使用Spring MVC搭建了web项目(~/IdeaProjects/Beautiful1205/test-springmvc/springmvctest,有时间上传至github)后,我们来探索一下原理...
一、Spring MVC 与 Spring Boot
Spring MVC提供了一种轻度耦合的方式来开发web应用。它是Spring的一个模块,是一个web框架。通过DispatcherServlet, ModelAndView 和 ViewResolver,开发web应用变得很容易。(实际上还有很多其他的web框架,同样可以跟Spring进行整合。这就要求Spring有一些通用的配置,不但能支持Spring MVC也能支持Structs等其他web框架。这里看下官网吧)
Spring Boot实现了自动配置,降低了项目搭建的复杂度。它主要是为了解决使用Spring框架需要进行大量的配置太麻烦的问题,所以它并不是用来替代Spring的解决方案,而是和Spring框架紧密结合用于提升Spring开发者体验的工具。同时它集成了大量常用的第三方库配置(例如Jackson, JDBC, Mongo, Redis, Mail等等),Spring Boot应用中这些第三方库几乎可以零配置的开箱即用(out-of-the-box)。
在SpringBoot项目中整合Spring MVC只需要添加对应的starer依赖即可。
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>SpringBoot、SpringMVC和Spring区别_努力的土豆的博客-CSDN博客_springboot springmvc
SpringBoot、SpringMVC整合与比较:_kingmax54212008的博客-CSDN博客
二、Spring MVC原理
http://www.it165.net/pro/html/201604/66385.html
2.1、从Web应用角度看Spring MVC
在Servlet模型中,请求-响应的实现依赖于两大元素的共同配合:
- 在web.xml中配置Servlet及其映射关系
- 在Servlet实现类中完成响应逻辑
项目规模扩大之后,请求-响应的映射关系全部定义在web.xml中,将造成web.xml的不断膨胀而变得难以维护。针对这个问题,SpringMVC提出的方案就是:提炼一个核心的Servlet覆盖对所有Http请求的处理。这一被提炼出来的Servlet,通常被我们称之为:核心分发器。在SpringMVC中,核心分发器就是org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet。
核心分发器要解决的是下面两个问题:
- 问题1:核心Servlet应该能够建立起一整套完整的对所有Http请求进行规范化处理的流程。
- 问题2:核心Servlet应该能够根据一定的规则对不同的Http请求分发到不同的Servlet对象上去进行处理。
针对上面的这个两个问题,SpringMVC的解决方案是:将整个处理流程规范化,并把每一个处理步骤分派到不同的组件中进行处理。
- 处理流程规范化 :将处理流程划分为若干个步骤(任务),并使用一条明确的逻辑主线将所有的步骤串联起来
- 处理流程组件化 : 将处理流程中的每一个步骤(任务)都定义为接口,并为每个接口赋予不同的实现模式
处理流程规范化的首要内容就是考虑一个通用的Servlet响应程序大致应该包含的逻辑步骤:对Http请求进行初步处理 -> 查找与之对应的Controller处理类(方法) -> 调用相应的Controller处理类(方法) -> 完成业务逻辑 -> 对Controller处理类(方法)调用时可能发生的异常进行处理 -> 根据Controller处理类(方法)的调用结果进行Http响应处理。
所谓的组件化,实际上也就是使用编程语言将这些逻辑语义表达出来。在Java语言中,最适合表达逻辑处理语义的语法结构是接口,而接口可以有不同的实现,因此上述的四个流程也就被定义为了四个不同接口,它们分别是:HandlerMapping、HandlerAdapter、HandlerExceptionResolver、ViewResolver
2.2、从Spring角度看Spring MVC
从上面可以看出,组件是核心分发器(DispatchServlet)的核心所在,它们是http请求处理的逻辑载体,DispatcherServlet是逻辑处理的调度中心,组件则是被调度的操作对象。
而Spring容器在这里所起到的作用是协助DispatcherServlet更好地对组件进行管理。
我们知道,SpringMVC的组件是一个个的接口定义,当我们在SpringMVC的核心配置文件中定义一个组件时,使用的却是组件的实现类。
用具体的实现类来指定组件的行为模式,不同的实现类代表了不同的行为模式,它们在Spring中是可以共存的。
Spring容器对这些实现类进行管理,具体如何使用,由应用程序本身来决定。

上图是Spring官方reference中的一幅图,DispatchServlet对外接收http的请求,而请求的处理是依靠组件来完成的。
组件的接口实现的是依靠Spring IOC容器(WebApplicationContext)来管理的。
从这个图中我们可以看出,Spring MVC实现web应用是依赖于Spring提供的基础特性(IOC等)的。(图中的两个WebApplicationContext的父子关系)
三、上下文初始化过程
3.1、Spring MVC 入口配置文件web.xml
遵循servlet规范,Spring MVC的web应用的入口配置文件也是web.xml。在web.xml配置文件中,有两个主要的配置:ContextLoaderListener和DispatcherServlet。同样的关于spring配置文件的相关配置也有两部分:context-param和DispatcherServlet中的init-param。
在ContextLoaderListener中创建的Spring容器主要用于整个Web应用程序需要共享的一些组件,比如DAO、数据库的ConnectionFactory等;而由DispatcherServlet创建的Spring MVC的容器主要用于和该Servlet相关的一些组件,比如Controller、ViewResovler等。在实际工程中,一个项目中会包括很多配置,根据不同的业务模块来划分,我们一般思路是:Spring根容器负责所有其他非controller的Bean的注册,而SpringMVC只负责controller相关的Bean的注册。参考链接。
Spring Framework本身没有Web功能,Spring MVC使用WebApplicationContext类扩展ApplicationContext,使得拥有web功能。
先看一下WebApplicationContext是如何扩展ApplicationContext来添加对Web环境的支持的。WebApplicationContext接口定义如下:
package org.springframework.web.context;
