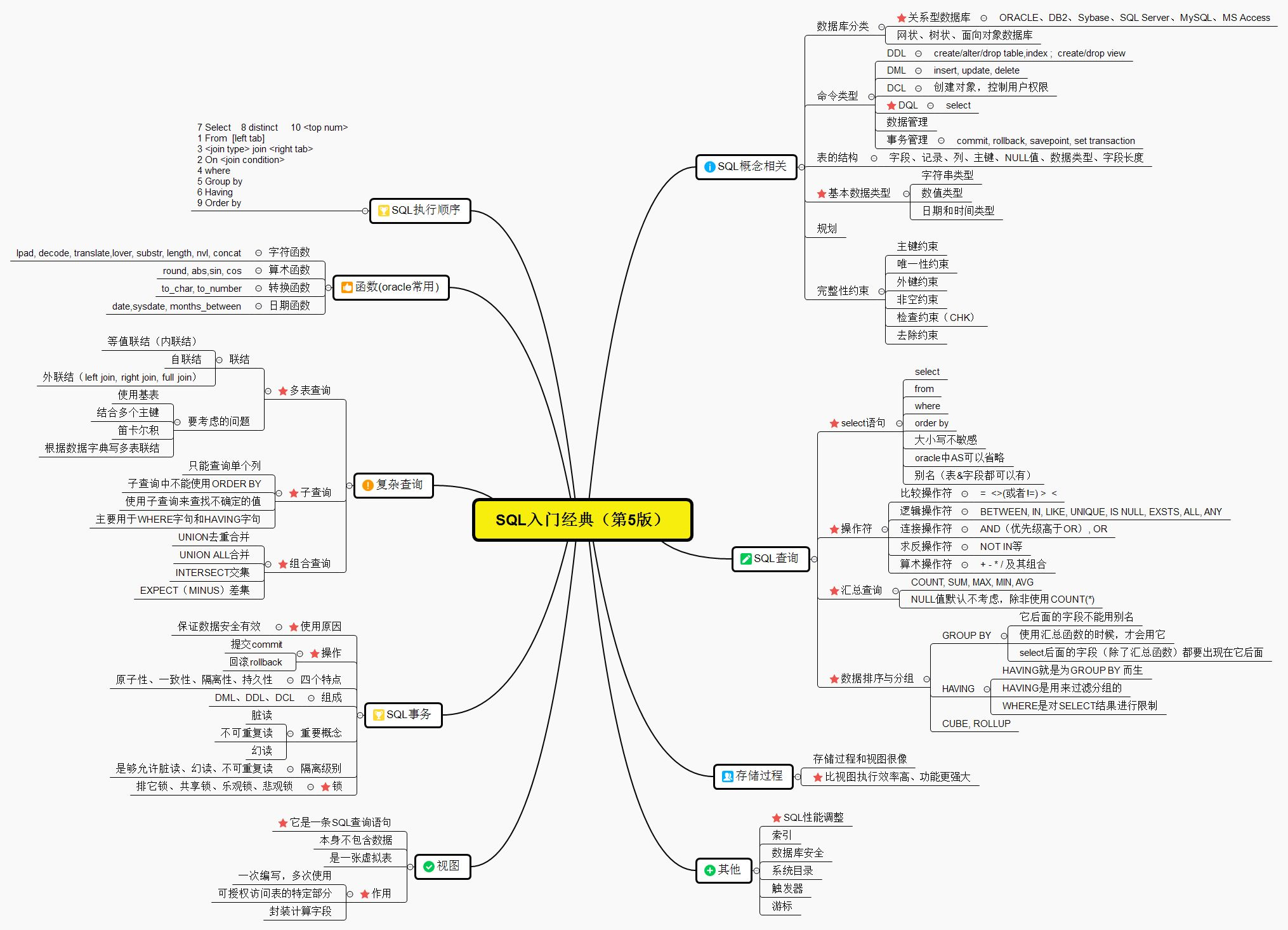
目录
SQL基础知识整理:
select 查询结果 如: [学号,平均成绩:组函数avg(成绩)]from 从哪张表中查找数据 如:[涉及到成绩:成绩表score]where 查询条件 如:[b.课程号='0003' and b.成绩>80]group by 分组 如:[每个学生的平均:按学号分组](oracle,SQL server中出现在select 子句后的非分组函数,必须出现 在group by子句后出现),MySQL中可以不用having 对分组结果指定条件 如:[大于60分]order by 对查询结果排序 如:[增序: 成绩 ASC / 降序: 成绩 DESC];
limit 使用limt子句返回topN(对应这个问题返回的成绩前两名)如:[ limit 2 ==>从0索引开始读取2个]
limit==>从0索引开始 [0,N-1]
组函数: 去重 distinct() 统计总数sum() 计算个数count() 平均数avg() 最大值max() 最小数min()
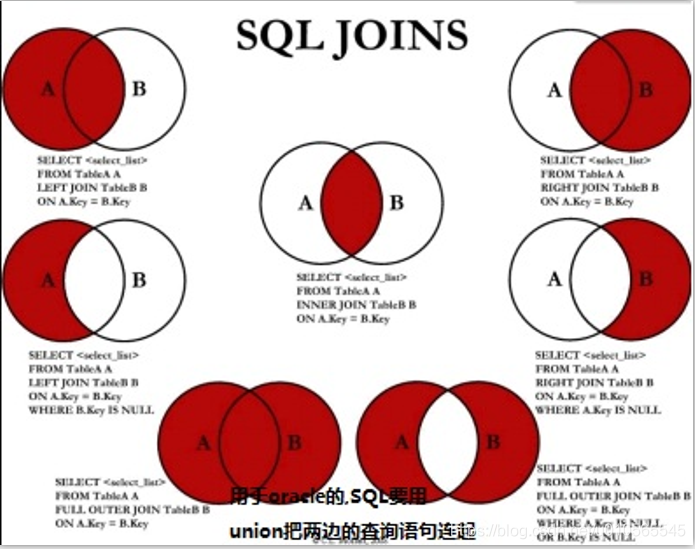
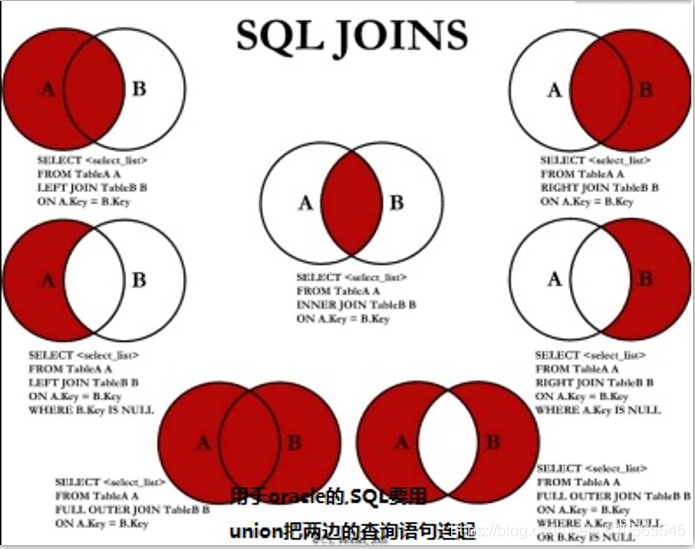
多表连接: 内连接(省略默认inner) join ...on..左连接left join tableName as b on a.key ==b.key右连接right join 连接union(无重复(过滤去重))和union all(有重复[不过滤去重])
--union 并集
--union all(有重复)
oracle(SQL server)数据库--intersect 交集
--minus(except) 相减(差集)
oracle
一、数据库对象: 表(table) 视图(view) 序列(sequence) 索引(index) 同义词(synonym)
1. 视图: 存储起来的 select 语句create view emp_vwas
select employee_id, last_name, salary
from employees
where department_id = 90;select * from emp_vw;
--可以对简单视图进行 DML 操作
update emp_vw
