自身整除的数)
* @author jackfrued
*
*/
public class Test12 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
for(int i = 1; i <= 100; i++) {
// 假定当前的i是素数将isPrime赋值为true
boolean isPrime = true;
// 在2-(i-1)之间找寻i的因子
for(int j = 2; isPrime && j <= i - 1; j++) {
// i能被j整除说明它不是素数
if(i % j == 0) {
// 将isPrime修改成false表示i不是素数
isPrime = false;
}
}
// 如果isPrime的值是true说明i是素数就打印它
if(isPrime) {
System.out.println(i);
}
}
}
}练习10:找出1-100之间的完美数。
提示:完美数是该数除自身外的所有因子之和等于这个数本身的数。如28=1+2+4+7+14。
package com.lovoinfo;
/**
* 找出1-100之间的完美数
* @author jackfrued
*
*/
public class Test01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
for(int i = 1; i <= 10000; i++) {
int sum = 0;
for(int j = 1; j <= i - 1; j++) {
if(i % j == 0) {
sum += j;
}
}
if(sum == i) {
System.out.println(i);
}
}
}
}练习11:找出100-999之间的水仙花数。
提示:水仙花数是各位立方和等于这个数本身的数,如153=1^3^+5^3^+3^3^。
package com.lovoinfo;
public class Test11 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
for(int i = 100; i <= 999; i++) {
int gw = i % 10;
int sw = i / 10 % 10;
int bw = i / 100;
if(gw * gw * gw + sw * sw * sw + bw * bw * bw == i) {
System.out.println(i);
}
}
// for(int bw = 1; bw <= 9; bw++) {
// for(int sw = 0; sw <= 9; sw++) {
// for(int gw = 0; gw <= 9; gw++) {
// int num = bw * 100 + sw * 10 + gw;
// if(bw * bw * bw + sw * sw * sw + gw * gw * gw == num) {
// System.out.println(num);
// }
// }
// }
// }
}
}练习12:输入两个正整数,计算最大公约数和最小公倍数。
package com.lovoinfo;
import java.util.Scanner;
/**
* 输入两个正整数计算最大公约数和最小公倍数
* @author jackfrued
*
*/
public class Test02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("请输入两个正整数: ");
int num1 = sc.nextInt();
int num2 = sc.nextInt();
if (num1 > num2) {
int temp = num1;
num1 = num2;
num2 = temp;
}
boolean found = false;
for(int i = num1; !found && i >= 1; i--) {
if(num1 % i == 0 && num2 % i == 0) {
System.out.println("最大公约数是: " + i);
System.out.println("最小公倍数是: " + num1 / i * num2);
found = true;
}
}
sc.close();
}
}第四天:程序逻辑-2(分支和循环)
练习1:猜数字
计算机出一个1-100之间的随机数,玩家输入猜测的数字,计算机会给出相应的提示:如果玩家猜测的数字大于计算机出的数字,则提示"小一点";如果玩家猜测的数字小于计算机出的数字,则提示"大一点";如果猜对了就给出恭喜信息和猜的次数,游戏结束。
package com.lovoinfo;
import java.util.Scanner;
/**
* 猜数字
* @author jackfrued
*
*/
public class Test04 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int correctAnswer = (int) (Math.random() * 100 + 1);
int counter = 0;
int thyAnswer;
do {
System.out.print("请输入你猜的数字: ");
thyAnswer = sc.nextInt();
counter += 1;
if (thyAnswer == correctAnswer) {
System.out.println("恭喜你猜对了!总共猜了" + counter + "次");
if(counter > 7) {
System.out.println("智商拙计!!!");
}
} else if (thyAnswer > correctAnswer) {
System.out.println("小一点!");
} else {
System.out.println("大一点");
}
} while (thyAnswer != correctAnswer);
sc.close();
}
}
练习2:人机猜拳
package com.lovoinfo;
import java.util.Scanner;
/**
* 人机猜拳
* @author jackfrued
*
*/
public class Test05 {
/**
* 将出拳对应的数字变成中文
* @param fist 出拳的数字
* @return 出拳字对应的中文
*/
public static String getFist(int fist) {
String str;
if(fist == 1) {
str = "剪刀";
}
else if(fist == 2) {
str = "石头";
}
else {
str = "布";
}
return str;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int money = 1000;
do {
int debt;
do {
System.out.println("你总共有" + money + "元");
System.out.print("请下注: ");
debt = sc.nextInt();
} while(debt <= 0 || debt > money);