import javax.servlet.ServletContext;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.lang.Nullable;
/**
* Interface to provide configuration for a web application. This is read-only while
* the application is running, but may be reloaded if the implementation supports this.
*
* <p>This interface adds a {@code getServletContext()} method to the generic
* ApplicationContext interface, and defines a well-known application attribute name
* that the root context must be bound to in the bootstrap process.
*
* <p>Like generic application contexts, web application contexts are hierarchical.
* There is a single root context per application, while each servlet in the application
* (including a dispatcher servlet in the MVC framework) has its own child context.
*
* <p>In addition to standard application context lifecycle capabilities,
* WebApplicationContext implementations need to detect {@link ServletContextAware}
* beans and invoke the {@code setServletContext} method accordingly.
*
* @author Rod Johnson
* @author Juergen Hoeller
* @since January 19, 2001
* @see ServletContextAware#setServletContext
*/
public interface WebApplicationContext extends ApplicationContext {
/**
* Context attribute to bind root WebApplicationContext to on successful startup.
* <p>Note: If the startup of the root context fails, this attribute can contain
* an exception or error as value. Use WebApplicationContextUtils for convenient
* lookup of the root WebApplicationContext.
* @see org.springframework.web.context.support.WebApplicationContextUtils#getWebApplicationContext
* @see org.springframework.web.context.support.WebApplicationContextUtils#getRequiredWebApplicationContext
*/
String ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE = WebApplicationContext.class.getName() + ".ROOT";
/**
* Scope identifier for request scope: "request".
* Supported in addition to the standard scopes "singleton" and "prototype".
*/
String SCOPE_REQUEST = "request";
/**
* Scope identifier for session scope: "session".
* Supported in addition to the standard scopes "singleton" and "prototype".
*/
String SCOPE_SESSION = "session";
/**
* Scope identifier for the global web application scope: "application".
* Supported in addition to the standard scopes "singleton" and "prototype".
*/
String SCOPE_APPLICATION = "application";
/**
* Name of the ServletContext environment bean in the factory.
* @see javax.servlet.ServletContext
*/
String SERVLET_CONTEXT_BEAN_NAME = "servletContext";
/**
* Name of the ServletContext init-params environment bean in the factory.
* <p>Note: Possibly merged with ServletConfig parameters.
* ServletConfig parameters override ServletContext parameters of the same name.
* @see javax.servlet.ServletContext#getInitParameterNames()
* @see javax.servlet.ServletContext#getInitParameter(String)
* @see javax.servlet.ServletConfig#getInitParameterNames()
* @see javax.servlet.ServletConfig#getInitParameter(String)
*/
String CONTEXT_PARAMETERS_BEAN_NAME = "contextParameters";
/**
* Name of the ServletContext attributes environment bean in the factory.
