LIFo栈之逆序链表
第一题

int* reversePrint(struct ListNode* head, int* returnSize){
int vec[10000];//辅助栈
int top=0;
struct ListNode*cur=head;
while(cur)//入栈
{
vec[top++]=cur->val;
cur=cur->next;
}
int i=top;
*returnSize=i;
int temp=0;
int*ret=(int *)malloc(sizeof(int)*(*returnSize));
for(int j=i-1;j>=0;j--)
{
ret[temp]=vec[j];
temp++;
}
return ret;
}入栈,打印,元素顺序相反
第二题
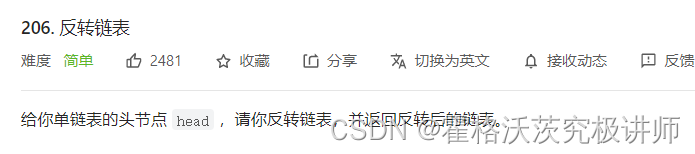
struct ListNode* reverseList(struct ListNode* head){
struct ListNode*stack[5001];//辅助栈
int top=0;
struct ListNode*cur=head;
if(head==NULL)
{
return NULL;
}
while(cur)
{
stack[top++]=cur;
cur=cur->next;
}
for(int j=top-1;j>0;j--)
{
stack[j]->next=stack[j-1];
}
stack[0]->next=NULL;
return stack[top-1];
}括号匹配
第一题

int maxDepth(char * s){
int depth=0;
int maxdepth=-1;
for(int i=0;s[i];i++)
{
if(s[i]=='(')
{
depth++;
}
else if(s[i]==')')
{
depth--;//表示匹配成功,前提为保证s中括号有效
}
maxdepth=maxdepth>depth?maxdepth:depth;//实时更新最大深度
}
return maxdepth;
}前提是字符串有效,
第二题