int computerFist = (int) (Math.random() * 3 + 1);
int thyFist;
do {
System.out.print("请出拳(1. 剪刀; 2. 石头; 3. 布): ");
thyFist = sc.nextInt();
} while (thyFist < 1 || thyFist > 3);
System.out.println("计算机出的是" + getFist(computerFist));
System.out.println("你出的是" + getFist(thyFist));
if(computerFist == thyFist) {
System.out.println("平局!");
}
else {
if(computerFist == 1) {
if(thyFist == 2) {
money += debt;
System.out.println("你赢了!");
}
else {
money -= debt;
System.out.println("计算机赢了!");
}
}
else if(computerFist == 2) {
if(thyFist == 1) {
money -= debt;
System.out.println("计算机赢了!");
}
else {
money += debt;
System.out.println("你赢了!");
}
}
else {
if(thyFist == 1) {
money += debt;
System.out.println("你赢了!");
}
else {
money -= debt;
System.out.println("计算机赢了!");
}
}
}
} while(money > 0);
System.out.println("你破产了!游戏结束!");
sc.close();
}
}练习3:Craps赌博游戏。
玩家摇两颗色子,如果第一次摇出了7点和11点,则玩家胜;如果第一次摇出了2点、3点、12点,则庄家胜;如果摇出其他点数,游戏继续,在继续的过程中,如果玩家摇出了第一次摇的点数,则玩家胜;如果摇出了7点,则庄家胜;否则游戏继续,直到分出胜负。
package com.lovoinfo;
import java.util.Scanner;
/**
* Craps赌博游戏
* @author jackfrued
*
*/
public class Test03 {
/**
* 摇两颗色子
* @return 两个色子摇出的点数之和
*/
public static int rollDice() {
int face1 = (int) (Math.random() * 6 + 1);
int face2 = (int) (Math.random() * 6 + 1);
return face1 + face2;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int money = 1000;
do {
int debt = 0; // 下注的金额
do {
System.out.println("你的余额" + money + "元");
System.out.print("请下注: ");
if(sc.hasNextInt()) { // 判断能否读到一个整数
debt = sc.nextInt();
}
else {
System.out.println("输入错误!");
sc.nextLine(); // 把错误的输入读走
}
} while (debt <= 0 || debt > money);
int firstPoint = rollDice();
System.out.println("玩家摇出了" + firstPoint + "点");
boolean gameOver = true; // 表示游戏是否应该结束的布尔值
switch(firstPoint) {
case 7:
case 11:
money += debt;
System.out.println("玩家胜!");
break;
case 2:
case 3:
case 12:
money -= debt;
System.out.println("庄家胜!");
break;
default:
gameOver = false; // 如果第一次没有分出胜负游戏就没有结束
}
while(!gameOver) { // 只要游戏没有结束就要继续摇色子
int currentPoint = rollDice();
System.out.println("玩家摇出了" + currentPoint + "点");
if(currentPoint == 7) {
money -= debt;
System.out.println("庄家胜!");
gameOver = true;
}
else if(currentPoint == firstPoint) {
money += debt;
System.out.println("玩家胜!");
gameOver = true;
}
}
} while(money > 0);
System.out.println("恭喜你, 破产了!");
sc.close();
}
}练习4:九九表
package com.lovoinfo;
public class Test09 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
for(int i = 1; i <= 9; i++) {
for(int j = 1; j <= i; j++) {
System.out.printf("%d*%d=%d\t", i, j, i * j);
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}作业:输出直角三角形图案。
package com.lovoinfo;
public class Test10 {
private static final int ROW = 10;
public static void main(String[] args) {
for(int i = 1; i <= ROW; i++) {
for(int j = 1; j <= i; j++) {
System.out.print("*");
}
System.out.println();
}
System.out.println("\n---华丽的分隔线---\n");
for(int i = 1; i <= ROW; i++) {
for(int j = ROW; j >= i; j--) {
System.out.print("*");
}
System.out.println();
}
System.out.println("\n---华丽的分隔线---\n");
for(int i = 1; i <= ROW; i++) {
for(int j = 1; j <= ROW; j++) {
if((ROW - i) >= j) {
System.out.print(" ");
}
else {
System.out.print("*");
}
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}练习5:百钱百鸡。
公鸡5元一只,母鸡3元一只,小鸡1元三只,用100元买100只鸡,问公鸡、母鸡和小鸡各有多少只?