* @see javax.servlet.ServletContext#getAttributeNames()
* @see javax.servlet.ServletContext#getAttribute(String)
*/
String CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTES_BEAN_NAME = "contextAttributes";
/**
* Return the standard Servlet API ServletContext for this application.
*/
@Nullable
ServletContext getServletContext();
}
* <p>Like generic application contexts, web application contexts are hierarchical.
* There is a single root context per application, while each servlet in the application
* (including a dispatcher servlet in the MVC framework) has its own child context.注释翻译过来就是:Web环境中的每个应用都有一个根上下文,同时每个servlet还都持有一个子上下文。
ContextLoaderListener:spring-web-5.1.10.RELEASE.jar!/org/springframework/web/context/ContextLoaderListener.class
DispatcherServlet
(/Users/-/.m2/repository/org/springframework/boot/spring-boot/2.1.9.RELEASE/spring-boot-2.1.9.RELEASE.jar!/org/springframework/boot/web/servlet/context/ServletWebServerApplicationContext.class prepareWebApplicationContext() 方法)
3.2、Spring容器(根上下文)的初始化
Web环境中的每个应用都有一个根上下文,同时每个servlet还都持有一个子上下文。对于这样的Context结构在Spring MVC中是如何实现的呢?下面就先从ROOT Context入手,ROOT Context是在ContextLoaderListener中配置的,ContextLoaderListener读取context-param中的contextConfigLocation指定的配置文件,创建ROOT Context。下面看一下ContextLoaderListener中创建context的源码:(注意看注释第一句话)
package org.springframework.web.context;
import javax.servlet.ServletContextEvent;
import javax.servlet.ServletContextListener;
/**
* Bootstrap listener to start up and shut down Spring's root {@link WebApplicationContext}.
* Simply delegates to {@link ContextLoader} as well as to {@link ContextCleanupListener}.
*
* <p>As of Spring 3.1, {@code ContextLoaderListener} supports injecting the root web
* application context via the {@link #ContextLoaderListener(WebApplicationContext)}
* constructor, allowing for programmatic configuration in Servlet 3.0+ environments.
* See {@link org.springframework.web.WebApplicationInitializer} for usage examples.
*
* @author Juergen Hoeller
* @author Chris Beams
* @since 17.02.2003
* @see #setContextInitializers
* @see org.springframework.web.WebApplicationInitializer
*/
public class ContextLoaderListener extends ContextLoader implements ServletContextListener {
...
/**
* Initialize the root web application context.
*/
@Override
public void contextInitialized(ServletContextEvent event) {
initWebApplicationContext(event.getServletContext());
}
...
}package org.springframework.web.context;
import *****;
/**
* Performs the actual initialization work for the root application context.
* Called by {@link ContextLoaderListener}.
*
* <p>Looks for a {@link #CONTEXT_CLASS_PARAM "contextClass"} parameter at the
* {@code web.xml} context-param level to specify the context class type, falling
* back to {@link org.springframework.web.context.support.XmlWebApplicationContext}
* if not found. With the default ContextLoader implementation, any context class
* specified needs to implement the {@link ConfigurableWebApplicationContext} interface.
*
* <p>Processes a {@link #CONFIG_LOCATION_PARAM "contextConfigLocation"} context-param
* and passes its value to the context instance, parsing it into potentially multiple
* file paths which can be separated by any number of commas and spaces, e.g.
* "WEB-INF/applicationContext1.xml, WEB-INF/applicationContext2.xml".
* Ant-style path patterns are supported as well, e.g.
* "WEB-INF/*Context.xml,WEB-INF/spring*.xml" or "WEB-INF/**/*Context.xml".
* If not explicitly specified, the context implementation is supposed to use a
* default location (with XmlWebApplicationContext: "/WEB-INF/applicationContext.xml").
*
* <p>Note: In case of multiple config locations, later bean definitions will
* override ones defined in previously loaded files, at least when using one of
* Spring's default ApplicationContext implementations. This can be leveraged
* to deliberately override certain bean definitions via an extra XML file.
*
* <p>Above and beyond loading the root application context, this class can optionally
* load or obtain and hook up a shared parent context to the root application context.
* See the {@link #loadParentContext(ServletContext)} method for more information.