bool isValid(char * s){
int len=strlen(s);
char stack[len];
int top=0;//辅助栈
for(int i=0;i<len;i++)
{
if(s[i] == '(' || s[i] == '[' || s[i] == '{')
{
stack[top]=s[i];
top++;
}
else{
if(top==0)
{
return false;
}
char topElem=stack[top-1];
top--;//栈顶出栈
if(s[i] == ')' && topElem != '(')
return false; //左右括号不匹配
if(s[i] == ']' && topElem != '[')
return false; //左右括号不匹配
if(s[i] == '}' && topElem != '{')
return false; //左右括号不匹配
}
}
if(top!=0)
{
return false;//表示栈里还有没匹配的元素
}
return true;
}出入栈版本:
左括号就入栈,右括号就出栈(top--)并检验是否能匹配
回文链表
bool isPalindrome(struct ListNode* head){
int stack[100001];
int top=0;
struct ListNode*fast=head;
struct ListNode*slow=head;
if(head==NULL||head->next==NULL)
{
return true;
}
if(head->next->next==NULL)
{
if(head->val==head->next->val)
{
return true;
}
return false;
}
while(fast!=NULL&&fast->next!=NULL)
{
fast=fast->next->next;
slow=slow->next;
}//slow是中间结点
struct ListNode*temp=slow->next;
if(head==NULL||head->next==NULL)
{
return true;
}
while(temp!=NULL)
{
stack[top]=temp->val;
top++;
temp=temp->next;
}//把后面的入栈
struct ListNode*cur=head;
while(top)
{
int vtx=stack[top-1];
top--;
if(cur->val!=vtx)
{
return false;
}
cur=cur->next;
}
return true;
}将后半段入栈,再依次出栈与head相比较,作用相当于翻转链表
表达式求值
第一题
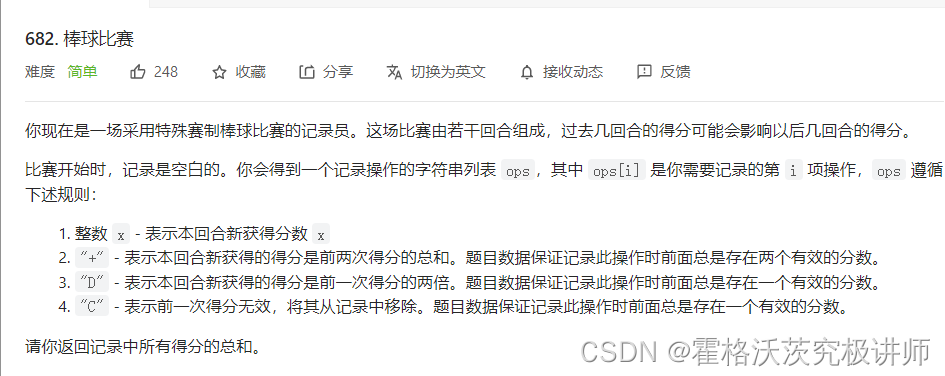
int calPoints(char ** ops, int opsSize){
int ret = 0;
int * points = (int *)malloc(sizeof(int) * opsSize);
int pos = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < opsSize; i++) {
switch (ops[i][0]) {
case '+':
ret += points[pos - 1] + points[pos - 2];
points[pos++] = points[pos - 1] + points[pos - 2];
break;
case 'D':
ret += 2 * points[pos - 1];
points[pos++] = 2 * points[pos - 1];
break;
case 'C':
ret -= points[pos - 1];
pos--;
break;
default:
ret += atoi(ops[i]);
points[pos++] = atoi(ops[i]);
break;
}
}
free(points);
return ret;
}第二题
逆波兰表达式
bool isNumber(char* token) {
return strlen(token) > 1 || ('0' <= token[0] && token[0] <= '9');
}
int evalRPN(char** tokens, int tokensSize) {
int n = tokensSize;
int stk[n], top = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
char* token = tokens[i];
if (isNumber(token)) {
stk[top++] = atoi(token);
} else {
int num2 = stk[--top];
int num1 = stk[--top];
switch (token[0]) {
case '+':
stk[top++] = num1 + num2;
break;
case '-':
stk[top++] = num1 - num2;
break;
case '*':
stk[top++] = num1 * num2;
break;
case '/':
stk[top++] = num1 / num2;
break;
}
}
}
return stk[top - 1];
}
是数字的写法'0'<=token[0]&&'9'<=token[0]
出栈一个元素只需要vtx=token[--top]
双栈判等
第一题
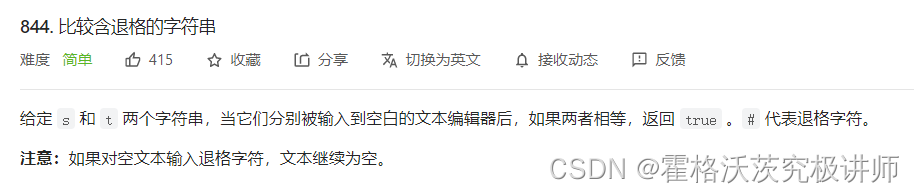
char* build(char*str)
{
int n=strlen(str);
int top=0;
char*stack=malloc(sizeof(char)*(n+1));
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
{
if(str[i]!='#')
{
stack[top++]=str[i];
}
else if(top>0)
{
top--;
}
}
stack[top]='\0';
return stack;
}
bool backspaceCompare(char * s, char * t){
return strcmp(build(s),build(t))==0;
}知识点:
1.初始化stack都用malloc
2.字符串比较strcmp
其他
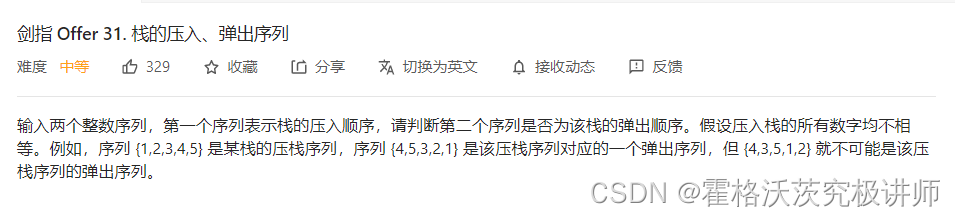
先pop,循环判断pop进的是不是push的首元素,是就push出来,最后剩下的一定是123 321这样的,判断然后把他push出来,判断栈是否为空






















 2812
2812











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