package com.lovoinfo;
/**
* 百钱买百鸡(穷举法)
* @author jackfrued
*
*/
public class Test14 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("公鸡\t母鸡\t小鸡");
// 假设公鸡x只, 母鸡y只, 小鸡z只
for(int x = 0; x <= 20; x++) {
for(int y = 0; y <= 33; y++) {
int z = 100 - x - y;
if(5 * x + 3 * y + z / 3 == 100 && z % 3 == 0) {
System.out.printf("%d\t%d\t%d\n", x, y, z);
}
}
}
}
}作业:21根火柴游戏。
桌上有21根火柴,人和计算机轮流拿火柴,每次最少1根,最多4根,谁拿到最后一根火柴谁就输了。编程模拟此游戏,每次都由人先拿,并保证计算机一定能够获得胜利。
第五天:数组、方法和字符串
数组
- 定义数组的语法:
T[] x = new T[size]; T[] y = { value1, value2, ... };- 操作数组元素可以使用下标运算[ ],数组的下标范围0-(数组大小-1)。
- 数组有一个length属性表示数组元素的个数。
- 通常可以用循环来对数组中的元素进行操作。
二维数组
- 定义二维数组的语法:
T[][] x = new T[size1][size2]; T[][] y = new T[size][]; T[][] z = {{v1, v2}, {v3, v4, v5, v6}, {v7}};- 二维数组的应用场景:表格、矩阵、棋盘、2D游戏中的地图。
方法的定义和使用
public static T foo(T1 param1, T2 param2, ...) { // 方法体 }方法的递归调用
- 方法直接或间接的调用自身
字符串用法及常用方法
- 字符串对象的创建
String s1 = "Hello"; String s1 = new String("Hello");- 字符串常用方法
- equals:比较两个字符串内容是否相同
- equalsIgnoreCase:忽略大小写比较两个字符串内容是否相同
- compareTo:比较两个字符串的大小
- length:计算字符串的长度
- concat:字符串连接
- charAt:从字符串中取指定位置的字符
- indexOf/lastIndexOf:字符串的匹配
- trim:修剪字符串左右两端的空白
- toUpperCase/toLowerCase:将字符串变成大写/小写
- substring:从字符串中取指定位置的子串
- startsWith/endsWith:判断字符串是否以指定的字符串开头/结尾
- replace:将字符串中指定内容替换为另外的字符串
练习1:录入5名学生的成绩,计算平均分,找出最高分和最低分。
package com.lovoinfo;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Test01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
String[] names = {"关羽", "张飞", "赵云", "黄忠", "马超"};
double[] scores = new double[5];
double sum = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < scores.length; i++) {
System.out.print("请输入" + names[i] + "的成绩: ");
scores[i] = sc.nextDouble();
sum = sum + scores[i];
}
System.out.println("平均分为: " + sum / scores.length);
int maxIndex = 0, minIndex = 0;
for(int i = 1; i < scores.length; i++) {
if(scores[i] > scores[maxIndex]) {
maxIndex = i;
}
else if(scores[i] < scores[minIndex]) {
minIndex = i;
}
}
System.out.println(names[maxIndex] + "考了最高分" + scores[maxIndex]);
System.out.println(names[minIndex] + "考了最低分" + scores[minIndex]);
sc.close();
}
}
练习2:输出前20个Fibonacci数。
1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13, 21, 34, …
package com.lovoinfo;
/**
* 输出前20个Fibonacci数
* @author jackfrued
*
*/
public class Test04 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] f = new int[20];
f[0] = f[1] = 1;
for(int i = 2; i < f.length; i++) {
f[i] = f[i - 1] + f[i - 2];
}
for(int x : f) {
System.out.println(x);
}
}
}练习3:随机产生10个数,并对其进行排序。
package com.lovoinfo;
public class Test05 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] a = new int[10];
System.out.println("排序前: ");
for (int i = 0; i < a.length; i++) {
a[i] = (int) (Math.random() * 100);
System.out.print(a[i] + "\t");
}
bubbleSort(a);
System.out.println("\n排序后: ");