set last_name = 'HelloKitty'
where employee_id = 100;select * from employees
where employee_id = 100;1). 复杂视图
create view emp_vw2
as
select department_id, avg(salary) avg_sal
from employees
group by department_id;select * from emp_vw2;
--复杂视图不能进行 DML 操作
update emp_vw2
set avg_sal = 10000
where department_id = 100;2. 序列:用于生成一组有规律的数值。(通常用于为主键设置值)
create sequence emp_seq1
start with 1
increment by 1
maxvalue 10000
minvalue 1
cycle
nocache;select emp_seq1.currval from dual;
select emp_seq1.nextval from dual;
--问题:裂缝 . 原因:①当多个表共用同一个序列时。 ②rollback ③发生异常
create table emp1(
id number(10),
name varchar2(30)
);insert into emp1
values(emp_seq1.nextval, '张三');select * from emp1;
3. 索引:提高查询效率
--自动创建:Oracle 会为具有唯一约束(唯一约束,主键约束)的列,自动创建索引
create table emp2(
id number(10) primary key,
name varchar2(30)
)--手动创建
create index emp_idx
on emp2(name);create index emp_idx2
on emp2(id, name);4. 同义词
create synonym d1 for departments;select * from d1;
5. 表:
DDL :数据定义语言 create table .../ drop table ... / rename ... to..../ truncate table.../alter table ...
