You are given nn segments on a coordinate line; each endpoint of every segment has integer coordinates. Some segments can degenerate to points. Segments can intersect with each other, be nested in each other or even coincide.
Your task is the following: for every k∈[1..n]k∈[1..n], calculate the number of points with integer coordinates such that the number of segments that cover these points equals kk. A segment with endpoints lili and riri covers point xx if and only if li≤x≤rili≤x≤ri.
The first line of the input contains one integer nn (1≤n≤2⋅1051≤n≤2⋅105) — the number of segments.
The next nn lines contain segments. The ii-th line contains a pair of integers li,rili,ri (0≤li≤ri≤10180≤li≤ri≤1018) — the endpoints of the ii-th segment.
Print nn space separated integers cnt1,cnt2,…,cntncnt1,cnt2,…,cntn, where cnticnti is equal to the number of points such that the number of segments that cover these points equals to ii.
3 0 3 1 3 3 8
6 2 1
3 1 3 2 4 5 7
5 2 0
The picture describing the first example:
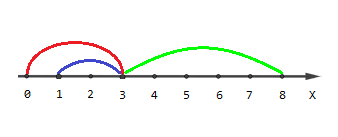
Points with coordinates [0,4,5,6,7,8][0,4,5,6,7,8] are covered by one segment, points [1,2][1,2] are covered by two segments and point [3][3] is covered by three segments.
The picture describing the second example:
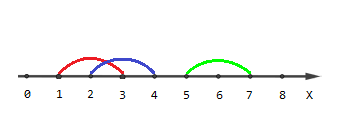
Points [1,4,5,6,7][1,4,5,6,7] are covered by one segment, points [2,3][2,3] are covered by two segments and there are no points covered by three segments.
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int MAXN = 200000 + 10;
struct f
{
long long head;
int shu;
}a[2 * MAXN];
long long mark[MAXN];
int com(const f &u , const f &v)
{
if(u.head == v.head)
return u.shu > v.shu;
return u.head < v.head;
}
int main()
{
int n;
cin >> n;
int num = 0;
for(int i = 1; i <= n * 2; i ++)
{
cin >> a[i].head;
if(i & 1)
a[i].shu = 1;
else
a[i].shu = 0;
}
//a[n + 1].head = a[n + 1].tail = 1e18 + 1;
//cout << endl;
sort( a + 1, a + 2 * n + 1, com);
//for(int i = 1 ; i <= 2 * n ; i ++)
// cout << a[i].head << " " << a[i].shu << endl;
//cout << endl;
int temp ;
long long f = 0;
for(int i = 1 ; i <= n * 2; i ++)
{
//mark[num] += a[i].head - a[i - 1].head;
if(a[i].shu == 1)
{
if(a[i].head - f - 1 >=0)
mark[num] += a[i].head - f - 1;
f = a[i].head;
temp = i;
int t = num;
//cout << "!" << " " << t << endl;
while(a[temp].head == a[temp + 1].head && temp + 1 <= n * 2)
{
//cout << a[temp + 1].shu << endl;
//t ++;
if(a[temp + 1].shu > 0)
{
num ++;
t ++;
//cout << "!" << endl;
}
//num ++;
else
num --;
temp ++;
}
//cout << t << endl;
num ++;
t ++;
//cout << num << " " << t << endl;
mark[t] ++;
i += (temp - i);
//for(int j = 1; j <= 3 ; j ++)
// cout << mark[j] << " ";
//cout << endl;
}
else
{
if(a[i].head - f - 1 >= 0)
mark[num] += a[i].head - f - 1;
f = a[i].head;
int t = num ;
temp = i;
while(a[temp].head == a[temp + 1].head && temp + 1 <= n * 2)
{
if(a[temp + 1].shu > 0)
{
num ++;
t ++;
}
// num ++;
else
num --;
temp ++;
}
//cout << num << " " << t << endl;
mark[t] ++ ;
num --;
//for(int j = 1 ; j <= 3; j ++)
// cout << mark[j] << " ";
//cout << endl;
i += (temp - i) ;
}
}
cout << mark[1];
for(int i = 2; i <= n ; i ++)
cout << " " << mark[i];
return 0;
}




















 1113
1113











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