for (int x : a) {
System.out.print(x + "\t");
}
}
/**
* 冒泡排序
* @param a 待排序的数组
*/
public static void bubbleSort(int[] a) {
// N个元素排序需要N-1趟循环
for (int i = 0; i < a.length - 1; i++) {
// 相邻元素两两比较
for(int j = 0; j < a.length - 1 - i; j++) {
if(a[j] > a[j + 1]) { // 如果前面元素大于后面元素就交换
int temp = a[j];
a[j] = a[j + 1];
a[j + 1] = temp;
}
}
}
}
/**
* 简单选择排序
* @param a 待排序的数组
*/
public static void selectionSort(int[] a) {
for (int i = 0; i < a.length - 1; i++) {
int minIndex = i; // 假设当前的i是最小元素所在的位置
for (int j = i + 1; j < a.length; j++) {
if (a[j] < a[minIndex]) { // 发现更小的元素
minIndex = j; // 记录更小的元素所在的位置
}
}
// 将i位置上的元素和最小元素交换位置
int temp = a[i];
a[i] = a[minIndex];
a[minIndex] = temp;
}
}
}
练习4:输入5个学生三门课的成绩,计算每个学生的平均分以及每门课程的平均分。
package com.lovoinfo;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Test07 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
String[] stuNames = {"关羽", "张飞", "赵云", "黄忠", "马超"};
String[] subNames = {"语文", "数学", "英语"};
int[][] scores = new int[stuNames.length][subNames.length];
for(int i = 0; i < scores.length; i++) {
System.out.println("请录入" + stuNames[i] + "的成绩");
for(int j = 0; j < scores[i].length; j++) {
System.out.print("\t" + subNames[j] + ": ");
scores[i][j] = sc.nextInt();
}
}
// 后面的代码自行完成
sc.close();
}
}练习5:输出10行杨辉三角。
package com.lovoinfo;
/**
* 杨辉三角
* @author jackfrued
*
*/
public class Test08 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[][] y = new int[10][];
for(int i = 0; i < y.length; i++) {
y[i] = new int[i + 1];
for(int j = 0; j < y[i].length; j++) {
if(j == 0 || j == i) {
y[i][j] = 1;
}
else {
y[i][j] = y[i - 1][j] + y[i - 1][j - 1];
}
}
}
for(int[] a : y) {
for(int b : a) {
System.out.print(b + "\t");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}练习6:输入用户名和密码,验证用户身份。
package com.lovoinfo;
import java.util.Scanner;
/**
* 用户登录验证
* @author jackfrued
*
*/
public class Test03 {
/**
* 在数组中查找有没有指定的元素
* @param x 数组
* @param y 指定的元素
* @return 找到了返回元素在数组中的位置,没有找到返回-1
*/
public static int findUsername(String[] x, String y) {
for(int i = 0; i < x.length; i++) {
if(x[i].equals(y)) {
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
String[] usernames = {"admin", "jack", "guest"};
String[] passwords = {"123456", "abcdefg", "000000"};
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
boolean isLogin = false; // 是否登录成功
do {
System.out.print("请输入用户名: ");
String username = sc.nextLine().trim();
System.out.print("请输入密码: ");
String password = sc.nextLine();
int index = findUsername(usernames, username);
if(index != -1) {
if(password.equals(passwords[index])) {
isLogin = true;
}
}
if(!isLogin) {
System.out.println("用户名或密码错误!!!");
}
} while (!isLogin);
// 登录成功就结束do...while循环显示欢迎信息
System.out.println("登录成功!欢迎使用本系统...");
sc.close();
}
}练习7:跑马灯效果。
package com.lovoinfo;