DML : 数据操纵语言insert into ... values ...
update ... set ... where ...
delete from ... where ...【重要】select ... 组函数(MIN()/MAX()/SUM()/AVG()/COUNT())from ...join ... on ... 左外连接:left join ... on ... 右外连接: right join ... on ...where ...
group by ... (oracle,SQL server中出现在select 子句后的非分组函数,必须出现在 group by子句后)having ... 用于过滤 组函数order by ... asc 升序, desc 降序limit (0,4) 限制N条数据 如: topN数据
--union 并集
--union all(有重复)
--intersect 交集
--minus 相减
DCL : 数据控制语言 commit : 提交 / rollback : 回滚 / 授权grant...to... /revoke
索引
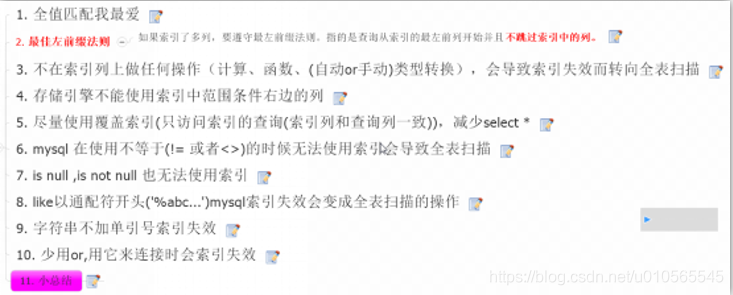
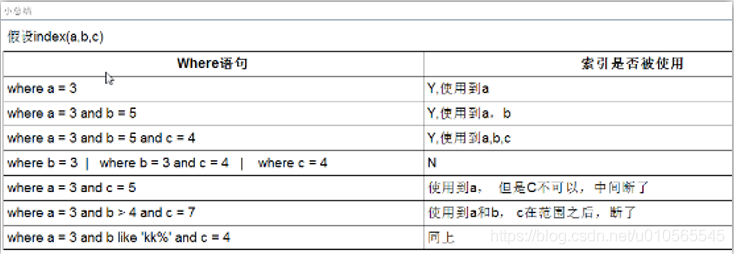

何时创建索引:


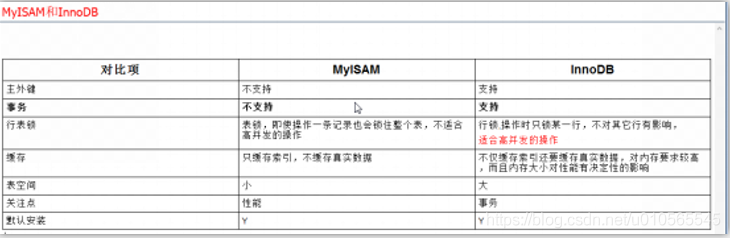
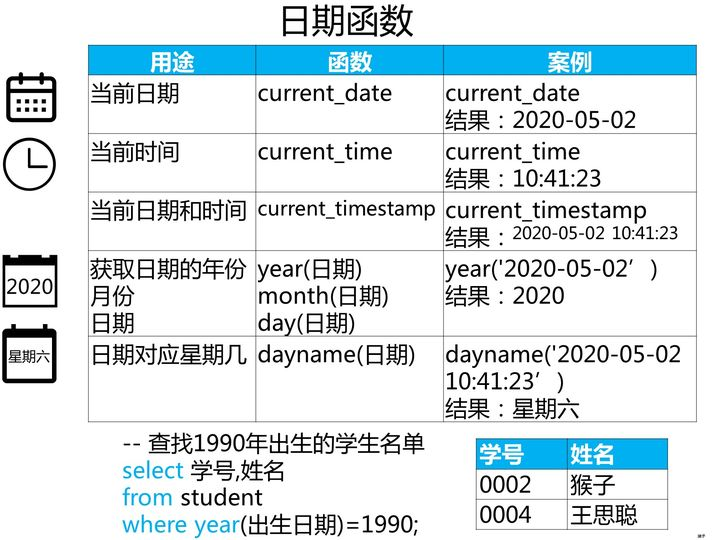
一、
select employee_id, last_name, salary, department_id
from employees
where department_id in (70, 80) --> 70:1 80:34--union 并集
--union all(有重复部分)
--intersect 交集
--minus 相减
select employee_id, last_name, salary, department_id
from employees
where department_id in (80, 90) --> 90:4 80:34
--问题:查询工资大于149号员工工资的员工的信息
select *
from employees
where salary > (