*
* <p>As of Spring 3.1, {@code ContextLoader} supports injecting the root web
* application context via the {@link #ContextLoader(WebApplicationContext)}
* constructor, allowing for programmatic configuration in Servlet 3.0+ environments.
* See {@link org.springframework.web.WebApplicationInitializer} for usage examples.
*
* @author Juergen Hoeller
* @author Colin Sampaleanu
* @author Sam Brannen
* @since 17.02.2003
* @see ContextLoaderListener
* @see ConfigurableWebApplicationContext
* @see org.springframework.web.context.support.XmlWebApplicationContext
*/
public class ContextLoader {
}
/spring-web-5.2.5.RELEASE.jar!/org/springframework/web/context/ContextLoader.class类中initWebApplicationContext()方法如下:
/**
* Initialize Spring's web application context for the given servlet context,
* using the application context provided at construction time, or creating a new one
* according to the "{@link #CONTEXT_CLASS_PARAM contextClass}" and
* "{@link #CONFIG_LOCATION_PARAM contextConfigLocation}" context-params.
* @param servletContext current servlet context
* @return the new WebApplicationContext
* @see #ContextLoader(WebApplicationContext)
* @see #CONTEXT_CLASS_PARAM
* @see #CONFIG_LOCATION_PARAM
*/
public WebApplicationContext initWebApplicationContext(ServletContext servletContext) {
//在整个web应用中,只能有一个根上下文
if (servletContext.getAttribute(WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE) != null) {
throw new IllegalStateException(
"Cannot initialize context because there is already a root application context present - " +
"check whether you have multiple ContextLoader* definitions in your web.xml!");
}
servletContext.log("Initializing Spring root WebApplicationContext");
Log logger = LogFactory.getLog(ContextLoader.class);
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Root WebApplicationContext: initialization started");
}
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
try {
// Store context in local instance variable, to guarantee that it is available on ServletContext shutdown.
if (this.context == null) {
// 在这里执行了创建WebApplicationContext的操作
this.context = createWebApplicationContext(servletContext);
}
if (this.context instanceof ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) {
ConfigurableWebApplicationContext cwac = (ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) this.context;
if (!cwac.isActive()) {
// The context has not yet been refreshed -> provide services such as
// setting the parent context, setting the application context id, etc
if (cwac.getParent() == null) {
// The context instance was injected without an explicit parent ->
// determine parent for root web application context, if any.
ApplicationContext parent = loadParentContext(servletContext);
cwac.setParent(parent);
}
configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(cwac, servletContext);
}
}
//将根上下文放置在servletContext中
servletContext.setAttribute(WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE, this.context);
ClassLoader ccl = Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader();
if (ccl == ContextLoader.class.getClassLoader()) {
currentContext = this.context;
}
else if (ccl != null) {
currentContextPerThread.put(ccl, this.context);
}
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
long elapsedTime = System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime;
logger.info("Root WebApplicationContext initialized in " + elapsedTime + " ms");
}
return this.context;
}
catch (RuntimeException | Error ex) {
logger.error("Context initialization failed", ex);
servletContext.setAttribute(WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE, ex);
throw ex;
}
}
再看一下WebApplicationContext对象是如何创建的:
/**
* Instantiate the root WebApplicationContext for this loader, either the
* default context class or a custom context class if specified.
* <p>This implementation expects custom contexts to implement the
* {@link ConfigurableWebApplicationContext} interface.
* Can be overridden in subclasses.
* <p>In addition, {@link #customizeContext} gets called prior to refreshing the
* context, allowing subclasses to perform custom modifications to the context.