public class Test04 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
String str = "欢迎来朗沃学习 ";
while(true) {
System.out.println(str);
str = str.substring(1) + str.charAt(0);
Thread.sleep(200);
}
}
}练习8:实现字符串倒转、字符串去掉空格、字符串大小写互换的方法。
package com.lovoinfo;
public class Test05 {
/**
* 字符串倒转
* @param str 原来的字符串
* @return 倒转后的字符串
*/
public static String reverse(String str) {
String newStr = "";
for(int i = str.length() - 1; i >= 0; --i) {
newStr += str.charAt(i);
}
return newStr;
}
/**
* 修剪字符串中所有的空白字符
* @param str 原来的字符串
* @return 去掉空白字符后的字符串
*/
public static String trimAll(String str) {
String newStr = "";
for(int i = 0; i < str.length(); i++) {
if(str.charAt(i) != ' ') {
newStr += str.charAt(i);
}
}
return newStr;
}
/**
* 将字符串中的小写字母变大写,大写字母变小写
* @param str 原来的字符串
* @return 变换后的字符串
*/
public static String switchUpperLower(String str) {
String newStr = "";
for(int i = 0; i < str.length(); i++) {
char ch = str.charAt(i);
if(ch >= 'A' && ch <= 'Z') {
ch += 32; // 相当于 ch = (char)(ch + 32);
}
else if(ch >= 'a' && ch <= 'z') {
ch -= 32; // 相当于 ch = (char)(ch - 32);
}
newStr += ch;
}
return newStr;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// hELLO, wORLD!
System.out.println(switchUpperLower("Hello, World!"));
System.out.println(reverse("hello")); // olleh
System.out.println(reverse("我爱你")); // 你爱我
System.out.println(reverse("i love you")); // uoy evol i
System.out.println(trimAll(" h e l l o ")); // hello
}
}
第六天:面向对象入门
基本概念
- 对象:①一切皆为对象;②每个对象都是唯一的;③对象都属于某个类;④对象都有属性和行为。
- 类:类是将一类对象共同的特征抽取出来的结果,是对象的蓝图和模板。
四大支柱
- 抽象(abstraction):寻找共性。定义类的过程就是一个抽象的过程,需要做数据抽象和行为抽象。
- 封装(encapsulation):隐藏一切可以隐藏的复杂繁琐的实现细节,只提供清晰简单的接口(界面)。
- 继承(inheritance):从已有的类创建新类的过程。提供继承信息的类叫父类(超类、基类),得到继承信息的类叫子类(派生类、衍生类)。继承是一种复用代码的手段。
- 多态(polymorphism):执行相同的行为却做了不同的事情(产生了不同的结果)。
定义类
创建和使用对象
发现问题域中的类
从问题描述中找名词和动词,名词会成为类或者对象的属性,动词会成为对象的方法。
类的结构
public class 类名 {
// 属性(数据抽象)
// 构造器
// 方法(行为抽象)
}创建和使用对象的语法
类型 变量名 = new 构造器([参数列表]);
变量名.方法([参数列表]);练习1:写一个类,模拟数字时钟。
package com.lovoinfo;
import java.util.Calendar;
/**
* 时钟
* @author jackfrued
*
*/
public class Clock {
private int hour; // 时
private int minute; // 分
private int second; // 秒
/**
* 构造器
*/
public Clock() {
Calendar cal = Calendar.getInstance();
hour = cal.get(Calendar.HOUR_OF_DAY);
minute = cal.get(Calendar.MINUTE);
second = cal.get(Calendar.SECOND);
}
/**
* 构造器
* @param hour 时
* @param minute 分
* @param second 秒
*/
public Clock(int hour, int minute, int second) {
this.hour = hour;
this.minute = minute;
this.second = second;
}
/**
* 走字
*/
public void go() {
second += 1;
if(second == 60) {
second = 0;
minute += 1;
if(minute == 60) {
minute = 0;
hour += 1;
if(hour == 24) {
hour = 0;
}
}
}
}
/**
* 显示时间
* @return 返回当前时间
*/
public String display() {
String str = "";
if(hour < 10) {
str += "0";
}
str += hour + ":";
if(minute < 10) {
str += "0";