select salary
from employees
where employee_id = 149
)--问题:查询与141号或174号员工的manager_id和department_id相同的其他员工的
--employee_id, manager_id, department_id
select employee_id, manager_id, department_id
from employees
where manager_id in (
select manager_id
from employees
where employee_id in(141, 174)
) and department_id in (
select department_id
from employees
where employee_id in(141, 174)
) and employee_id not in (141, 174);select employee_id, manager_id, department_id
from employees
where (manager_id, department_id) in (
select manager_id, department_id
from employees
where employee_id in (141, 174)
) and employee_id not in(141, 174);--1. from 子句中使用子查询
select max(avg(salary))
from employees
group by department_id;select max(avg_sal)
from (
select avg(salary) avg_sal
from employees
group by department_id
) e--问题:返回比本部门平均工资高的员工的last_name, department_id, salary及平均工资
select last_name, department_id, salary, (select avg(salary) from employees where department_id = e1.department_id)
from employees e1
where salary > (
select avg(salary)
from employees e2
where e1.department_id = e2.department_id
)select last_name, e1.department_id, salary, avg_sal
from employees e1, (
select department_id, avg(salary) avg_sal
from employees
group by department_id
) e2
where e1.department_id = e2.department_id
and e1.salary > e2.avg_sal;
--case...when ... then... when ... then ... else ... end
--查询:若部门为10 查看工资的 1.1 倍,部门号为 20 工资的1.2倍,其余 1.3 倍
select employee_id, last_name, salary, case department_id when 10 then salary * 1.1
when 20 then salary * 1.2
else salary * 1.3
end "new_salary"
from employees;select employee_id, last_name, salary, decode(department_id, 10, salary * 1.1,
20, salary * 1.2,
salary * 1.3) "new_salary"
from employees;
--问题:显式员工的employee_id,last_name和location。其中,若员工
--department_id与location_id为1800的department_id相同,则location为’Canada’,其余则为’USA’。
select employee_id, last_name, case department_id when (
select department_id
from departments
where location_id = 1800
) then 'Canada' else 'USA' end "location"
from employees;--问题:查询员工的employee_id,last_name,要求按照员工的department_name排序