* @param sc current servlet context
* @return the root WebApplicationContext
* @see ConfigurableWebApplicationContext
*/
protected WebApplicationContext createWebApplicationContext(ServletContext sc) {
Class<?> contextClass = determineContextClass(sc);
if (!ConfigurableWebApplicationContext.class.isAssignableFrom(contextClass)) {
throw new ApplicationContextException("Custom context class [" + contextClass.getName() +
"] is not of type [" + ConfigurableWebApplicationContext.class.getName() + "]");
}
return (ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) BeanUtils.instantiateClass(contextClass);
}以上是web容器中根上下文的加载与初始化,下面介绍一下Spring MVC对应的上下文是如何加载的。
3.3、Spring MVC容器(子上下文)的初始化
以上是web容器中根上下文的加载与初始化,在完成对ContextLoaderListener的初始化以后,web容器开始初始化DispatchServlet,DispatchServlet会建立自己的上下文来管理Spring MVC的bean对象。在建立这个自己持有的上下文的时候,会从ServletContext中得到根上下文作为DispatchServlet持有的上下文的双亲上下文,再对自己持有的上下文进行初始化,最后把自己持有的这个上下文也保存到ServletContext中。
我们先看下DispatchServlet的继承关系,如下图,

DispatchServlet通过继承FrameworkServlet和HttpServletBean而继承了HttpServlet。HttpServletBean是Spring对于Servlet最低层次的抽象。
在这一层抽象中,Spring会将这个Servlet视作是一个Spring的bean,并将web入口配置文件web.xml中DispatchServlet定义的init-param参数中的值作为bean的属性注入进来。
DispatcherServlet也是一个Servlet,根据Servlet规范的定义,其中有两大核心方法:init()方法和service()方法。
- init()方法:在整个系统启动时运行,且只运行一次。主要的调用顺序是GenericServlet#init() --> HttpServletBean#init() -->FrameworkServlet#initServletBean() --> FrameworkServlet#initWebApplicationContext()。在init方法中我们往往会对整个应用程序进行初始化操作。这些初始化操作包括对容器(WebApplicationContext)的初始化、组件和外部资源的初始化等等。
- service()方法:在整个系统运行的过程中处于侦听模式,侦听并处理所有的Web请求。因此,在service及其相关方法中,我们看到的则是对Http请求的处理流程。
DispatchServlet、FrameworkServlet和HttpServletBean之间的调用关系如下,首先是HttpServletBean,其次是FrameworkServlet,最后是DispatchServlet。FrameworkServlet是在HttpServletBean的基础之上的进一步抽象。通过FrameworkServlet真正初始化了一个Spring的容器(WebApplicationContext),并引入到ServletContext之中(注意这个子上下文放到ServletContext时的key和根上下文是不一样的)。在这个调用关系中,可以看到MVC的初始化是再DispatchServlet的initStrategies方法中完成的,包括对各种MVC框架的实现元素,比如支持国际化的LocaleResolver、支持request映射的HandlerMappings、以及视图生成的ViewResolver等的初始化。
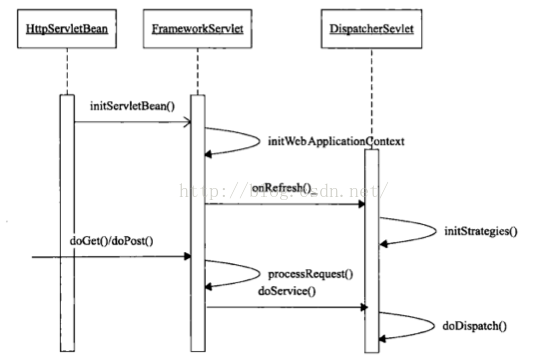
看下FrameworkServlet#initServletBean()的实现,
/**
* Overridden method of {@link HttpServletBean}, invoked after any bean properties
* have been set. Creates this servlet's WebApplicationContext.
*/
@Override
protected final void initServletBean() throws ServletException {
getServletContext().log("Initializing Spring " + getClass().getSimpleName() + " '" + getServletName() + "'");
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Initializing Servlet '" + getServletName() + "'");
}
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
try {
this.webApplicationContext = initWebApplicationContext();
initFrameworkServlet();
}
catch (ServletException | RuntimeException ex) {
logger.error("Context initialization failed", ex);
throw ex;
}
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
String value = this.enableLoggingRequestDetails ?
"shown which may lead to unsafe logging of potentially sensitive data" :
"masked to prevent unsafe logging of potentially sensitive data";
logger.debug("enableLoggingRequestDetails='" + this.enableLoggingRequestDetails +
"': request parameters and headers will be " + value);
}
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Completed initialization in " + (System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime) + " ms");
}
}其中,FrameworkServlet#initWebApplicationContext的实现
/**
* Initialize and publish the WebApplicationContext for this servlet.
* <p>Delegates to {@link #createWebApplicationContext} for actual creation
* of the context. Can be overridden in subclasses.