}
str += minute + ":";
if(second < 10) {
str += "0";
}
str += second;
return str;
}
/**
* 调整小时
* @param up true表示上调, false表示下调
*/
public void setHour(boolean up) {
if(up) {
hour = (hour + 1) % 24;
}
else {
hour -= 1;
if(hour == -1) {
hour = 23;
}
}
}
/**
* 调整分钟
* @param up true表示上调, false表示下调
*/
public void setMinute(boolean up) {
if(up) {
minute = (minute + 1) % 60;
}
else {
minute -= 1;
if(minute == -1) {
minute = 59;
}
}
}
/**
* 调整秒
* @param up true表示上调, false表示下调
*/
public void setSecond(boolean up) {
if(up) {
second = (second + 1) % 60;
}
else {
second -= 1;
if(second == -1) {
second = 59;
}
}
}
}
package com.lovoinfo;
public class Test03 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Clock c = new Clock();
while(true) {
System.out.println(c.display());
Thread.sleep(1000);
c.go();
}
}
}练习2:计划修一个圆形的游泳池,半径尚未确定,游泳池的外围修建宽度为3m的环形过道,过道的外围修建一圈围墙,已知围墙的造价为5元/m,过道的造价为18元/m^2^,写一个程序,输入游泳池的半径,计算出过道和围墙的造价。
package com.lovoinfo;
// 1. 定义类(数据抽象[属性]、行为抽象[方法]、构造器)
/**
* 圆
* @author jackfrued
*
*/
public class Circle {
private double radius; // 半径
/**
* 构造器
* @param radius 半径
*/
public Circle(double radius) {
this.radius = radius;
}
/**
* 获得周长
* @return 圆的周长
*/
public double circumference() {
return 2 * Math.PI * radius;
}
/**
* 获得面积
* @return 圆的面积
*/
public double area() {
return Math.PI * radius * radius;
}
}package com.lovoinfo;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Test01 {
private static final double FUNIT = 5.5; // 围墙的单位造价
private static final double CUNIT = 18; // 过道的单位造价
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("请输入游泳池的半径: ");
double r = sc.nextDouble();
// 2. 创建对象
Circle c1 = new Circle(r);
Circle c2 = new Circle(r + 3);
// 3. 让对象发生行为(对象调用方法)求解问题
System.out.printf("围墙的造价为: ¥%.2f元\n",
c2.circumference() * FUNIT);
System.out.printf("过道的造价为: ¥%.2f元\n",
(c2.area() - c1.area()) * CUNIT);
sc.close();
}
}练习3:学生类和老师类。
package com.lovoinfo;
/**
* 人(父类)
* @author jackfrued
*
*/
public class Person {
protected String name; // 姓名
protected int age; // 年龄
/**
* 构造器
* @param name 姓名
* @param age 年龄
*/
public Person(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
/**
* 吃饭
*/
public void eat() {
System.out.println(name + "在吃饭");
}
/**
* 睡觉
*/
public void sleep() {
System.out.println(name + "在睡觉");
}
/**
* 玩耍
*/
public void play() {
}
}
package com.lovoinfo;
/**
* 学生(人的子类)
* @author jackfrued
*
*/
public class Student extends Person {
private String grade; // 年级
/**
* 构造器
* @param name 姓名
* @param age 年龄
* @param grade 年级
*/
public Student(String name, int age, String grade) {
super(name, age); // 调用父类构造器
this.grade = grade;
}
/**
* 学习
* @param courseName 课程名称
*/
public void study(String courseName) {
System.out.println(name + "在学习" + courseName);
}
/**
* 玩耍(对父类中的play方法进行重新实现[重写])
*/
public void play() {