select employee_id, last_name
from employees e1
order by (
select department_name
from departments d1
where e1.department_id = d1.department_id
)-- SQL 优化:能使用 EXISTS 就不要使用 IN
--问题:查询公司管理者的employee_id,last_name,job_id,department_id信息
select employee_id, last_name, job_id, department_id
from employees
where employee_id in (
select manager_id
from employees
)
select employee_id, last_name, job_id, department_id
from employees e1
where exists (
select 'x'
from employees e2
where e1.employee_id = e2.manager_id
)-- 问题:查询departments表中,不存在于employees表中的部门的department_id和department_name
select department_id, department_name
from departments d1
where not exists (
select 'x'
from employees e1
where e1.department_id = d1.department_id
)--55. 更改 108 员工的信息: 使其工资变为所在部门中的最高工资, job 变为公司中平均工资最低的 job
update employees e1
set salary = (
select max(salary)
from employees e2
where e1.department_id = e2.department_id
), job_id = (
select job_id
from employees
group by job_id
having avg(salary) = (
select min(avg(salary))
from employees
group by job_id
)
)
where employee_id = 108;
--56. 删除 108 号员工所在部门中工资最低的那个员工.
delete from employees e1
where salary = (
select min(salary)
from employees
where department_id = (
select department_id
from employees
where employee_id = 108
)
)select * from employees where employee_id = 108;
select * from employees where department_id = 100
order by salary;rollback;
常见的SQL面试题:经典50题
========================================================
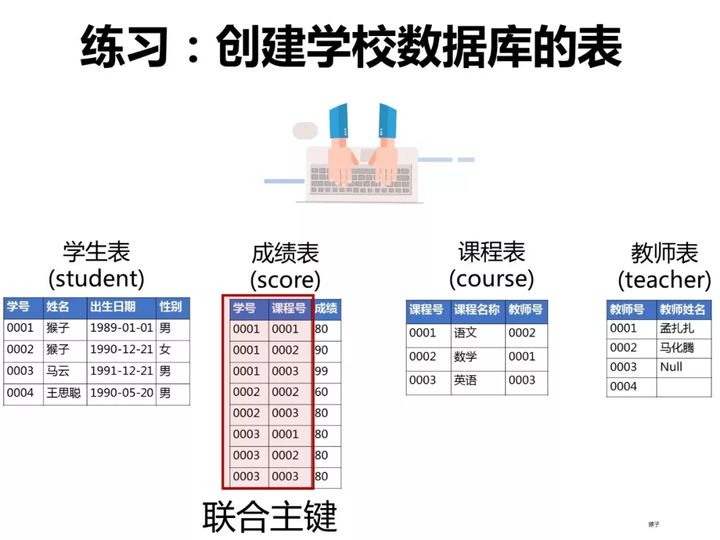
已知有如下4张表:
学生表:student(学号,学生姓名,出生年月,性别)
成绩表:score(学号,课程号,成绩)
课程表:course(课程号,课程名称,教师号)
教师表:teacher(教师号,教师姓名)
根据以上信息按照下面要求写出对应的SQL语句。
ps:这些题考察SQL的编写能力,对于这类型的题目,需要你先把4张表之间的关联关系搞清楚了,最好的办法是自己在草稿纸上画出关联图,然后再编写对应的SQL语句就比较容易了。下图是我画的这4张表的关系图,可以看出它们之间是通过哪些外键关联起来的:
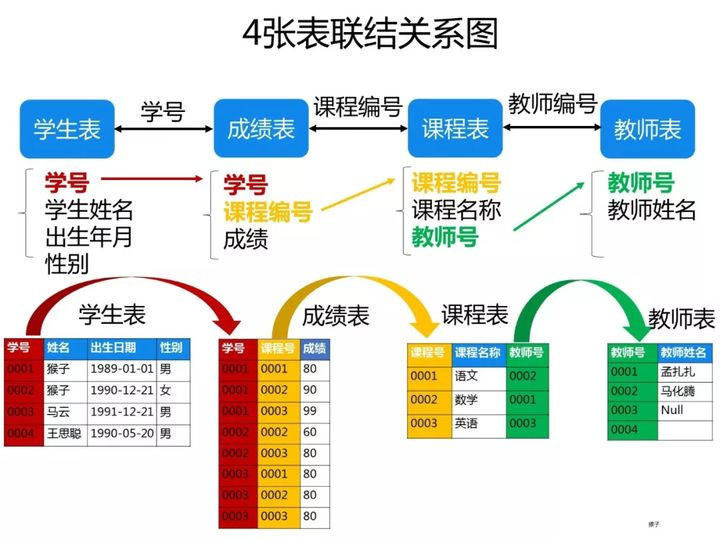
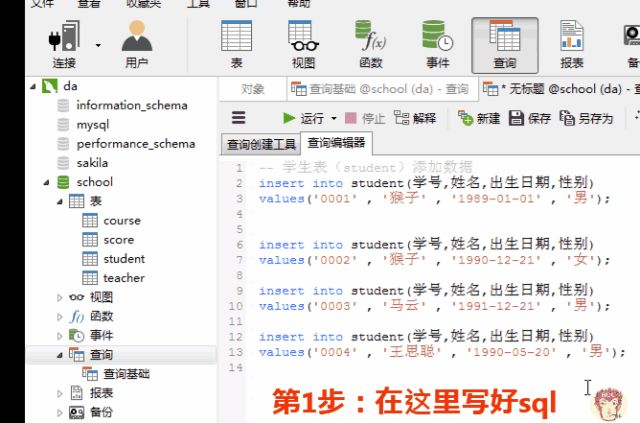
一、创建数据库和表
为了演示题目的运行过程,我们先按下面语句在客户端navicat中创建数据库和表。
(如何你还不懂什么是数据库,什么是客户端navicat,可以先学习这个:
1.创建表
1)创建学生表(student)
按下图在客户端navicat里创建学生表
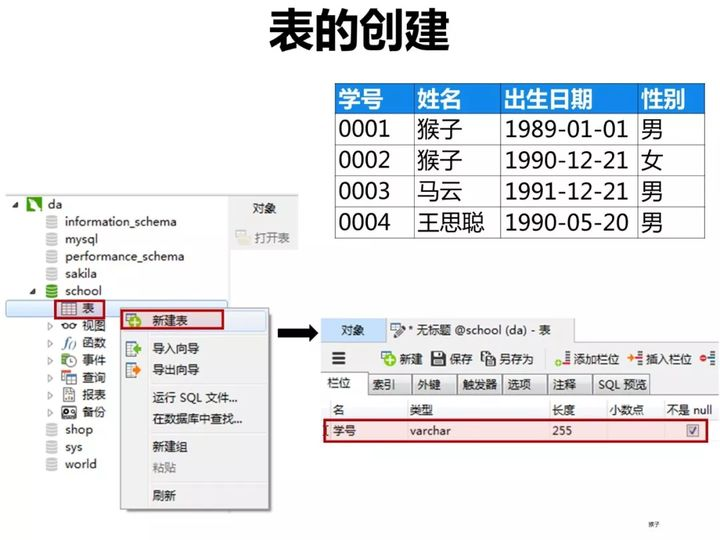
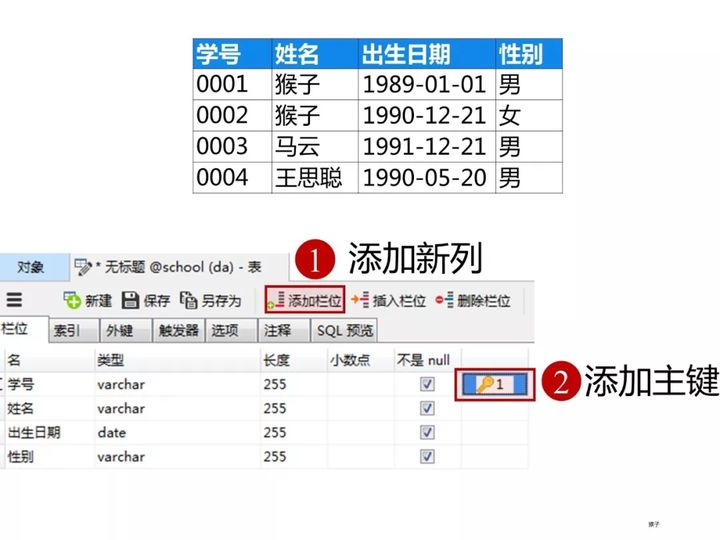