* @return the WebApplicationContext instance
* @see #FrameworkServlet(WebApplicationContext)
* @see #setContextClass
* @see #setContextConfigLocation
*/
protected WebApplicationContext initWebApplicationContext() {
//从ServletContext中取得根上下文
WebApplicationContext rootContext = WebApplicationContextUtils.getWebApplicationContext(getServletContext());
WebApplicationContext wac = null;
if (this.webApplicationContext != null) {
// A context instance was injected at construction time -> use it
//如果在构造时已经注入了context则直接使用
wac = this.webApplicationContext;
if (wac instanceof ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) {
ConfigurableWebApplicationContext cwac = (ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) wac;
if (!cwac.isActive()) {
// The context has not yet been refreshed -> provide services such as
// setting the parent context, setting the application context id, etc
if (cwac.getParent() == null) {
// The context instance was injected without an explicit parent -> set
// the root application context (if any; may be null) as the parent
cwac.setParent(rootContext);
}
configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(cwac);
}
}
}
if (wac == null) {
// No context instance was injected at construction time -> see if one has been registered in the servlet context.
// If one exists, it is assumed that the parent context (if any) has already been set
// and that the user has performed any initialization such as setting the context id
wac = findWebApplicationContext();
}
if (wac == null) {
// No context instance is defined for this servlet -> create a local one
//创建Spring MVC的上下文,并将根上下文作为起双亲上下文
wac = createWebApplicationContext(rootContext);
}
if (!this.refreshEventReceived) {
// Either the context is not a ConfigurableApplicationContext with refresh
// support or the context injected at construction time had already been
// refreshed -> trigger initial onRefresh manually here.
synchronized (this.onRefreshMonitor) {
//会最终DispatchServlet的initStrategies()方法, 进行MVC的初始化
onRefresh(wac);
}
}
if (this.publishContext) {
// Publish the context as a servlet context attribute.
// 名字前缀是 public static final String SERVLET_CONTEXT_PREFIX = FrameworkServlet.class.getName() + ".CONTEXT.";
String attrName = getServletContextAttributeName();
getServletContext().setAttribute(attrName, wac);
}
return wac;
}通过initWebApplicationContext方法的调用,创建了DispatcherServlet对应的context,并将其放置到ServletContext中,这样就完成了在web容器中构建Spring MVC容器的过程。
四、Spring MVC 上下初始化流程图
ServletContext是Spring容器的宿主环境,Spring容器又包含整个应用的根上下文和每个servlet的子上下文。
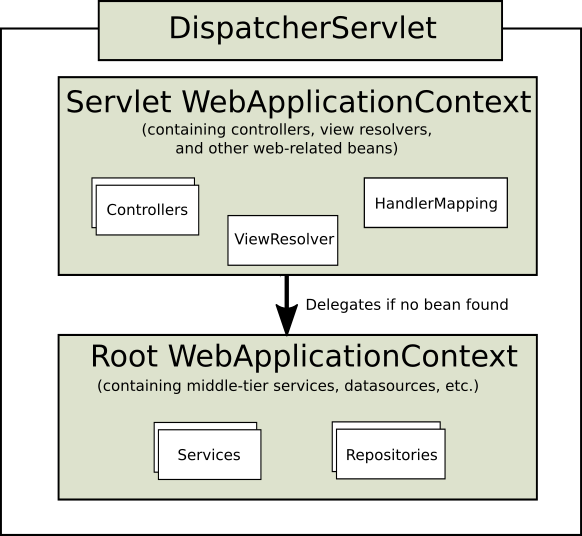

用到的组件:(https://blog.csdn.net/lu930124/article/details/51586031)
| 组件 | 作用 |
|---|---|
| 前端控制器 | 接收请求 响应结果 相当于转发器 |
| 处理器映射器 | 根据请求的url查找handler |
| 处理器适配器 | 按照特定规则去执行handler 注意:在开发handler时按照handleradapter的要求去做,这样适配器才可以去执行handler |
| 视图解析器 | 进行视图解析,根据逻辑视图名解析成真正的视图 |
| 视图 | 是一个接口,实现类支持不同的view类型(jsp freemarker, pdf……) |
| 处理器handler | 编写handler时按照handleradapter的要求去做,这样适配器才可以去正确执行handler |























 853
853











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