System.out.println(name + "在玩LOL");
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return name + " - " + age + " - " + grade;
}
}package com.lovoinfo;
/**
* 老师(人的子类)
* @author jackfrued
*
*/
public class Teacher extends Person {
private String title; // 职称
/**
* 构造器
* @param name 姓名
* @param age 年龄
* @param title 职称
*/
public Teacher(String name, int age, String title) {
super(name, age);
this.title = title;
}
/**
* 授课
* @param courseName 课程名称
*/
public void teach(String courseName) {
System.out.println(name + "正在教" + courseName);
}
/**
* 玩耍(对父类中的play进行重新实现[重写])
*/
public void play() {
System.out.println(name + "在打麻将");
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return name + " - " + age + " - " + title;
}
}
练习4:编程模拟银行账户及其操作。
package com.lovoinfo;
/**
* 银行账户
* @author jackfrued
*
*/
public class Account {
private String cardNumber; // 卡号
private String password; // 密码
private double balance; // 余额
/**
* 构造器
* @param cardNumber 卡号
* @param password 初始密码
*/
public Account(String cardNumber, String password) {
this.cardNumber = cardNumber;
this.password = password;
this.balance = 0.0;
}
/**
* 验证密码
* @param thyPassword 输入的密码
* @return 验证通过返回true否则返回false
*/
public boolean verify(String thyPassword) {
return password.equals(thyPassword);
}
/**
* 取款
* @param money 取款金额
* @return 取款成功返回true否则返回false
*/
public boolean withdraw(double money) {
if(money > 0 && money <= balance) {
balance -= money;
return true;
}
return false;
}
/**
* 存款
* @param money 存款金额
* @return 存款成功返回true否则返回false
*/
public boolean deposit(double money) {
if(money > 0) {
balance += money;
return true;
}
return false;
}
/**
* 转账
* @param other 转入账户
* @param money 转出金额
* @return 转账成功返回true否则返回false
*/
public boolean transfer(Account other, double money) {
if(this.withdraw(money)) { // 如果当前账户扣款成功才能向转入账户存钱
boolean flag = other.deposit(money);
if(!flag) { // 如果向转入账户存钱不成功则应返还转出金额
this.deposit(money);
}
return flag;
}
return false;
}
/**
* 查询余额
* @return 账户余额
*/
public double getBalance() {
return balance;
}
/**
* 获得卡号
* @return 卡号
*/
public String getCardNumber() {
return cardNumber;
}
/**
* 修改密码
* @param newPassword 新密码
*/
public void changePassword(String newPassword) {
this.password = newPassword;
}
}练习5:双色球随机选号程序。
package com.lovoinfo;
/**
* 球
* @author jackfrued
*
*/
public class Ball {
private int number; // 数字
private boolean used; // 是否被使用过
/**
* 构造器
* @param number 球上面的数字
*/
public Ball(int number) {
this.number = number;
// this.used = false;
}
/**
* 球是否被使用过
* @return 使用过返回true否则返回false
*/
public boolean isUsed() {
return used;
}
/**
* 设置球有没有被使用过
* @param used true表示使用过false表示没有使用过
*/
public void setUsed(boolean used) {
this.used = used;
}
/**
* 获得球上的号码(如果号码小于10前面要补0)
* @return 号码补0后的字符串
*/
public String getNumber() {
return number < 10? "0" + number : "" + number;