学生表的“学号”列设置为主键约束,下图是每一列设置的数据类型和约束
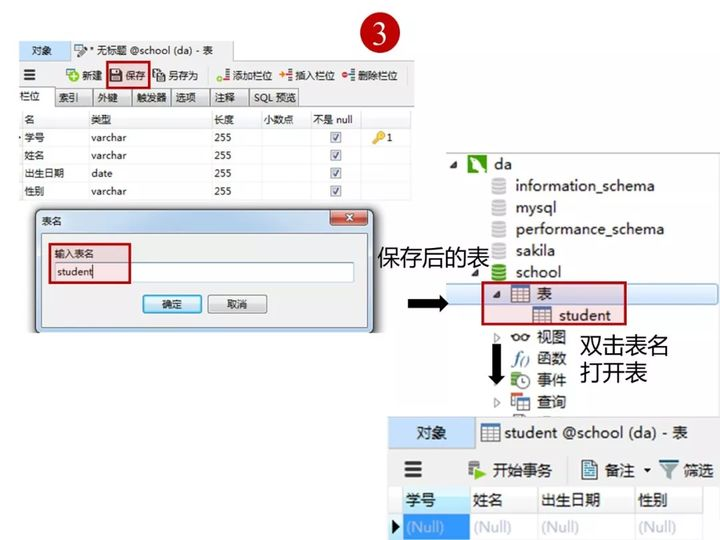
创建完表,点击“保存”
2)创建成绩表(score)
同样的步骤,创建"成绩表“。“课程表的“学号”和“课程号”一起设置为主键约束(联合主键),“成绩”这一列设置为数值类型(float,浮点数值)
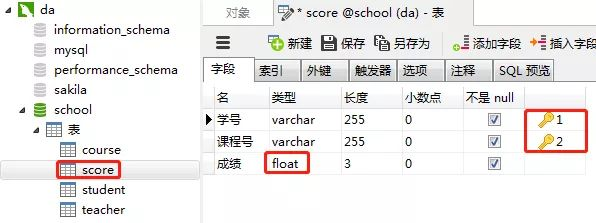
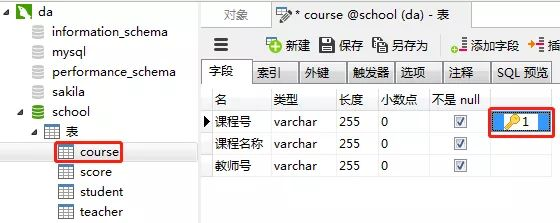
3)创建课程表(course)
课程表的“课程号”设置为主键约束
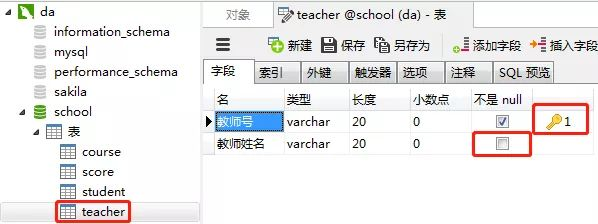
4)教师表(teacher)
教师表的“教师号”列设置为主键约束,
教师姓名这一列设置约束为“null”(红框的地方不勾选),表示这一列允许包含空值(null)
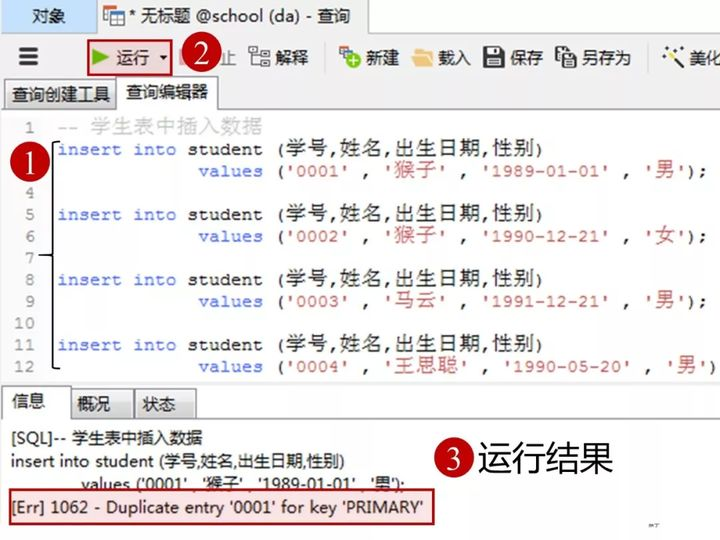
2.向表中添加数据
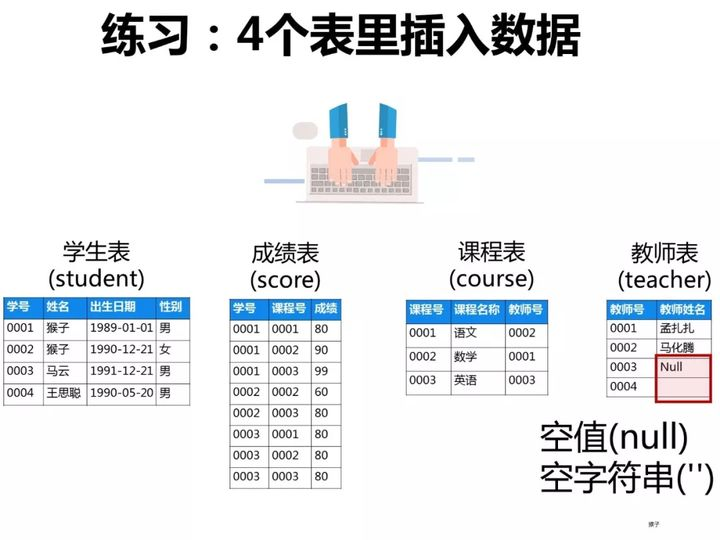
1)向学生表里添加数据
添加数据的sql
-
insert into student(学号,姓名,出生日期,性别)
-
values( '0001' , '猴子' , '1989-01-01' , '男');
-
insert into student(学号,姓名,出生日期,性别)
-
values( '0002' , '猴子' , '1990-12-21' , '女');
-
insert into student(学号,姓名,出生日期,性别)
-
values( '0003' , '马云' , '1991-12-21' , '男');
-
insert into student(学号,姓名,出生日期,性别)
-
values( '0004' , '王思聪' , '1990-05-20' , '男');
在客户端navicat里的操作








 最低0.47元/天 解锁文章
最低0.47元/天 解锁文章















 3336
3336











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