}
/**
* 获得球上的号码
* @return 号码的数字
*/
public int getNum() {
return number;
}
}package com.lovoinfo;
/**
* 双色球选号机
* @author jackfrued
*
*/
public class LotteryMachine {
private Ball[] redBalls = new Ball[33]; // 33个红球
private Ball[] blueBalls = new Ball[16]; // 16个蓝球
// 装入红色球和蓝色球
public void load() {
for(int i = 0; i < redBalls.length; i++) {
redBalls[i] = new Ball(i + 1); // 创建一颗球
}
for(int i = 0; i < blueBalls.length; i++) {
blueBalls[i] = new Ball(i + 1);
}
}
// 摇出6个红色球
public Ball[] getRedBalls() {
Ball[] rBalls = new Ball[6];
for(int i = 0; i < rBalls.length; i++) {
Ball currentBall = null;
do {
int index = (int) (Math.random() * redBalls.length);
currentBall = redBalls[index];
} while(currentBall.isUsed());
rBalls[i] = currentBall;
currentBall.setUsed(true);
}
for(int i = 1; i < rBalls.length; i++) {
for(int j = 0; j < rBalls.length - i; j++) {
if(rBalls[j].getNum() > rBalls[j + 1].getNum()) {
Ball temp = rBalls[j];
rBalls[j] = rBalls[j + 1];
rBalls[j + 1] = temp;
}
}
}
return rBalls;
}
// 摇出1个蓝色球
public Ball getBlueBall() {
return blueBalls[(int) (Math.random() * blueBalls.length)];
}
// 产生一个随机号码
public String generateRandomNumber() {
load(); // 装入红色球和蓝色球
Ball[] myRedBalls = getRedBalls(); // 摇出6个红色球
Ball myBlueBall = getBlueBall(); // 摇出1个蓝色球
String myNumber = "";
for(int i = 0; i < myRedBalls.length; i++) {
myNumber += myRedBalls[i].getNumber() + " ";
}
myNumber += "|";
myNumber += " " + myBlueBall.getNumber();
return myNumber;
}
}package com.lovoinfo;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Test06 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
LotteryMachine lm = new LotteryMachine();
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("机选几注: ");
int n = sc.nextInt();
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
System.out.println(lm.generateRandomNumber());
}
sc.close();
}
}第七天:深入面向对象-1
- 继承:从已有的类创建新类的过程,提供继承信息的类称为父类(超类、基类),得到继承信息的类称为子类(派生类、衍生类)。继承使用extends关键字,Java中的继承是单继承(一个类之只能有一个父类)。
- 多态:子类在继承父类的过程中可以对父类已有的方法进行重写,不同的子类给出不同的实现版本,那么同样类型的引用调用同样的方法将发生不同的行为,这就是多态。
- 相关概念
- 抽象类:被abstract关键字修饰的类,抽象类不能实例化(不能创建对象),专门为其他类提供继承信息。
- 抽象方法:如果一个方法没有方法体,就可以定义为抽象方法,也是用abstract关键字修饰,如果一个类有抽象方法,这个类必须被声明为抽象类。子类继承该抽象类时必须重写抽象方法。
- 终结类:被final关键字修饰的类,终结类不能被继承,工具类通常声明为终结类。
- 终结方法:被final关键字修饰的方法,子类中不能重写终结方法。
- 静态方法:被static修饰的方法,静态的方法和属性属于类,不属于对象,在内存中只有唯一的拷贝,静态方法和属性调用的方式是用类名调用,而不是通过对象的引用来调用。
- 实例1:绘图系统
- 实例2:工资结算
第八天:深入面向对象-2
- 接口:在Java中,接口是实现可插入特性的保证。定义接口的关键字是interface,实现接口的关键字是implements,一个类可以实现多个接口,接口之间的继承支持多重继承。
- 接口和抽象类的异同
- 类/接口和类/接口之间的关系
- IS-A关系:继承/实现
- HAS-A关系:关联/聚合/合成
- USE-A关系:依赖
- UML:统一建模语言(标准的图形化符号)
- 类图:描述类以及类和类之间关系的图形符号。
- 面向对象的设计原则
- 单一职责原则:
- 开闭原则:
- 依赖倒转原则:
- 里氏替换原则:
- 接口隔离原则:
- 合成聚合复用原则:
- 迪米特法则:




















 14万+
14万+











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








